ASTM B472-04a(2009)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Nickel Alloy Billets and Bars for Reforging
Standard Specification for Nickel Alloy Billets and Bars for Reforging
ABSTRACT
This specification covers UNS N06002, UNS N06030, UNS N06035, UNS N06022, UNS N06200, UNS N06230, UNS N06600, UNS N06617, UNS N06625, UNS N08020, UNS N08026, UNS N08024, UNS N08120, UNS N08926, UNS N08367, UNS N10242, UNS N10276, UNS N10665, UNS N10675, UNS N12160, UNS R20033, UNS N06059, UNS N06686, UNS N10629, UNS N08031, UNS N06045, UNS N06025, and UNS R30556 nickel alloy billets and bars for reforging. The products shall be hot worked from ingots by rolling, forging, extruding, hammering, or pressing. The material shall conform to the chemical composition requirements prescribed by the reference material. The chemical composition of the material shall be determined by chemical analysis in accordance with test method E1473.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers UNS N06002, UNS N06030, UNS N06035, UNS N06022, UNS N06200, UNS N06230, UNS N06600, UNS N06617, UNS N06625, UNS N08020, UNS N08026, UNS N08024, UNS N08120, UNS N08926, UNS N08367, UNS N10242, UNS N10276, UNS N10665, UNS N10675, UNS N12160, UNS R20033, UNS N06059, UNS N06686, UNS N10629, UNS N08031, UNS N06045, UNS N06025, and UNS R30556* billets and bars for reforging.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B472 – 04a (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Nickel Alloy Billets and Bars for Reforging
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B472; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
1.1 This specification covers UNS N06002, UNS N06030, 3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
UNS N06035, UNS N06022, UNS N06200, UNS N06230, 3.1.1 billets and bars, n—terms billets and bars as used in
UNS N06600, UNS N06617, UNS N06625, UNS N08020, this specification shall be understood as billets and bars for
UNS N08026, UNS N08024, UNS N08120, UNS N08926, reforging.
UNS N08367, UNS N10242, UNS N10276, UNS N10665,
4. Ordering Information
UNS N10675, UNS N12160, UNS R20033, UNS N06059,
UNS N06686, UNS N10629, UNS N08031, UNS N06045, 4.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all
requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
UNS N06025, and UNS R30556* billets and bars for reforg-
ing. specification. Examples of such requirements include, but are
not limited to, the following:
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical 4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
4.1.2 Name of material or UNS number,
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
and are not considered standard. 4.1.3 Form (bar or billet),
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 4.1.4 Dimensions,
4.1.5 ASTM designation and year of issue,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to become familiar 4.1.6 Inspection (12.1),
4.1.7 Certification—State if certification or a report of test
with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material results is required (Section 14),
4.1.8 Supplementary requirements, if any, and
as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate
safety and health practices, and determine the applicability of 4.1.9 If possible, the intended end use.
regulatory limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—Atypical ordering description is as follows: 10 000 lb (4536
kg), UNS N08020, forging bar, 4 ⁄4 in. (107.95 mm) round, Specification
2. Referenced Documents
B472.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5. Materials and Manufacture
A262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular
Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
5.1 Theproductsshallbehotworkedfromingotsbyrolling,
B880 Specification for General Requirements for Chemical
forging, extruding, hammering, or pressing.
Check Analysis Limits for Nickel, Nickel Alloys and
5.2 The products may be conditioned by chipping, grinding,
Cobalt Alloys
or machining to remove injurious surface defects provided the
E1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel,
depthofconditioningdoesnotexceedthatwhichwillaffectthe
Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys
surfaceconditionordimensionsofthearticletobeforgedfrom
the bar or billet.
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B02 on
6. Chemical Composition
Nonferrous Metals and Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
6.1 The material shall conform to the requirements as to
B02.07 on Refined Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2009. Published October 2009. Originally
chemical composition prescribed in Table 1.
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B472 - 04a. DOI:
6.2 If a product (check) analysis is performed by the
10.1520/B0472-04AR09.
