ASTM D4864-90(2013)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Traces of Methanol in Propylene Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Traces of Methanol in Propylene Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Methanol is a common impurity in propylene. It can have a deleterious effect on various processes that use propylene as a feedstock.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of methanol in propylene concentrates in the range of approximately 4 to 40 mg/kg (parts-per-million by weight).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only. Note 1—There is no direct acceptable SI equivalent for screw threads.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 11.1.1, 11.2.1, and 12.11.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4864 − 90(Reapproved 2013)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Traces of Methanol in Propylene
Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4864; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the determination of methanol 4.1 A known weight of water is pressured into a sample
inpropyleneconcentratesintherangeofapproximately4to40 cylinder containing a known amount of liquified propylene.
mg/kg (parts-per-million by weight). The contents in the cylinder are shaken and the water/methanol
phase is withdrawn. A reproducible volume of the extract is
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
then injected into a gas chromatograph (GC) equipped with
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
either a thermal conductivity or a flame ionization detector.
only.
The methanol concentration is calculated from the area of the
NOTE 1—There is no direct acceptable SI equivalent for screw threads.
methanolpeakusingcalibrationandextractionfactorsobtained
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the from synthetic blends of known methanol content.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
5. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 Methanol is a common impurity in propylene. It can
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning
have a deleterious effect on various processes that use propyl-
statements are given in 11.1.1, 11.2.1, and 12.11.
ene as a feedstock.
2. Referenced Documents
6. Interferences
2.1 ASTM Standards:
6.1 There are no known interferences using the GC columns
D4307 Practice for Preparation of Liquid Blends for Use as
referenced in this test method. However, any water-soluble
Analytical Standards
component that co-elutes with methanol on any other GC
E260 Practice for Packed Column Gas Chromatography
column used would interfere.
3. Terminology 7. Apparatus
3.1 Definitions: 7.1 Gas Chromatograph—Any GC equipped with either
3.1.1 propylene concentrate—concentrate containing more
flame ionization or thermal conductivity detectors with an
than 90 % propylene. overall sensitivity sufficient to detect at least 4 mg/kg of
methanol.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 outage tube—a length of 6.35-mm ( ⁄4 in.) outside 7.2 Column—Any GC column that separates methanol from
diameter SS tubing normally attached to the inside end of a water, other alcohols, and any co-extracted hydrocarbons.
valve used on a pressure sampling cylinder. It is used to
NOTE 2—See Table 1 for a suitable list of columns and Fig. 1 and Fig.
facilitate removal of a set quantity of liquified sample to
2 for examples of chromatograms.Also, refer to Practice E260 for typical
prevent overpressuring the cylinder.
instructions in preparing such columns. Alternatively, columns can be
purchased from commercial sources.
7.3 Data Handling System—Any commercially available
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
GC integrator or GC computer system capable of accurately
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricantsand is the direct responsibility of
integrating the area of the methanol peak is satisfactory.
Subcommittee D02.D0.03 on Propylene.
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2013. Published November 2013. Originally
7.4 Recorder—A strip-chart recorder with a full scale re-
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D4864 – 90 (2005).
sponse of2sor less and a maximum noise rate of 60.3 % full
DOI: 10.1520/D4864-90R13.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or scale.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
7.5 Sample Cylinders, 300-mL capacity, stainless steel,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. Type DOT 3E (12409 kPa (1800 psig) working pressure).
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4864 − 90 (2013)
A
TABLE 1 Suitable Gas Chromatographic Columns and Temperatures
Column Oven Temperature,°
Column Size, m × mm Tubing Type Packing Coating, µm Thickness
Number C
1 1.22 × 6.35 OD SS 15 % Carowax 1540 on 60/80 . 90
Chromosorb W AW
2 3.05 × 4.76 OD SS 80/100 mesh Porapak QS . 100
3 3.05 × 6.35 OD Cu 10 % Carbowax 1540 on . 120
30/60 mesh Chromosorb T
4 6.10 × 6.35 OD Cu 10 % Carbowax 1540 on . 120
30/60 mesh Chromosorb T
5 1.83 × 2 ID glass 10 % Carbowax 20 M on 80/ . 70
100 Chromosorb W AW
6 15 × 0.53 ID fused silica . J&W DB-5, 1.5 70 to 120 at 2°/min
A
These six columns have been tested cooperatively and have been found suitable for use with this test method.
