ASTM C1242-12
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selection, Design, and Installation of Dimension Stone Attachment Systems
Standard Guide for Selection, Design, and Installation of Dimension Stone Attachment Systems
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This guide is intended to be used by architects, engineers, and contractors who either design or install exterior stone cladding for architectural structures.
This guide is an industry standard for engineering design considerations, documentation, material considerations, anchor type applications, and installation workmanship to assist designers and installers to achieve a proper and durable stone cladding.
Stone and its support systems are part of a building's skin and shall be compatible with the behavior and performance of other interfacing systems, such as the curtainwall and superstructure frame.
Every stone work application shall comply with applicable building codes.
It is not the intent of this Guide to supercede published recommendations for specific stone types. Provisions of other dimension stone industry publications should be reviewed and considered in addition to this Guide's recommendations. All industry information should be considered with respect to project specifications and requirements. If provisions of such publications differ from those in this Guide, it is acceptable practice to follow the publication's provisions if recommended by the stone specialist defined in 4.4 for the specific conditions of the individual project.
Because stone properties vary, the range and variability of pertinent properties of the stone proposed for use should be determined by testing and statistical methods that are evaluated using sound engineering principles. Use recent test data where applicable. Always reference proven performance of relevant existing structures.
Changes in properties over time shall be considered.
Overall behaviors of all building systems and components including the stone shall be interactively compatible.
Stone Specialist—Some conditions require professional expertise to select and plan a proper anchoring system, establish appropriate testing requirements, interpret tests, design and engineer the anchoring system, or monitor ...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers the categories of anchors and anchoring systems and discusses the design principles to be considered in selecting anchors or systems that will resist gravity loads and applied loads.
1.2 This guide sets forth basic requirements for the design of stone anchorage and provides a practical checklist of those design considerations.
