ASTM F2213-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Magnetically Induced Torque on Passive Implants in the Magnetic Resonance Environment
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Magnetically Induced Torque on Passive Implants in the Magnetic Resonance Environment
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the magnetically induced torque produced by the static magnetic field in the magnetic resonance environment on passive implants (implants that function without the supply of electrical power) and the comparison of that torque to the equivalent torque applied by the gravitational force to the implant.
1.2 This test method does not address the issue of magnetically induced force due to spatial gradients in the static magnetic field.
1.3 The torque considered here is the static torque due to the interaction of the MRI static magnetic field with the magnetization in the implant. The dynamic torque due to interaction of the static field with eddy currents induced in a rotating device is not addressed in this test method.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 2213 – 02
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Magnetically Induced Torque on Passive
Implants in the Magnetic Resonance Environment
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 2213; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 60601-2-33 Ed. 2.0 Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 2:
Particular Requirements for the Safety of Magnetic Reso-
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the mag-
nance Equipment for Medical Diagnosis, 2002
netically induced torque produced by the static magnetic field
in the magnetic resonance environment on passive implants
3. Terminology
(implants that function without the supply of electrical power)
3.1 Definitions—For the purposes of this test method, the
and the comparison of that torque to the equivalent torque
definitions in 3.1.1-3.1.18 shall apply:
applied by the gravitational force to the implant.
3.1.1 diamagnetic material—a material whose relative per-
1.2 This test method does not address the issue of magneti-
meability is less than unity.
cally induced force due to spatial gradients in the static
3.1.2 ferromagnetic material—a material whose magnetic
magnetic field.
moments are ordered and parallel producing magnetization in
1.3 The torque considered here is the static torque due to the
one direction.
interaction of the MRI static magnetic field with the magneti-
3.1.3 magnetic induction or magnetic flux density (B in
zation in the implant. The dynamic torque due to interaction of
T)—that magnetic vector quantity which at any point in a
the static field with eddy currents induced in a rotating device
magnetic field is measured either by the mechanical force
is not addressed in this test method.
experienced by an element of electric current at the point, or by
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the electromotive force induced in an elementary loop during
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
any change in flux linkages with the loop at the point. The
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
magnetic induction is frequently referred to as the magnetic
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
field. B is the static field in an MR system. Plain type indicates
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
a scalar (for example, B) and bold type indicates a vector (for
2. Referenced Documents example, B).
3.1.4 magnetic field strength (H in A/m)—strength of the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
applied magnetic field.
A 340 Terminology of Symbols and Definitions Relating to
3.1.5 magnetic resonance (MR)—resonant absorption of
Magnetic Testing
electromagnetic energy by an ensemble of atomic particle
F 1542 Specification for the Requirements and Disclosure
situated in a magnetic field.
of Self-Closing Aneurysm Clips
3.1.6 magnetic resonance diagnostic device—a device in-
F 2052 Test Method for Measurement of Magnetically In-
tended for general diagnostic use to present images which
duced Displacement Force on Passive Implants in the
3 reflect the spatial distribution or magnetic resonance spectra, or
Magnetic Resonance Environment
both, which reflect frequency and distribution of nuclei exhib-
F 2119 Test Method for Evaluation of MR Image Artifacts
3 iting nuclear magnetic resonance. Other physical parameters
from Passive Implants
derived from the images or spectra, or both, may also be
F 2182 Test Method for Measurement of Radio Frequency
produced.
Induced Heating Near Passive Implants During Magnetic
3.1.7 magnetic resonance (MR) environment—area within
Resonance Imaging
the 5 gauss (G) line of an MR system.
2.2 IEC Standard:
3.1.8 magnetic resonance equipment—medical electrical
equipment which is intended for in-vivo magnetic resonance
examination of a patient. The MR equipment comprises all
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F04 on Medical
parts in hardware and software from the supply mains to the
and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F04.15 on Material Test Methods.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2002. Published February 2003.
