ASTM C611-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistivity of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Articles at Room Temperature
Standard Test Method for Electrical Resistivity of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Articles at Room Temperature
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 This test method provides a means of determining the electrical resistivity of carbon or graphite specimens. The use of specimens that do not conform to the specimen size limitations described in the test method may result in an alteration of test method accuracy.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the electrical resistivity of manufactured carbon and graphite articles at room temperature.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C611 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Electrical Resistivity of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite
1
Articles at Room Temperature
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C611; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* of specimens that do not conform to the specimen size
limitations described in the test method may result in an
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the elec-
alteration of test method accuracy.
tricalresistivityofmanufacturedcarbonandgraphitearticlesat
room temperature.
4. Apparatus
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
4.1 The means for applying current and potential terminals
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
to the specimen is specified in 5.2.3.1. A typical specimen
standard.
holder is shown in Fig. 1.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
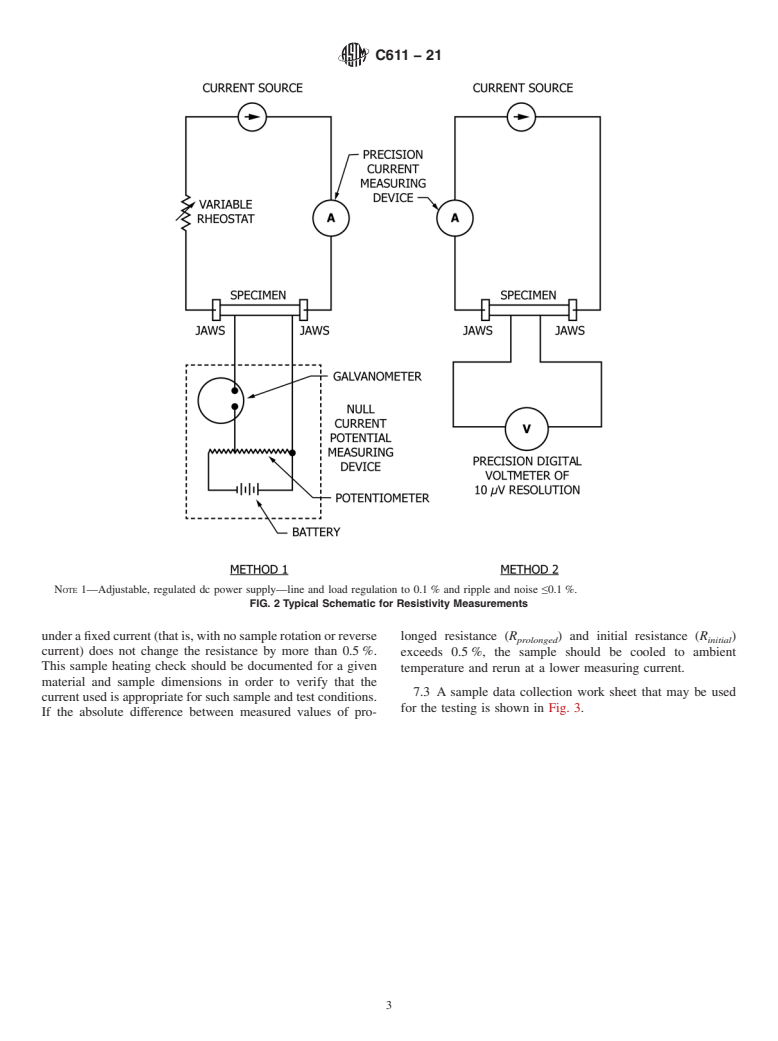
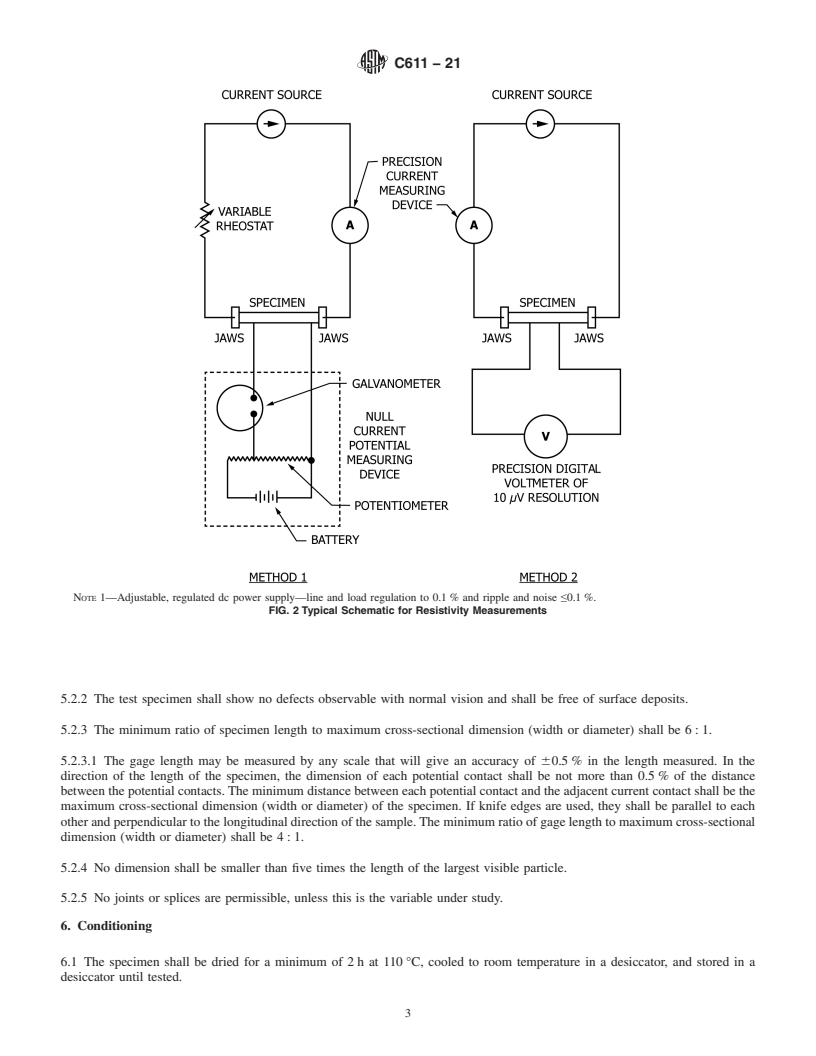
4.2 Bridge, Potentiometer, or Suitable Digital Voltmeter,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