purchaser, the material shall conform to the requirements
* New designation established in accordance withASTM E527 and SAE J1086,
Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS). specified in Table 1 subject to the permissible tolerances in
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Specification B880.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B472 – 04a (2009)
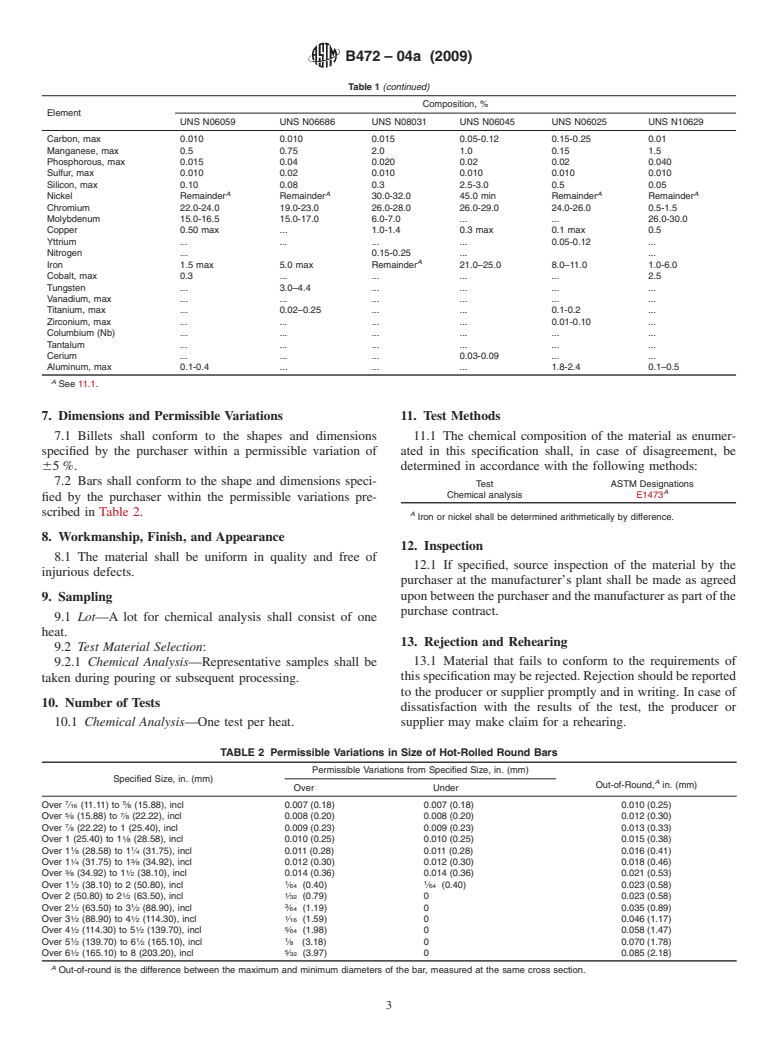
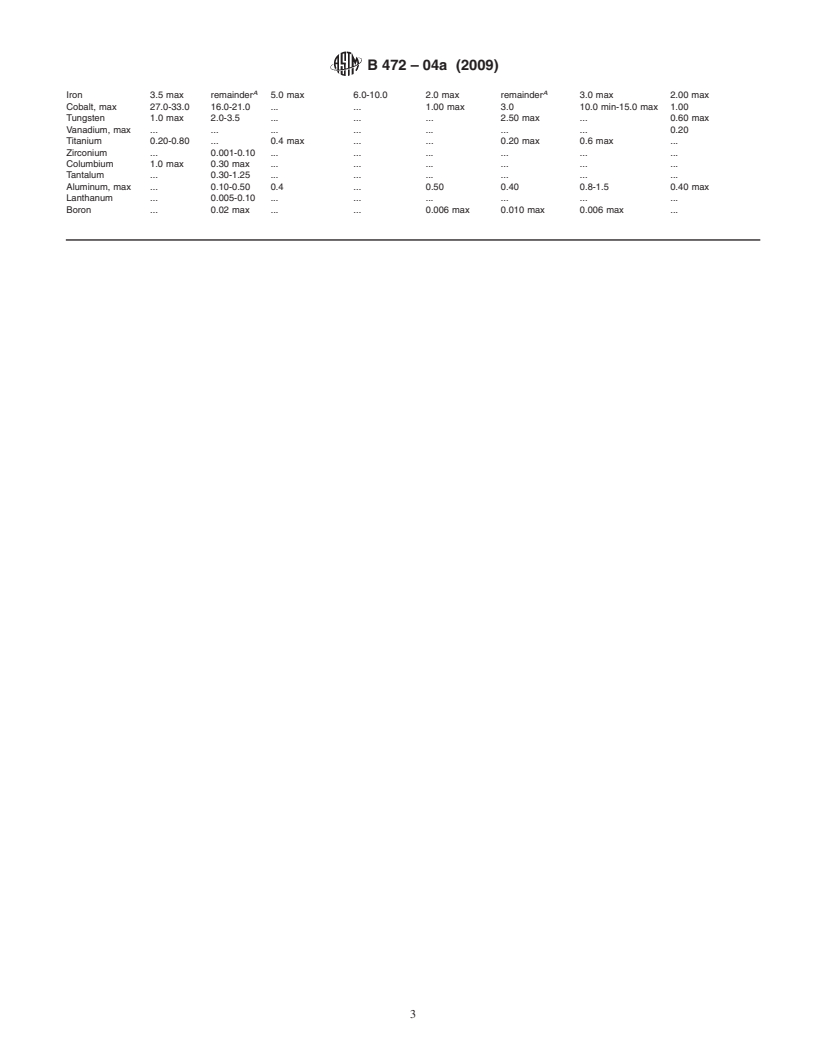
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Element
UNS N08026 UNS N08020 UNS N08024 UNS N08367 UNS N08926 UNS R20033
Carbon, max 0.03 0.07 0.03 0.030 0.020 0.015
Manganese, max 1.00 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.00 2.0
Phosphorus, max 0.03 0.045 0.035 0.040 0.03 0.02
Sulfur, max 0.03 0.035 0.035 0.030 0.01 0.01
Silicon, max 0.50 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.50 0.50
Nickel 33.00–37.20 32.00–38.00 35.00–40.00 23.50–25.50 24.00–26.00 30.0–33.0
Chromium 22.00–26.00 19.00–21.00 22.50–25.00 20.00–22.00 19.00–21.00 31.0–35.0
Molybdenum 5.00–6.70 2.00–3.00 3.50–5.00 6.00–7.00 6.0–7.0 0.50–2.0
Copper 2.00–4.00 3.00–4.00 0.50–1.50 0.75 max 0.5–1.5 0.30–1.20
Columbium (Nb) + . 8 3 carbon–1.00 0.15–0.35 . . .
tantalum
Nitrogen 0.10–0.16 . . 0.18–0.25 0.15–0.25 0.35–0.60
A
Iron remainder remainder remainder remainder balance balance
Composition, %
Element
UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS
N06030 N06022 N06200 N10276 N10665 N10675 N06002 N06230
Carbon, max 0.03 0.015 0.010 0.010 0.02 0.01 0.05-0.15 0.05-0.15
Manganese, max 1.5 0.50 0.50 1.0 1.0 3.0 1.00 0.30-1.00
Phosphorous, max 0.04 0.02 0.025 0.04 0.04 0.030 0.04 0.030
Sulfur, max 0.02 0.02 0.010 0.03 0.03 0.010 0.03 0.015
Silicon, max 0.8 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.10 0.10 1.00 0.25-0.75
