ASTM E2160-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Heat of Reaction of Thermally Reactive Materials by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Standard Test Method for Heat of Reaction of Thermally Reactive Materials by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is useful in determining the extrapolated onset temperature, the peak heat flow temperature and the heat of reaction of a material. Any onset temperature determined by this test method is not valid for use as the sole information used for determination of storage or processing conditions.
5.2 This test method is useful in determining the fraction of a reaction that has been completed in a sample prior to testing. This fraction of reaction that has been completed can be a measure of the degree of cure of a thermally reactive polymer or can be a measure of decomposition of a thermally reactive material upon aging.
5.3 The heat of reaction values may be used in Practice E1231 to determine hazard potential figures-of-merit Explosion Potential and Shock Sensitivity.
5.4 This test method may be used in research, process control, quality assurance, and specification acceptance.
SCOPE
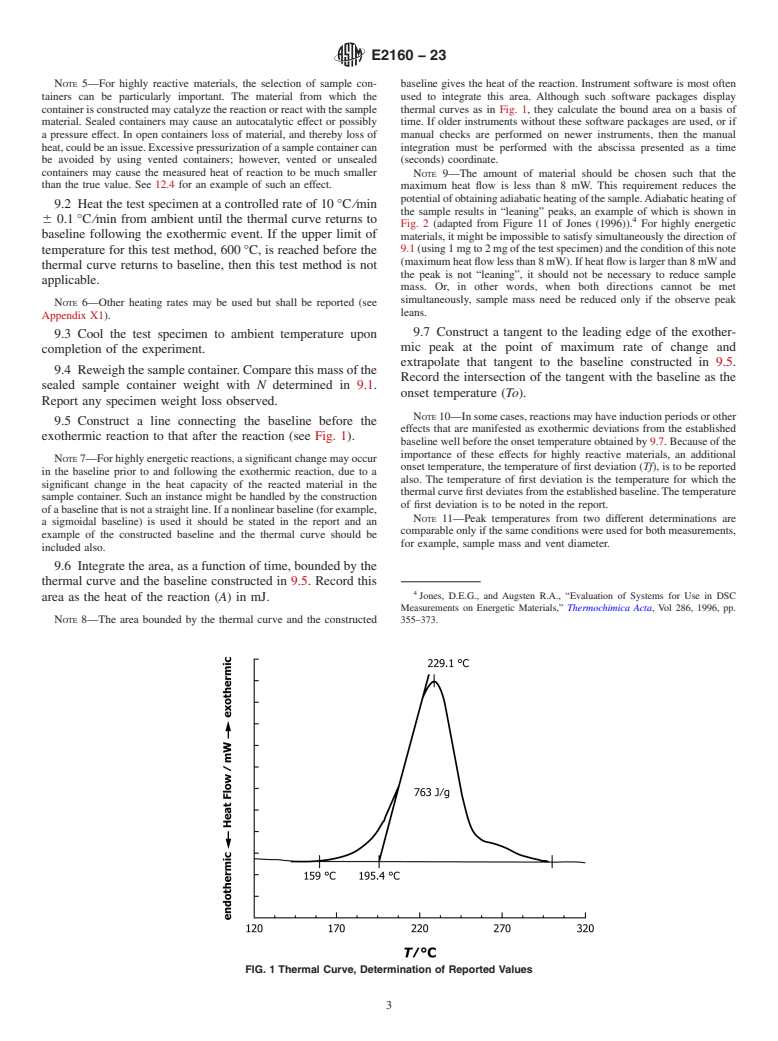
1.1 This test method determines the exothermic heat of reaction of thermally reactive chemicals or chemical mixtures, using milligram specimen sizes, by differential scanning calorimetry. Such reactive materials may include thermally unstable or thermoset materials.
1.2 This test method also determines the extrapolated onset temperature and peak heat flow temperature for the exothermic reaction.
1.3 This test method may be performed on solids, liquids or slurries.
1.4 The applicable temperature range of this test method is 25 °C to 600 °C.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard is related to Test Method E537, but provides additional information.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2160 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Heat of Reaction of Thermally Reactive Materials by
1
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2160; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method determines the exothermic heat of 2.1 ASTM Standards:
reaction of thermally reactive chemicals or chemical mixtures, E473 Terminology Relating to Thermal Analysis and Rhe-
using milligram specimen sizes, by differential scanning calo- ology
rimetry. Such reactive materials may include thermally un- E537 Test Method for Thermal Stability of Chemicals by
stable or thermoset materials. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
E967 Test Method for Temperature Calibration of Differen-
1.2 This test method also determines the extrapolated onset
tial Scanning Calorimeters and Differential Thermal Ana-
temperature and peak heat flow temperature for the exothermic
lyzers
reaction.