with necessary accessories for making resistance measure-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ments with a limit of error of less than 0.5 %. Fig. 2
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
schematically depicts two wiring diagrams that have been
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
found satisfactory for this purpose.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.3 The means for measuring the dimensions of the speci-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
men should be adequate to determine its gage length and its
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
mean area of cross section, each within 0.5 %.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
5. Test Specimen
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5.1 Thetestspecimenmaybeintheformofastrip,rod,bar,
or tube.
2. Terminology
5.2 In order to determine the resistivity, each specimen shall
2.1 Definitions:
conform to the following:
2.1.1 resistivity, n—the property of a material that deter-
5.2.1 The cross-sectional area shall be uniform within
mines its resistance to the flow of an electrical current. It is
0.75 %.Ingeneral,thediameterofcircularcrosssection,orthe
defined as the value of ρ, in milliohm metres, as follows:
thickness and width of a strip specimen shall be determined by
ρ 5 R·A /L
~ !
micrometer measurements, and a sufficient number of mea-
where: surements shall be made to obtain a mean cross-sectional area
to within 0.5 %. The test specimen shall be machined to yield
R = resistanceofaspecimenofthematerialofuniformcross
planar and parallel end faces. These faces shall be perpendicu-
section, ohms,
2
lar to the specimen length to within 0.001 mm⁄mm. All
A = uniform cross section, mm , and
surfaces shall have a surface finish visually comparable to
L = distance between potential contacts, mm.