A A
Nickel remainder remainder remainder remainder remainder 65.0 min remainder remainder
Chromium 28.0-31.5 20.0-22.5 22.0-24.0 14.5-16.5 1.0 max 1.0-3.0 20.5-23.0 20.0-24.0
Molybdenum 4.0-6.0 12.5-14.5 15.0-17.0 15.0-17.0 26.0-30.0 27.0-32.0 8.0-10.0 1.0-3.00
Copper 1.0-2.4 . 1.3-1.9 . . 0.20 . .
Columbium 0.30-1.50 . . . . . . .
(Nb) + tantalum
Iron 13.0-17.0 2.0-6.0 3.0 max 4.0-7.0 2.0 max 1.0-3.0 17.0-20.0 3.0 max
Cobalt, max 5.0 2.5 2.0 2.5 1.0 3.0 0.5-2.5 5.0
Tungsten 1.5-4.0 2.5-3.5 . 3.0-4.5 . 3.0 max 0.2-1.0 13.0-15.0
Vanadium, max . 0.35 . 0.35 . 0.20 . .
Titanium, max . . . . . 0.2 . .
Zirconium, max . . . . . 0.10 . .
Columbium (Nb) . . . . . 0.20 max . .
Tantalum . . . . . 0.20 max
Nickel + . . . . . 94.0-98.0 . .
Molybdenum
Aluminum, max . . 0.50 . . 0.50 . 0.20-0.50
Lanthanum . . . . . . . 0.005-0.050
Boron . . . . . . . 0.015 max
Composition, %
Element
UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS
N12160 R30556 N06625 N06600 N10242 N08120 N06617 N06035
Carbon 0.15 max 0.05-0.15 0.10 max 0.15 max 0.03 0.02-0.10 0.05-0.15 0.050 max
Manganese 1.5 max 0.50-2.00 0.50 max 1.0 max 0.80 max 1.5 max 1.0 max 0.50 max
Phosphorous 0.030 max 0.04 max 0.015 max . 0.030 max 0.040 max . 0.030 max
Sulfur 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.03 max 0.015 max 0.015 max
Silicon 2.4-3.0 0.20-0.80 0.50 max 0.50 max 0.80 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 0.60 max
A A A A A A
Nickel remainder 19.0-22.5 58.0 min 72.0 min remainder 35.0-39.0 44.5 min remainder
Chromium 26.0-30.0 21.0-23.0 20.0-23.0 14.0-17.0 7.0-9.0 23.0-27.0 20.0-24.0 32.25-34.25
Molybdenum 1.0 max 2.5-4.0 8.0-10.0 . 24.0-26.0 2.50 max 8.0-10.0 7.60-9.00
Copper . . . 0.5 max . 0.50 max 0.5 max 0.30 max
Columbium . . 3.15-4.15 . . 0.4-0.9 . .