E968 Practice for Heat Flow Calibration of Differential
3
1.3 This test method may be performed on solids, liquids or
Scanning Calorimeters (Withdrawn 2023)
slurries.
E1142 Terminology Relating to Thermophysical Properties
1.4 The applicable temperature range of this test method is E1231 Practice for Calculation of Hazard Potential Figures
of Merit for Thermally Unstable Materials
25 °C to 600 °C.
E1860 Test Method for Elapsed Time Calibration of Ther-
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
mal Analyzers
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
E3142 Test Method for Thermal Lag of Thermal Analysis
standard.
Apparatus
1.6 This standard is related to Test Method E537, but
3. Terminology
provides additional information.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3.1 Specific technical terms used in this standard are defined
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the in Terminologies E473 and E1142.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Summary of Test Method
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 4.1 A small (milligram) quantity of the reactive material is
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
heated at 10 °C ⁄min through a temperature region where a
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- chemical reaction takes place. The exothermic heat flow
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
produced by the reaction is recorded as a function of tempera-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- ture and time by a differential scanning calorimeter. Integration
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
of the exothermic heat flow over time yields the heat of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. reaction. If the heat flow is endothermic, then this test method
is not to be used.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E37 on Thermal For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Measurements and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E37.01 on Calo- contact ASTM Customer service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
rimetry and Mass Loss. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2023. Published November 2023. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as E2160 – 04 (2018). The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
DOI: 10.1520/E2160-23. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2160 − 23
4.2 The test method can be used to determine the fraction of selected temperature limits (ambient temperature to 600 °C) at
a reaction that has occurred in a partially reacted sample. The a heating rate between 2 °C ⁄min and 20 °C ⁄min constant to
heat of reaction is determined for a specimen that is known to within 60.1 °C ⁄min.
be 100 % unreacted and is compared to the heat of reaction 6.1.1.6 A Data Collection Device, to provide a means of
determined for the partially reacted sample. Appropriate cal- acquiring, storing, and displaying measu
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2160 − 04 (Reapproved 2018) E2160 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Heat of Reaction of Thermally Reactive Materials by
1
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2160; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method determines the exothermic heat of reaction of thermally reactive chemicals or chemical mixtures, using
milligram specimen sizes, by differential scanning calorimetry. Such reactive materials may include thermally unstable or
thermoset materials.
1.2 This test method also determines the extrapolated onset temperature and peak heat flow temperature for the exothermic
reaction.
1.3 This test method may be performed on solids, liquids or slurries.
1.4 The applicable temperature range of this test method is 25 to 600°C.25 °C to 600 °C.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 There is no ISO method equivalent to this standard.
1.6 This standard is related to Test Method E537 and to NAS 1613, , but provides additional information.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E473 Terminology Relating to Thermal Analysis and Rheology
E537 Test Method for Thermal Stability of Chemicals by Differential Scanning Calorimetry
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E37 on Thermal Measurements and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E37.01 on Calorimetry
and Mass Loss.
Current edition approved April 1, 2018Nov. 1, 2023. Published May 2018November 2023. Originally approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 20122018 as
E2160 – 04 (2012).(2018). DOI: 10.1520/E2160-04R18.10.1520/E2160-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2160 − 23
E967 Test Method for Temperature Calibration of Differential Scanning Calorimeters and Differential Thermal Analyzers
3
E968 Practice for Heat Flow Calibration of Differential Scanning Calorimeters (Withdrawn 2023)
E1142 Terminology Relating to Thermophysical Properties
E1231 Practice for Calculation of Hazard Potential Figures of Merit for Thermally Unstable Materials
E1860 Test Method for Elapsed Time Calibration of Thermal Analyzers
E3142 Test Method for Thermal Lag of Thermal Analysis Apparatus
2.2 Other Standard:
4
NAS 1613 Seal Element, Packing, Preformed, Ethylene Propylene Rubber
3. Terminology
3.1 Specific technical terms used in this standard are defined in Terminologies E473 and E1142.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A small (milligram) quantity of the reactive material is heated at 10°C/min10 °C ⁄min through a temperature region where a
chemical reaction takes place. The exothermic heat flow produced by the reaction is recorded as a function of temperature and time
by a differential scanning calorimeter. Integration of the exothermic heat flow over time yields the heat of reaction. If the heat flow
is endothermic, then this test method is not to be used.
4.2 The test method can be used to determine the fraction of a reaction that has occurred in a partially reacted sample. The heat
of reaction is determined for a specimen that is known to be 100 % unreacted and is compared to the heat of reaction determined
for the pa
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.