0.8 µm rms. Reasonable care should be exercised to assure that
3. Significance and Use
all edges are sharp and without chips or other flaws.
5.2.2 The test specimen shall show no defects observable
3.1 This test method provides a means of determining the
with normal vision and shall be free of surface deposits.
electrical resistivity of carbon or graphite specimens. The use
5.2.3 The minimum ratio of specimen length to maximum
cross-sectional dimension (width or diameter) shall be 6 : 1.
1
5.2.3.1 The gage length may be measured by any scale that
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
will give an accuracy of 60.5 % in the length measured. In the
Subcommittee D02.F0 on Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Products.
direction of the length of the specimen, the dimension of each
Current edition approved May 1, 2021. Published May 2021. Originally
potential contact shall be not more than 0.5 % of the distance
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as C611 – 98 (2016).
DOI:10.1520/C0611-21. betweenthepotentialcontacts.Theminimumdistancebetween
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C611 − 21
1—Base block 12—Wire g
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C611 − 98 (Reapproved 2016) C611 − 21
Standard Test Method for
Electrical Resistivity of Manufactured Carbon and Graphite
1
Articles at Room Temperature
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C611; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the electrical resistivity of manufactured carbon and graphite articles at room
temperature.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Terminology
2.1 Definitions:
2.1.1 resistivity—resistivity, n—the property of a material that determines its resistance to the flow of an electrical current. It is
defined as the value of ρ, in milliohm metres, as follows:
ρ5 ~R·A!/L
where:
R = resistance of a specimen of the material of uniform cross section, ohms,
2
A = uniform cross section, mm , and
L = distance between potential contacts, mm.
3. Significance and Use
3.1 This test method provides a means of determining the electrical resistivity of carbon or graphite specimens. The use of
specimens that do not conform to the specimen size limitations described in the test method may result in an alteration of test
method accuracy.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.F0 on Manufactured Carbon and Graphite Products.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2016May 1, 2021. Published November 2016May 2021. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 20102016 as
ε1
C611 – 98 (2010)(2016). . DOI:10.1520/C0611-98R16. DOI:10.1520/C0611-21.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C611 − 21
4. Apparatus
4.1 The means for applying current and potential terminals to the specimen is specified in 5.2.3.1. A typical specimen holder is
shown in Fig. 1.
4.2 Bridge, Potentiometer, or Suitable Digital Voltmeter, with necessary accessories for making resistance measurements with a
limit of error of less than 0.5 %. Fig. 2 schematically depicts two wiring diagrams that have been found satisfactory for this
purpose.
4.3 The means for measuring the dimensions of the specimen should be adequate to determine its gage length and its mean area
of cross section, each within 0.5 %.
5. Test Specimen
5.1 The test specimen may be in the form of a strip, rod, bar, or tube.
5.2 In order to determine the resistivity, each specimen shall conform to the following:
5.2.1 The cross-sectional area shall be uniform within 0.75 %. In general, the diameter of circular cross section, or the thickness
and width of a strip specimen shall be determined by micrometer measurements, and a sufficient number of measurements shall
be made to obtain a mean cross-sectional area to within 0.5 %. The test specimen shall be machined to yield planar and parallel
end faces. These faces shall be perpendicular to the specimen length to within 0.001 mm ⁄mm. All surfaces shall have a surface
finish visually comparable to 0.8 μm rms. Reasonable care should be exercised to assure that all edges are sharp and without chips
or other flaws.
1—Base block 12—Wire gauze holder
2—Pivot block 13—Pivot red
3—Current block adjustable 14—Screw: sockethead
4—Current block stationary 15—Roundhead screw
5—Clamp block 16—Roundhead screw
6—Clamp screw 17—Roundhead screw
7—Brush holder 18—Screw, sockethead
8—Contacts 19—Set screw
9—Current b
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.