NOTE 1—Column used: No. 4 of Table 1; detector: thermal conductiv-
ity.
FIG. 2 Chromatogram of Water/Methanol/Propylene Extract
1 1
7.9 RegulatingValves, ⁄4-in.maleNPTand ⁄4-in.maleNPT
to ⁄4-in. female NPT.
7.10 Hex Nipple, SS, ⁄4-in. male NPT by 102 mm (4 in.)
long.
7.11 Hex Coupling, SS, ⁄4-in. female NPT by 30 mm (1.2
in.) long.
7.12 Brass Cap, ⁄4-in. NPT or optionally, a tube fitting nut,
6.35 mm outside diameter ( ⁄4 in.). (See Note 3.)
7.13 Septum, TFE-fluorocarbon lined, 11-mm diameter.
7.14 Syringes, 10 and 25 µL.
8. Reagents and Materials
8.1 Methanol, reagent grade or better.
NOTE 1—Column used: No. 5 of Table 1; detector: flame ionization.
FIG. 1 Chromatograms of Water/Methanol Standard and Water/
8.2 Propylene,92+ %puritycontaining<0.2mg/kg(ppmw)
A
Methanol/Propylene Extract
methanol.
9. Sampling
9.1 The propylene sample shall be in the liquified state and
7.6 Balances—Any types capable of weighing a 300-mL
be representative of the material in the storage tank or process
sample cylinder and contents accurately to 0.1 g and a 25-mL
line. Also, for purposes of this method as well as for safety
volumetric flask and contents accurately to 0.0001 g.
considerations, there must be a vapor space of about 15 % in
1 1
7.7 Plug Valve, ⁄4-in. male NPT or optionally, ⁄4-in. male
the sampling container. It is recommended that sampling
NPTto 6.35 mm outside diameter ( ⁄4 in.) tubing. (See Note 3.)
cylinders of the type listed in Section 7 be used. They can be
7.8 Shut-off Valves, ⁄4-in. male NPT to 6.35 mm outside equipped with an outage tube to effect the 15 % vapor space
diameter ( ⁄4 in.) tubing. requirement.
D4864 − 90 (2013)
10. Preparation of Apparatus
10.1 Prepare a water injection device. A suitable device is
shown in Fig. 3. However, any other device that will deliver
from 8 to 15 g of water can be used.