1.3 This guide pertains to:
1.3.1 The anchoring of stone panels directly to the building structure for support,
1.3.2 The anchoring of stone panels to subframes or to curtainwall components after these support systems are attached to the building structure,
1.3.3 The anchoring of stone panels to subframes or to curtainwall components with stone cladding preassembled before these support systems are attached to the building structure, and
1.3.4 The supervision and inspection of fabrication and installation of the above.
1.4 Observe all applicable regulations, specific recommendations of the manufacturers, and standards governing interfacing work.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
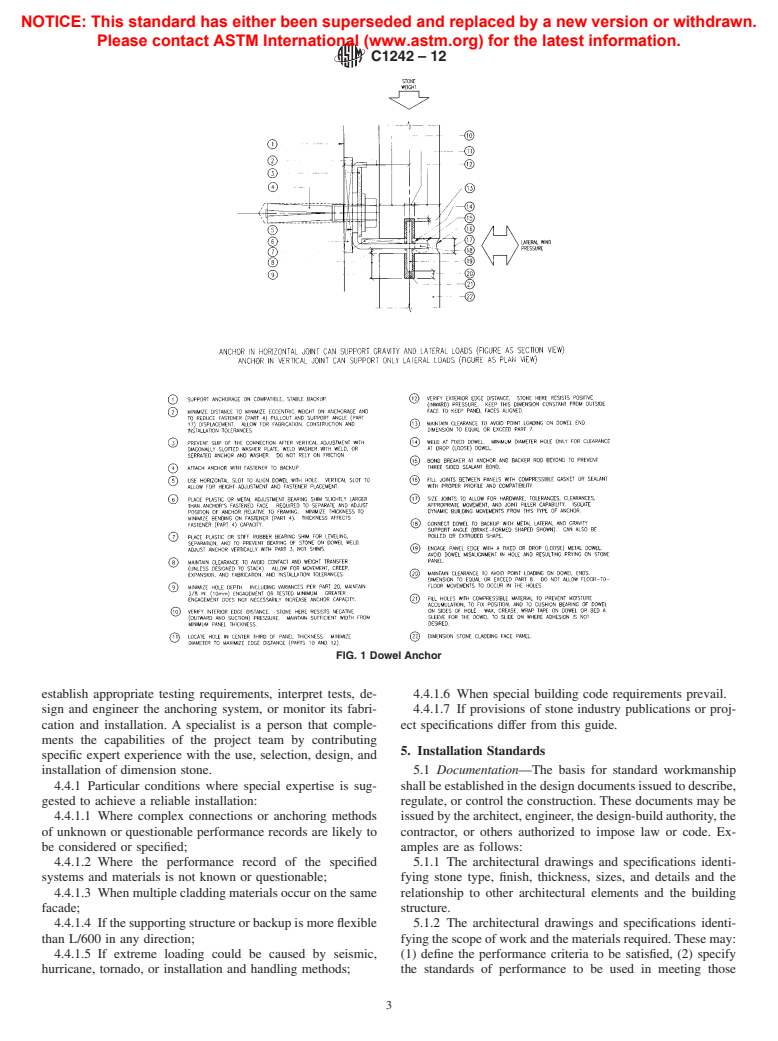
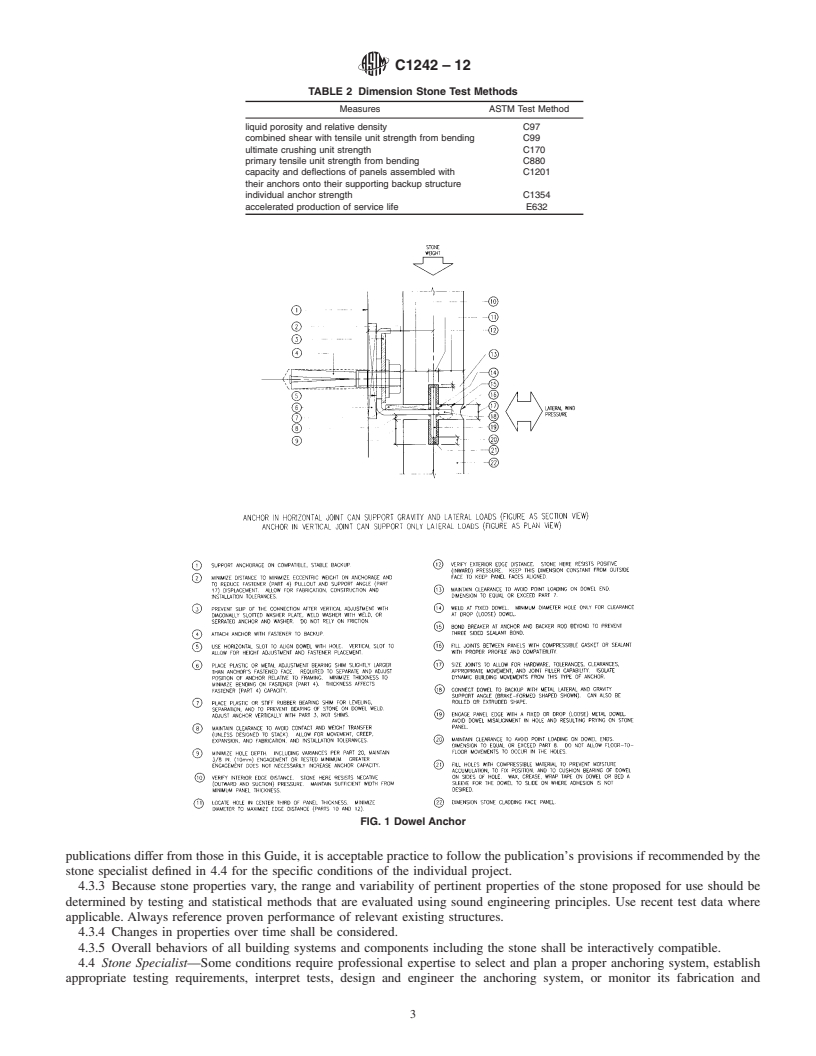
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (See Tables 1 and 2.)
TABLE 1 Dimension Stone Specifications Stone TypeASTM Specification CalciteAC503 DolomiteAC503 GraniteC615 LimestoneBC568 Marble (exterior)BC503 Quartz-BasedBC616 QuartziteAC616 Quartzitic SandstoneAC616 SandstoneAC616 SerpentineAC503 SerpentineC1526 Slate (roof)C406 Slate (walls)C629 TravertineAC1527
A This stone type is a subclassification.
B This stone type has subclassifications or grades...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C1242 – 12
Standard Guide for
Selection, Design, and Installation of Dimension Stone
1
Attachment Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1242; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Natural building stone is chosen as a building’s cladding for its beauty which endures with minimal
maintenance. Stone is durable when used properly. Exercising good judgment when selecting the
particular stone, determining the quarrying and fabrication techniques, designing the method of
attachment, and installing all components correctly maximizes these benefits. A properly executed
stonecladdingisdesignedandinstalledwithinthecapabilitiesandlimitationsofthestoneandsupport
system to resist all forces that work on them.
This guide presents design principles that require consideration when designing anchorages and
evaluating exterior stone to be compatible with its proposed use. It is an overview of current
techniques and a review of minimum requirements for sound stone engineering and construction. The
guide does not list all possible methods of attachment nor does it provide a step-by-step procedure for
stone anchor engineering. Knowledge gained from new engineering designs, testing of applications,
and the investigation of existing problems are continually reviewed to update this guide. Comment
from users is encouraged.
