ASTM D5742-95(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Butane Activity of Activated Carbon
Standard Test Method for Determination of Butane Activity of Activated Carbon
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The butane activity as determined by this test method is a measure of the ability of an activated carbon to adsorb butane from dry air under specified conditions. It is useful for the quality control and evaluation of granular activated carbons. The butane activity is an indication of the micropore volume of the activated carbon sample. This activity number does not necessarily provide an absolute or relative measure of the effectiveness of the tested carbon for other adsorbates or at other conditions of operation.
The butane activity test can be used as a non-ozone depleting substitute for the carbon tetrachloride activity test in Test Method D 3467. Fig. 1 shows an experimental correlation of activity values obtained using the two adsorbates.
Note 1—This test has not been designed for use with powdered activated carbon, but it has been used successfully when the flow rate or time are adjusted or the sample volume is decreased to keep the pressure drop at an acceptable value.
FIG. 1 Butane Versus Carbon Tetrachloride Correlation
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers determination of the activation level of activated carbon. Butane activity (BA) is defined herein as the ratio (in percent) of the mass of butane adsorbed by an activated carbon sample to the mass of the sample, when the carbon is saturated with butane under the conditions listed in this test method.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific warning statement, see 7.1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D5742–95 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Butane Activity of Activated Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5742; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers determination of the activation 4.1 An activated carbon bed of known volume and mass is
level of activated carbon. Butane activity (BA) is defined saturatedwithbutanevapor.Themassadsorbedatsaturationis
herein as the ratio (in percent) of the mass of butane adsorbed noted and reported as mass of butane per unit mass of carbon.
byanactivatedcarbonsampletothemassofthesample,when
5. Significance and Use
the carbon is saturated with butane under the conditions listed
5.1 The butane activity as determined by this test method is
in this test method.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as ameasureoftheabilityofanactivatedcarbontoadsorbbutane
from dry air under specified conditions. It is useful for the
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
quality control and evaluation of granular activated carbons.
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the Thebutaneactivityisanindicationofthemicroporevolumeof
the activated carbon sample. This activity number does not
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- necessarily provide an absolute or relative measure of the
effectiveness of the tested carbon for other adsorbates or at
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific other conditions of operation.
5.2 The butane activity test can be used as a non-ozone
warning statement, see 7.1.
depleting substitute for the carbon tetrachloride activity test in
2. Referenced Documents
Test Method D3467. Fig. 1 shows an experimental correlation
2.1 ASTM Standards: of activity values obtained using the two adsorbates.
D2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
NOTE 1—This test has not been designed for use with powdered
D2854 Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated
activated carbon, but it has been used successfully when the flow rate or
Carbon
time are adjusted or the sample volume is decreased to keep the pressure
D2867 Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon drop at an acceptable value.
D3195 Practice for Rotameter Calibration
6. Apparatus
D3467 Test Method for Carbon Tetrachloride Activity of
Activated Carbon 6.1 Water Bath, capable of maintaining a temperature of 25
60.2°Candofsufficientdepthsothattheentirecarbonbedin
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ASTM Test Methods the sample tube is immersed in the water.
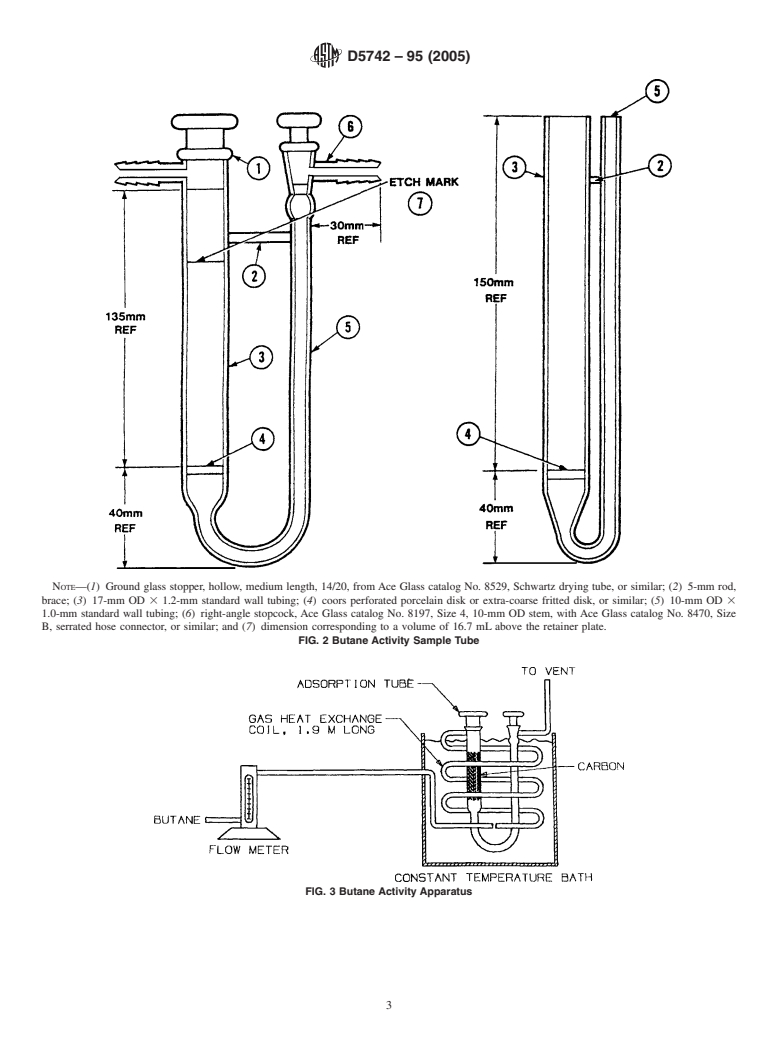
6.2 Sample Tube, with the options shown in Fig. 2.
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
6.3 Flowmeter, capable of delivering butane at 0 to 500
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method mL/min, calibrated in accordance with Practice D3195.
6.4 Balance, capable of weighing to within 60.01 g.
3. Terminology
6.5 Fill Device—The vibration feed device used in Test
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test Method D2854.
method, refer to Terminology D2652. 6.6 Apparatus Assembly, shown in Fig. 3.
7. Reagents
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on
Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas 7.1 n-Butane, C. P. Grade. (Warning—Butane is a flam-
Phase Evaluation Tests.
mable gas with a flash point of −138°C and a boiling point of
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2005. Published October 2005. Originally
0.5°C. Its specific gravity is 2.046 relative to air. Butane may
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2000 as D5742–95 (2000).
be narcotic in high concentrations and is considered a simple
DOI: 10.1520/D5742-95R05.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
asphyxiant.Iftheentireapparatusisnotsetupinafumehood,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
provision must be made to vent the gas coming from the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
discharge stem of the sample tube.)
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D5742–95 (2005)
FIG. 1 Butane Versus Carbon Tetrachloride Correlation
8. Sampling 10.5 Weigh the filled sample tube and stoppers to the
nearest 0.01 g and record.
8.1 Refer to Practice E300 for guidance in sampling granu-
10.6 Set the water bath control to maintain a temperature of
lar activated carbon.
25 6 0.2°C.
9. Maintenance of Bath Water
10.7 Clamp the sample tube in a vertical position in the 25
6 0.2°C water bath, and attach the tube to the output of the
9.1 The bath water should be changed periodically in order
flowmeter. If the entire apparatus is not in a hood, attach a
to prevent mold formation.
length of tubing from the effluen
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.