(Nb) + tantalum
Nitrogen . 0.10-0.30 . . . 0.15-0.30 . .
A A
Iron 3.5 max remainder 5.0 max 6.0-10.0 2.0 max remainder 3.0 max 2.00 max
Cobalt, max 27.0-33.0 16.0-21.0 . . 1.00 max 3.0 10.0 min-15.0 max 1.00
Tungsten 1.0 max 2.0-3.5 . . . 2.50 max . 0.60 max
Vanadium, max . . . . . . . 0.20
Titanium 0.20-0.80 . 0.4 max . . 0.20
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B472–04a Designation: B 472 – 04a (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Specification for
Nickel Alloy Billets and Bars for Reforging
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 472; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers UNS N06002, UNS N06030, UNS N06035, UNS N06022, UNS N06200, UNS N06230, UNS
N06600, UNS N06617, UNS N06625, UNS N08020, UNS N08026, UNS N08024, UNS N08120, UNS N08926, UNS N08367,
UNS N10242, UNS N10276, UNS N10665, UNS N10675, UNS N12160, UNS R20033, UNS N06059, UNS N06686, UNS
N10629, UNS N08031, UNS N06045, UNS N06025, and UNS R30556* billets and bars for reforging.
1.2The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to become familiar with all hazards including those identified in the appropriate Material Safety Data
Sheet (MSDS) for this product/material as provided by the manufacturer, to establish appropriate safety and health practices, and
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A 262 Practices for Detecting Susceptibility to Intergranular Attack in Austenitic Stainless Steels
B 880 SpecificationforGeneralRequirementsforChemicalCheckAnalysisLimitsforNickel,NickelAlloysandCobaltAlloys
E 1473 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel, Cobalt, and High-Temperature Alloys
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 billets and bars, n—terms billets and bars as used in this specification shall be understood as billets and bars for reforging.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 It is the responsibility of the purchaser to specify all requirements that are necessary for material ordered under this
specification. Examples of such requirements include, but are not limited to, the following:
4.1.1 Quantity (weight or number of pieces),
4.1.2 Name of material or UNS number,
4.1.3 Form (bar or billet),
4.1.4 Dimensions,
4.1.5 ASTM designation and year of issue,
4.1.6 Inspection (12.1),
4.1.7 Certification—State if certification or a report of test results is required (Section 14),
4.1.8 Supplementary requirements, if any, and
4.1.9 If possible, the intended end use.
NOTE 1—Atypical ordering description is as follows: 10 000 lb (4536 kg), UNS N08020, forging bar, 4 ⁄4 in. (107.95 mm) round, Specification B 472.
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB02onNonferrousMetalsandAlloysandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeB02.07onRefined
Nickel and Cobalt and Their Alloys.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2004.2009. Published October 2004.2009. Originally approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B 472 - 04a.
* New designation established in accordance with ASTM E 527 and SAE J1086, Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys (UNS).
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
B 472 – 04a (2009)
5. Materials and Manufacture
5.1 The products shall be hot worked from ingots by rolling, forging, extruding, hammering, or pressing.
5.2 The products may be conditioned by chipping, grinding, or machining to remove injurious surface defects provided the
depth of conditioning does not exceed that which will affect the surface condition or dimensions of the article to be forged from
the bar or billet.
6. Chemical Composition
6.1 The material shall conform to the requirements as to chemical composition prescribed in Table 1.
6.2 Ifaproduct(check)analysisisperformedbythepurchaser,thematerialshallconformtotherequirementsspecifiedinTable
1 subject to the permissible tolerances in Specification B880.B 880.
