ASTM C857-19
(Practice)Standard Practice for Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground Precast Concrete Utility Structures
Standard Practice for Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground Precast Concrete Utility Structures
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This practice is intended to standardize the minimum structural design loading for underground precast concrete utility structures.
5.2 The user shall verify the anticipated field conditions and requirements with design loads greater than those specified in this standard.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes the minimum live loads and dead loads to be applied when designing monolithic or sectional precast concrete utility structures. Concrete pipe, box culverts, and material covered in Specification C478 are excluded from this practice.
Note 1: For additional information see AASHTO Standard Specification for Highway Bridges, Seventeenth Edition.
Note 2: The purchaser is cautioned that he must properly correlate the anticipated loading conditions and the field requirements with the design loads used.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C857 − 19
Standard Practice for
Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground
1
Precast Concrete Utility Structures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C857; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 AASHTO Standard:
3
Specification for Highway Bridges, Seventeenth Edition
1.1 Thispracticedescribestheminimumliveloadsanddead
loads to be applied when designing monolithic or sectional
3. Terminology
precast concrete utility structures. Concrete pipe, box culverts,
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
and material covered in Specification C478 are excluded from
3.1.1 dead loads—will consist of any other load that can
this practice.
affect the design of the structure.
NOTE 1—For additional information seeAASHTO Standard Specifica-
3.1.2 lateral earth loads—the lateral pressure due to the
tion for Highway Bridges, Seventeenth Edition.
effective weight of adjacent earth backfill.
NOTE2—Thepurchaseriscautionedthathemustproperlycorrelatethe
anticipated loading conditions and the field requirements with the design 3.1.3 lifting insert—device embedded or otherwise attached
loads used.
to the structure, designed and manufactured to support a
measured, sustained, concentrated load.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1.4 live loads—will consist of any moving loads that can
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
affect the design of the structure and their associated impact
and are not considered standard.
and surcharge loads.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.5 utility structure—a structure that is used by electric,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
gas, communication, or similar industries.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Design Loads
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 Roof—The design loads for the roof of any structure at
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
or below ground level consists of the live loads including
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- impact and dead loads that can develop as a result of earth
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
pressure, hydrostatic pressure, and construction materials such
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- as used for roadways and walkways.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
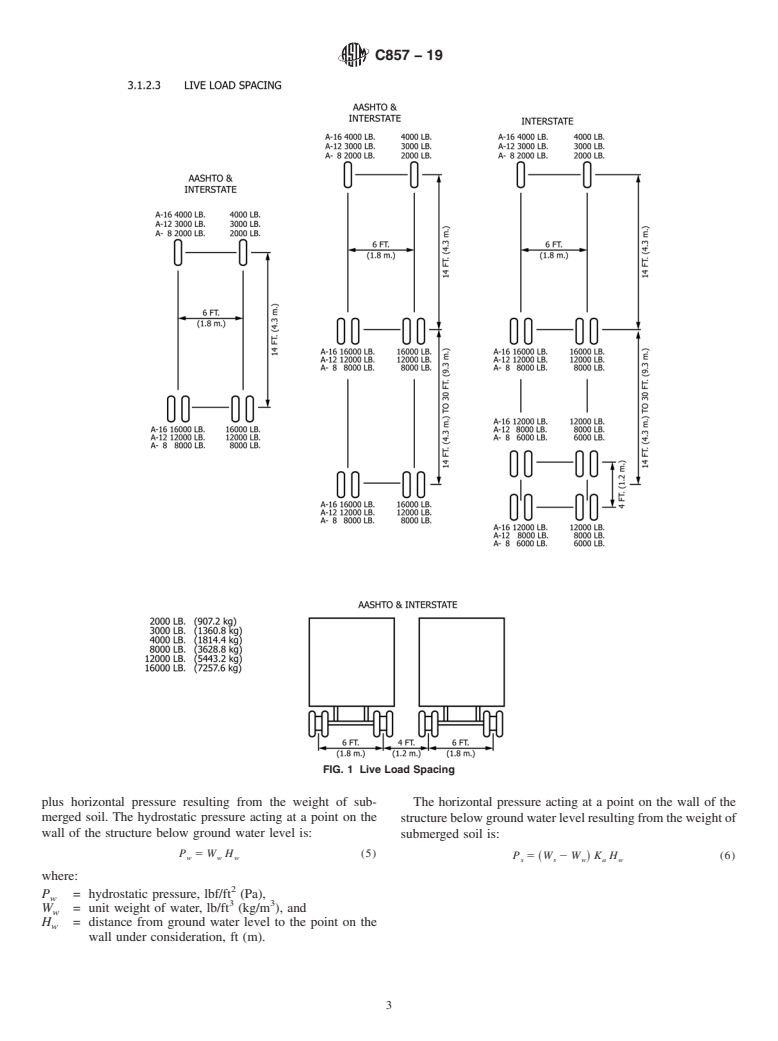
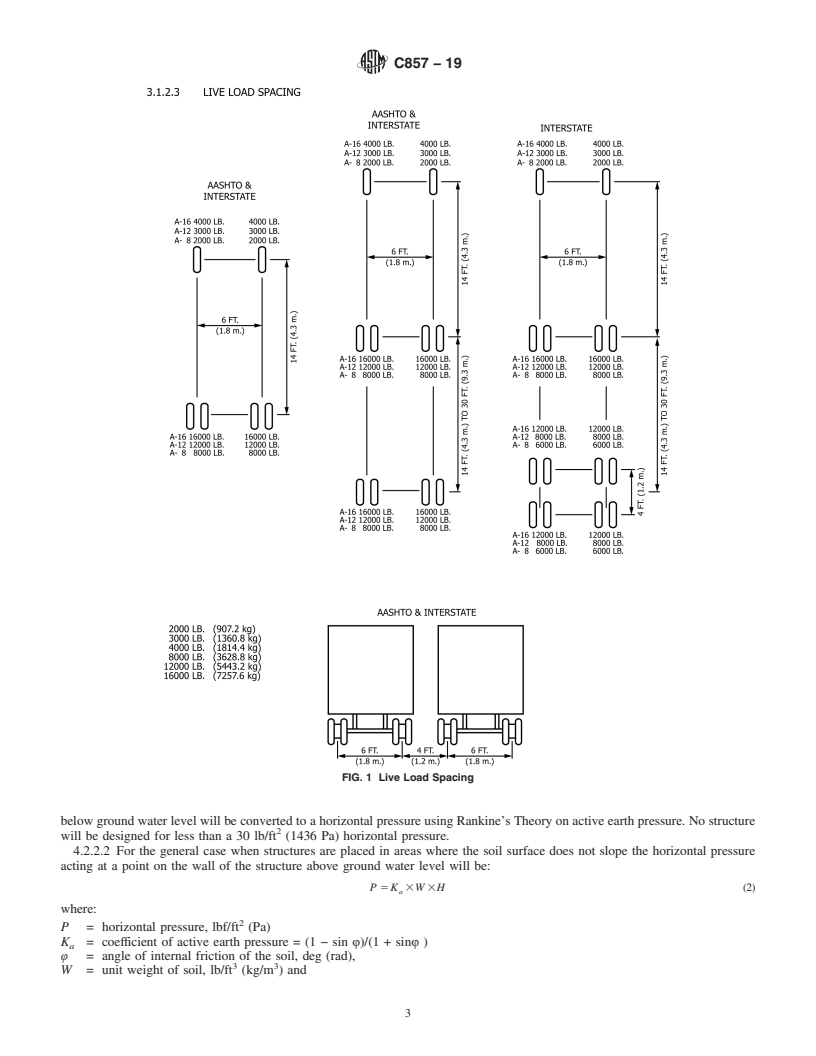
4.1.1 Live Loads—The vehicle and pedestrian load designa-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. tionsaregiveninTable1.Liveloadwheelspacingisshownin
Fig. 1.
2. Referenced Documents 4.1.2 Impact:
2 4.1.2.1 The live loads A-16, A-12, and A-8 shall be in-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
creased as follows to sustain the effect of impact:
C478SpecificationforCircularPrecastReinforcedConcrete