Good judgment by architects, engineers, and contractors when specifying, designing, engineering,
and constructing stone and other work that interfaces stone is necessary to use this guide. Users of this
guide should combine known performance characteristics of the stone, the building’s structural
behavior, and knowledge of materials and construction methods with proven engineering practice.
1. Scope 1.3.2 The anchoring of stone panels to subframes or to
curtainwall components after these support systems are at-
1.1 This guide covers the categories of anchors and anchor-
tached to the building structure,
ing systems and discusses the design principles to be consid-
1.3.3 The anchoring of stone panels to subframes or to
ered in selecting anchors or systems that will resist gravity
curtainwall components with stone cladding preassembled
loads and applied loads.
before these support systems are attached to the building
1.2 This guide sets forth basic requirements for the design
structure, and
of stone anchorage and provides a practical checklist of those
1.3.4 The supervision and inspection of fabrication and
design considerations.
installation of the above.
1.3 This guide pertains to:
1.4 Observe all applicable regulations, specific recommen-
1.3.1 The anchoring of stone panels directly to the building
dations of the manufacturers, and standards governing inter-
structure for support,
facing work.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C18 on Dimension
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Stone and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C18.06 on Attachment
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Components and Systems.
and are not considered standard.
Current edition approved Jan. 1, 2012. Published February 2012. Originally
approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as C1242 – 11. DOI:
10.1520/C1242-12.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
C1242 – 12
TABLE 2 Dimension Stone Test Methods
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the Measures ASTM Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
liquid porosity and relative density C97
combined shear with tensile unit strength from bending C99
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ultimate crushing unit strength C170
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. (See Tables 1 and
primary tensile unit strength from bending C880
2.)
capacity and deflections of panels assembled with C1201
their anchors onto their supporting backup structure
individual anchor strength C1354
2. Referenced Documents
accelerated production of service life E632
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C97 TestMethodsforAbsorptionandBulkSpecificGravity
of Dimension Stone
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C1242–11 Designation: C1242 – 12
Standard Guide for
Selection, Design, and Installation of Dimension Stone
1
Attachment Systems
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1242; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Natural building stone is chosen as a building’s cladding for its beauty which endures with minimal
maintenance. Stone is durable when used properly. Exercising good judgment when selecting the
particular stone, determining the quarrying and fabrication techniques, designing the method of
attachment, and installing all components correctly maximizes these benefits. A properly executed
stonecladdingisdesignedandinstalledwithinthecapabilitiesandlimitationsofthestoneandsupport
system to resist all forces that work on them.
This guide presents design principles that require consideration when designing anchorages and
evaluating exterior stone to be compatible with its proposed use. It is an overview of current
techniques and a review of minimum requirements for sound stone engineering and construction. The
guide does not list all possible methods of attachment nor does it provide a step-by-step procedure for
stone anchor engineering. Knowledge gained from new engineering designs, testing of applications,
and the investigation of existing problems are continually reviewed to update this guide. Comment
from users is encouraged.
Good judgment by architects, engineers, and contractors when specifying, designing, engineering,
and constructing stone and other work that interfaces stone is necessary to use this guide. Users of this
guide should combine known performance characteristics of the stone, the building’s structural
behavior, and knowledge of materials and construction methods with proven engineering practice.
1. Scope
1.1 This guide covers the categories of anchors and anchoring systems and discusses the design principles to be considered in
selecting anchors or systems that will resist gravity loads and applied loads.
1.2 This guide sets forth basic requirements for the design of stone anchorage and provides a practical checklist of those design
considerations.
1.3 This guide pertains to:
1.3.1 The anchoring of stone panels directly to the building structure for support,
1.3.2 The anchoring of stone panels to subframes or to curtainwall components after these support systems are attached to the
building structure,
1.3.3 The anchoring of stone panels to subframes or to curtainwall components with stone cladding preassembled before these
support systems are attached to the building structure, and
1.3.4 The supervision and inspection of fabrication and installation of the above.
1.4 Observe all applicable regulations, specific recommendations of the manufacturers, and standards governing interfacing
work.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. (See Tables 1 and 2.)
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C18 on Dimension Stone and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C18.06 onAttachment Components
and Systems.
Current edition approvedAug.Jan. 1, 2011.2012. Published September 2011.February 2012. Originally approved in 1993. Last previous edition approved in 20102011 as
C1242 – 101. DOI: 10.1520/C1242-112.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1242 – 12
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C97 Test Methods for Absorption and Bulk Specific Gravity of Dimension Stone
C99 Test Method for Modulus of Rupture of Dimension Stone
C119 Terminology Relating to Dimension Stone
C170 Test Method for Compressive Strength of Dimension Stone
C406 Specification for Roofing Slate
C482 Test Method for Bond Strength of Ceramic Tile to Portland Cement Paste
C503 Specification
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.