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Composition, %
Element
UNS N08026 UNS N08020 UNS N08024 UNS N08367 UNS N08926 UNS R20033
Carbon, max 0.03 0.07 0.03 0.030 0.020 0.015
Manganese, max 1.00 2.00 1.00 2.00 2.00 2.0
Phosphorus, max 0.03 0.045 0.035 0.040 0.03 0.02
Sulfur, max 0.03 0.035 0.035 0.030 0.01 0.01
Silicon, max 0.50 1.00 0.50 1.00 0.50 0.50
Nickel 33.00–37.20 32.00–38.00 35.00–40.00 23.50–25.50 24.00–26.00 30.0–33.0
Chromium 22.00–26.00 19.00–21.00 22.50–25.00 20.00–22.00 19.00–21.00 31.0–35.0
Molybdenum 5.00–6.70 2.00–3.00 3.50–5.00 6.00–7.00 6.0–7.0 0.50–2.0
Copper 2.00–4.00 3.00–4.00 0.50–1.50 0.75 max 0.5–1.5 0.30–1.20
Columbium (Nb) + . 8 3 carbon–1.00 0.15–0.35 . . .
tantalum
Nitrogen 0.10–0.16 . . 0.18–0.25 0.15–0.25 0.35–0.60
A
Iron remainder remainder remainder remainder balance balance
Composition, %
Element
UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS
N06030 N06022 N06200 N10276 N10665 N10675 N06002 N06230
Carbon, max 0.03 0.015 0.010 0.010 0.02 0.01 0.05-0.15 0.05-0.15
Manganese, max 1.5 0.50 0.50 1.0 1.0 3.0 1.00 0.30-1.00
Phosphorous, max 0.04 0.02 0.025 0.04 0.04 0.030 0.04 0.030
Sulfur, max 0.02 0.02 0.010 0.03 0.03 0.010 0.03 0.015
Silicon, max 0.8 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.10 0.10 1.00 0.25-0.75
A A
Nickel remainder remainder remainder remainder remainder 65.0 min remainder remainder
Chromium 28.0-31.5 20.0-22.5 22.0-24.0 14.5-16.5 1.0 max 1.0-3.0 20.5-23.0 20.0-24.0
Molybdenum 4.0-6.0 12.5-14.5 15.0-17.0 15.0-17.0 26.0-30.0 27.0-32.0 8.0-10.0 1.0-3.00
Copper 1.0-2.4 . 1.3-1.9 . . 0.20 . .
Columbium 0.30-1.50 . . . . . . .
(Nb) + tantalum
Iron 13.0-17.0 2.0-6.0 3.0 max 4.0-7.0 2.0 max 1.0-3.0 17.0-20.0 3.0 max
Cobalt, max 5.0 2.5 2.0 2.5 1.0 3.0 0.5-2.5 5.0
Tungsten 1.5-4.0 2.5-3.5 . 3.0-4.5 . 3.0 max 0.2-1.0 13.0-15.0
Vanadium, max . 0.35 . 0.35 . 0.20 . .
Titanium, max . . . . . 0.2 . .
Zirconium, max . . . . . 0.10 . .
Columbium (Nb) . . . . . 0.20 max . .
Tantalum . . . . . 0.20 max
Nickel + . . . . . 94.0-98.0 . .
Molybdenum
Aluminum, max . . 0.50 . . 0.50 . 0.20-0.50
Lanthanum . . . . . . . 0.005-0.050
Boron . . . . . . . 0.015 max
Composition, %
Element
UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS UNS
N12160 R30556 N06625 N06600 N10242 N08120 N06617 N06035
Carbon 0.15 max 0.05-0.15 0.10 max 0.15 max 0.03 0.02-0.10 0.05-0.15 0.050 max
Manganese 1.5 max 0.50-2.00 0.50 max 1.0 max 0.80 max 1.5 max 1.0 max 0.50 max
Phosphorous 0.030 max 0.04 max 0.015 max . 0.030 max 0.040 max . 0.030 max
Sulfur 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.015 max 0.03 max 0.015 max 0.015 max
Silicon 2.4-3.0 0.20-0.80 0.50 max 0.50 max 0.80 max 1.0 max 1.0 max 0.60 max
A A A A A A
Nickel remainder 19.0-22.5 58.0 min 72.0 min remainder 35.0-39.0 44.5 min remainder
Chromium 26.0-30.0 21.0-23.0 20.0-23.0 14.0-17.0 7.0-9.0 23.0-27.0 20.0-24.0 32.25-34.25
Molybdenum 1.0 max 2.5-4.0 8.0-10.0 . 24.0-26.0 2.50 max 8.0-10.0 7.60-9.00
Copper . . . 0.5 max . 0.50 max 0.5 max 0.30 max
Columbium . . 3.15-4.15 . . 0.4-0.9 . .
(Nb) + tantalum
Nitrogen . 0.10-0.30 . . . 0.15-0.30 . .
B 472 – 0
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.