2 4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.04. Available from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 3 rue de
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 13.01. Varembe, Case postale 131, CH-1211, Geneva 20, Switzerland.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
F2213–02
display monitor. The MR equipment is a Programmable nation and in the magnetic resonance environment. Other
Electrical Medical System (PEMS). safety issues which should be addressed include magnetically
3.1.9 magnetic resonance examination (MR induced force (see Test Method F 2052) and RF heating (see
Examination)—process of acquiring data by magnetic reso- Test Method F 2182).
nance from a patient. 5.2 If the maximal torque is less than the product of the
3.1.10 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)—imaging tech- longest dimension of the implant and its weight, then the
nique that uses static and time varying magnetic fields to magnetically induced deflection torque is less than the worst
provide images of tissue by the magnetic resonance of nuclei. case torque on the implant due to gravity. For this condition, it
3.1.11 magnetic resonance system (MR System)—ensemble is assumed that any risk imposed by the application of the
of MR equipment, accessories including means for display, magnetically induced torque is no greater than any risk
control, energy supplies, and the MR environment. imposed by normal daily activity in the Earth’s gravitational
3.1.12 magnetically induced displacement force—force pro- field. This is conservative; it is possible that greater torques
duced when a magnetic object is exposed to the spatial gradient would not pose a hazard to the patient.
of a magnetic field. This force will tend to cause the object to 5.3 This test method alone is not sufficient for determining
translate in the gradient field. if an implant is safe in the MR environment.
3.1.13 magnetically induced torque—torque produced when
a magnetic object is exposed to a magnetic field. This torque 6. Apparatus
will tend to cause the object to align itself along the magnetic
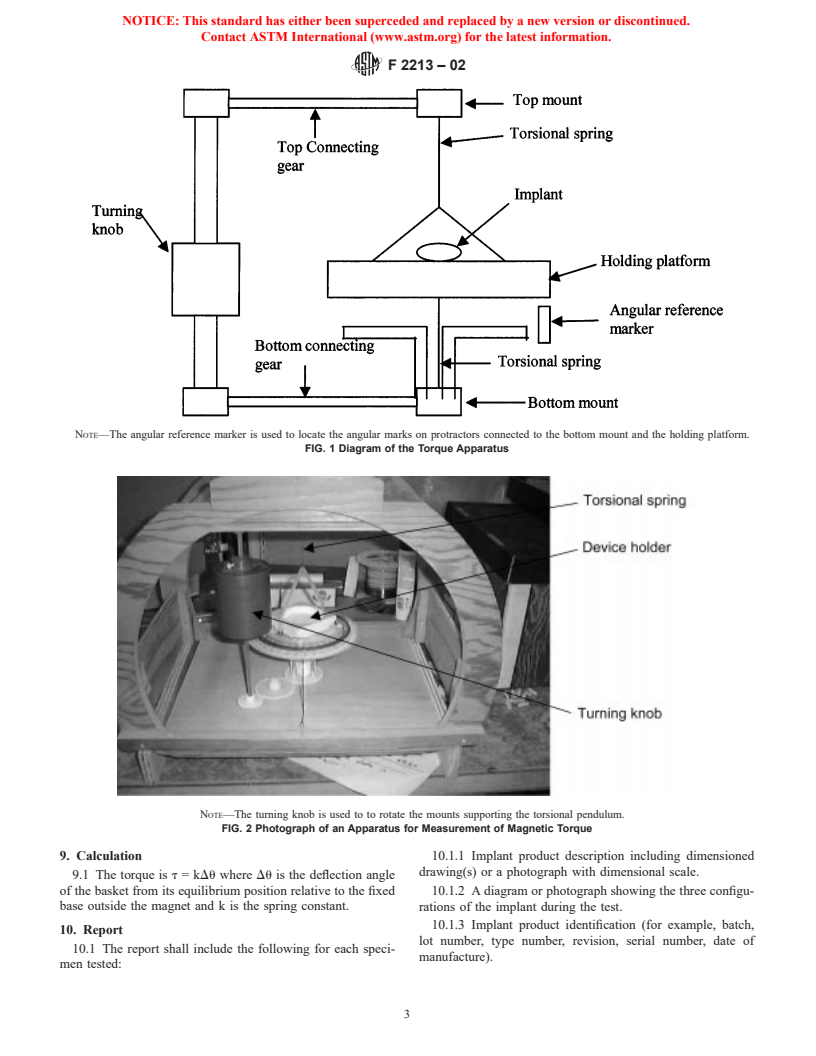
6.1 The test fixture is depicted in Fig. 1. It consists of a
field in an equilibrium direction that induces no torque.