4.1.2.2 Live Load Increase:
Manhole Sections
0 to 12 in. (0 to 305 mm) below ground level, 30%
13 to 24 in. (330 to 610 mm) below ground level, 20%
25 to 35 in. (635 to 889 mm) below ground level, 10%
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C27 on Precast
36 in. (914 mm) or more below ground level, 0%
Concrete Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C27.10 on
4.1.3 Dead Loads—Dead loads will consist of the weight of
Utility Structures.
the roof, roadbed, walkways, earth fill, access opening covers,
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2019.PublishedJuly2019.Originallyapproved
in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as C857–16. DOI: 10.1520/
and any other material that produces a static load.
C0857-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001,
the ASTM website. http://www.transportation.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C857 − 19
TABLE 1 Vehicle and Pedestrian Load Designations 2
A-16 16 000 lbf wheel load × 0.005
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C857 − 16 C857 − 19
Standard Practice for
Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground
1
Precast Concrete Utility Structures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C857; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice describes the minimum live loads and dead loads to be applied when designing monolithic or sectional precast
concrete utility structures. Concrete pipe, box culverts, and material covered in Specification C478 are excluded from this practice.
NOTE 1—For additional information see AASHTO Standard Specification for Highway Bridges, Seventeenth Edition.
NOTE 2—The purchaser is cautioned that he must properly correlate the anticipated loading conditions and the field requirements with the design loads
used.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C478 Specification for Circular Precast Reinforced Concrete Manhole Sections
2.2 AASHTO Standard:
3
Specification for Highway Bridges, Seventeenth Edition
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 dead loads—will consist of any other load that can affect the design of the structure.
3.1.2 lateral earth loads—the lateral pressure due to the effective weight of adjacent earth backfill.
3.1.3 lifting insert—device embedded or otherwise attached to the structure, designed and manufactured to support a measured,
sustained, concentrated load.
3.1.4 live loads—will consist of any moving loads that can affect the design of the structure and their associated impact and
surcharge loads.
3.1.5 utility structure—a structure that is used by electric, gas, communication, or similar industries.
4. Design Loads
4.1 Roof—The design loads for the roof of any structure at or below ground level consists of the live loads including impact
and dead loads that can develop as a result of earth pressure, hydrostatic pressure, and construction materials such as used for
roadways and walkways.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C27 on Precast Concrete Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C27.10 on Utility
Structures.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2016July 1, 2019. Published September 2016July 2019. Originally approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 20142016 as
C857 – 14.C857 – 16. DOI: 10.1520/C0857-16.10.1520/C0857-19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001,
http://www.transportation.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C857 − 19
4.1.1 Live Loads—The vehicle and pedestrian load designations are given in Table 1. Live load wheel spacing is shown in Fig.
1.
4.1.2 Impact:
4.1.2.1 The live loads A-16, A-12, and A-8 shall be increased as follows to sustain the effect of impact:
4.1.2.2 Live Load Increase:
0 to 12 in. (0 to 305 mm) below ground level, 30 %
13 to 24 in. (330 to 610 mm) below ground level, 20 %
25 to 35 in. (635 to 889 mm) below ground level, 10 %
36 in. (914 mm) or more below ground level, 0 %
4.1.3 Dead Loads—
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.