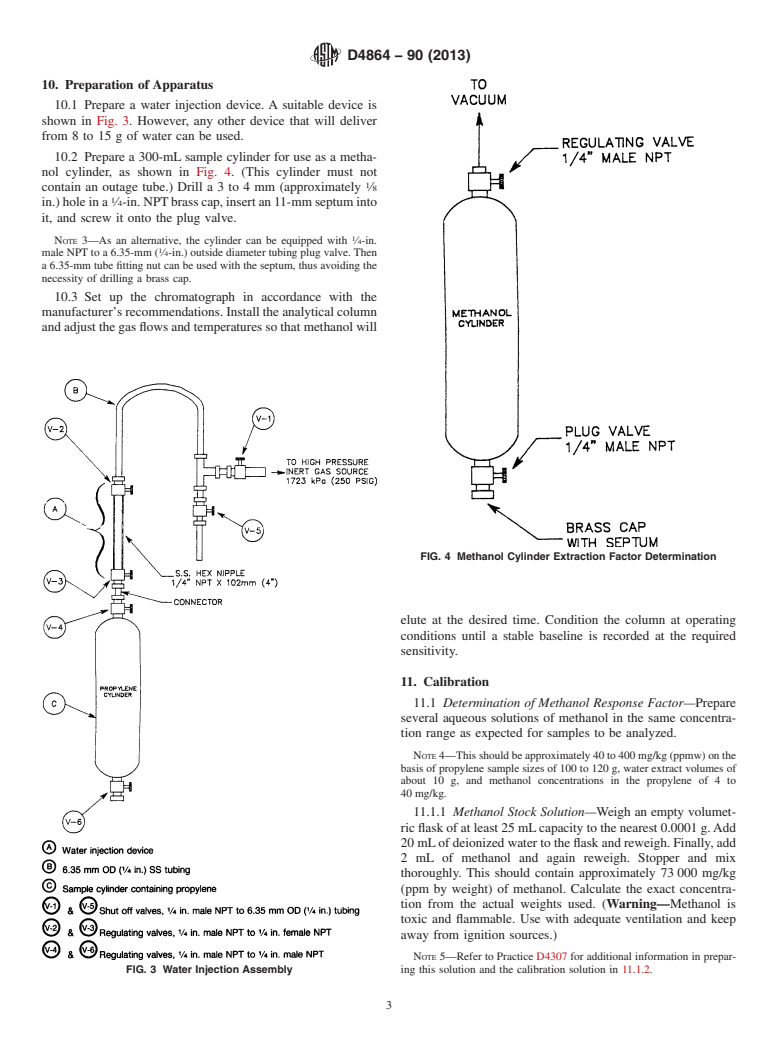
10.2 Prepare a 300-mL sample cylinder for use as a metha-
nol cylinder, as shown in Fig. 4. (This cylinder must not
contain an outage tube.) Drilla3to4mm (approximately ⁄8
in.)holeina ⁄4-in.NPTbrasscap,insertan11-mmseptuminto
it, and screw it onto the plug valve.
NOTE 3—As an alternative, the cylinder can be equipped with ⁄4-in.
male NPT to a 6.35-mm ( ⁄4-in.) outside diameter tubing plug valve. Then
a 6.35-mm tube fitting nut can be used with the septum, thus avoiding the
necessity of drilling a brass cap.
10.3 Set up the chromatograph in accordance with the
manufacturer’s recommendations. Install the analytical column
and adjust the gas flows and temperatures so that methanol will
FIG. 4 Methanol Cylinder Extraction Factor Determination
elute at the desired time. Condition the column at operating
conditions until a stable baseline is recorded at the required
sensitivity.
11. Calibration
11.1 Determination of Methanol Response Factor—Prepare
several aqueous solutions of methanol in the same concentra-
tion range as expected for samples to be analyzed.
NOTE 4—This should be approximately 40 to 400 mg/kg (ppmw) on the
basis of propylene sample sizes of 100 to 120 g, water extract volumes of
about 10 g, and methanol concentrations in the propylene of 4 to
40 mg/kg.
11.1.1 Methanol Stock Solution—Weigh an empty volumet-
ric flask of at least 25 mLcapacity to the nearest 0.0001 g.Add
20 mLof deionized water to the flask and reweigh. Finally, add
2 mL of methanol and again reweigh. Stopper and mix
thoroughly. This should contain approximately 73 000 mg/kg
(ppm by weight) of methanol. Calculate the exact concentra-
tion from the actual weights used. (Warning—Methanol is
toxic and flammable. Use with adequate ventilation and keep
away from ignition sources.)
NOTE 5—Refer to Practice D4307 for additional information in prepar-
FIG. 3 Water Injection Assembly ing this solution and the calibration solution in 11.1.2.
D4864 − 90 (2013)
11.1.2 Methanol Calibration Solutions—In similar manner, 11.2.7 As shown in Fig. 5, connect the cylinder containing
make serial dilutions by weight until two different concentra- propylene to the evacuated
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.