sturdy structure supporting a holding platform supported by a
3.1.14 magnetization (M in T)—magnetic moment per unit
torsional spring. Materials should be non-ferromagnetic. The
volume.
device may be taped or otherwise attached to the holding
3.1.15 medical device—an instrument, apparatus, imple-
platform. The supporting structure will have fixed to it a
ment, machine, contrivance, implant, or other similar or related
protractor with 1° graduated markings and the holding plat-
article, including any component, part, or accessory which is
form will have a marker so that the angle between the basket
intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions,
and the support structure can be measured. The supporting
or in the cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease,
structure is rotated with the turning knob. The equilibrium
in man or other animals, or is intended to affect the structure or
angle between the supporting structure and the holding plat-
any function of the body of man or other animals, and which
form outside the magnetic field represents the zero torque
does not achieve any of its principal intended purposes through
angle. The torque inside the magnet is equal to the product of
chemical action within or on the body of man or other animals
the deflection angle and spring constant. The torsional spring
and which is not dependent upon being metabolized for the
diameter should be chosen so that the maximal deflection angle
achievement of any of its principal intended purposes.
is less than 25°. A photograph of a torque apparatus is shown
3.1.16 paramagnetic material—a material having a relative
in Fig. 2.
permeability which is slightly greater than unity, and which is
practically independent of the magnetizing force.
7. Test Specimens
3.1.17 passive implant—an implant that serves its function
7.1 For purposes of device qualification, the device evalu-
without the supply of electrical power.
ated according to this test method should be representative of
3.1.18 tesla, (T)—the SI unit of magnetic induction equal to
manufactured implant devices that are in the finished sterilized
10 gauss (G).
condition.
7.2 For purposes of device qualification, the implant should
4. Summary of Test Method
not be altered in any manner prior to testing.
4.1 The static field in a magnetic resonance system produces
a torque on an implant that acts to align the long axis of the
8. Procedure
object with the magnetic field. The torque is evaluated using a
8.1 Fig. 1 depicts the test fixture, which is placed in the
torsional pendulum method. An implant is placed on a holder
middle of the magnet where the magnetic field is uniform. The
suspended by a torsional spring. The apparatus is placed in the
test device is placed on the holding platform with one of its
center of the magnetic resonance equipment magnet where the
principal axes in the vertical direction. The entire apparatus is
magnetic field is uniform. The torque is determined from the
placed in the center of the magnet in the region of uniform
measurement of the deflection angle of the holder from its
magnetic field. Rotate the fixed base and measure the deflec-
equilibrium position. The frame holding the spring and holder
tion of the device with respect to the base at 10° increments for
assembly is rotated and the torque as a function of angle of the
angles between 0° and 360°. Note that at angular values where
implant is determined. The maximal magnetic torque is com-
the angular derivative of the torque changes sign, there will be
pared to the worst case gravity torque, defined as the product of
an abrupt change in deflection angle as the device swings to the
device length and weight.
next equilibrium position. Try to measure the deflection angle
5. Significance and Use
as close as possible to this swing so that the maximal torque
5.1 This test
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.