ASTM E2749-10
(Practice)Standard Practice for Measuring the Uniformity of Furnace Exposure on Test Specimens
Standard Practice for Measuring the Uniformity of Furnace Exposure on Test Specimens
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This practice describes a procedure to gather data intended to measure the uniformity of exposure conditions upon test specimens for the fire test methods described in Test Methods E119, E814, E1529, E1725, E1966 and E2336. The collected data from furnaces are intended to form a basis for performance requirements for the furnaces described in the referenced standards.
This practice does not include requirements for furnace performance.
In this procedure, the standardized test specimen is subjected to one or more specific sets of laboratory test conditions. If different test conditions are substituted or the end-use conditions are changed, it is not always possible by or from this procedure to predict changes in the fire-test-response characteristics measured. Therefore, the results are valid only for the fire-test-exposure conditions described in this procedure.
The attention of all persons connected with the conduct of this practice is drawn to the fact that fire testing is hazardous and that there is a possibility that harmful smoke and gases are developed during the test. There is also a possibility that mechanical and operational hazards develop during the construction of the test specimen and the disposal of the test residues. An assessment of all potential hazards and risks to health shall be made and safety precautions shall be identified and provided. Written safety instructions shall be issued. Appropriate training shall be provided to relevant personnel. Laboratory personnel shall ensure that they follow written safety instructions at all times.
SCOPE
1.1 This standard provides general principles for measuring the uniformity of the furnace exposure on specimens tested in accordance with Test Methods E119, E814, E1529, E1725, E1966 and E2336.
1.2 This practice specifies the materials and the construction requirements for a standardized test specimen used to provide a mounting surface for the instrumentation that measures furnace exposure.
1.3 The instrumentation records temperatures, pressure differentials and oxygen content near the surface of the test specimen.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.6 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these tests.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E2749 − 10 AnAmerican National Standard
Standard Practice for
Measuring the Uniformity of Furnace Exposure on Test
Specimens
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2749; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E119 Test Methods for Fire Tests of Building Construction
and Materials
1.1 This standard provides general principles for measuring
E176 Terminology of Fire Standards
the uniformity of the furnace exposure on specimens tested in
E814 Test Method for Fire Tests of Penetration Firestop
accordance with Test Methods E119, E814, E1529, E1725,
Systems
E1966 and E2336.
E1529 Test Methods for Determining Effects of Large Hy-
1.2 Thispracticespecifiesthematerialsandtheconstruction
drocarbon Pool Fires on Structural Members and Assem-
requirements for a standardized test specimen used to provide
blies
a mounting surface for the instrumentation that measures
E1725 Test Methods for Fire Tests of Fire-Resistive Barrier
furnace exposure.
Systems for Electrical System Components
1.3 The instrumentation records temperatures, pressure dif-
E1966 Test Method for Fire-Resistive Joint Systems
ferentials and oxygen content near the surface of the test
E2336 Test Methods for Fire Resistive Grease Duct Enclo-
specimen.
sure Systems
2.2 ISO Technical Report:
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
ISO/TR 834-2 Fire resistance tests – Elements of building
standard. The units given in parentheses are for information
construction – Part 2: Guide on measuring uniformity of
only.
furnace exposure on test samples
1.5 This standard is used to measure and describe the
response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and
3. Terminology
flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this
incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk
practice, refer to Terminology E176.
assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under
actual fire conditions.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 effective area of the furnace opening—furnace open-
1.6 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safe-
ing within the boundaries of the monitoring instrumentation.
guards for personnel and property shall be employed in
conducting these tests.
4. Summary of Practice
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 This practice consists of preparing a standardized test
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
specimen to represent test specimens described in Test Meth-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
ods E119, E814, E1529, E1725, E1966 and E2336. The
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
standardized test specimen provides a low cost, easily con-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
structed supporting construction for the mounting of instru-
2. Referenced Documents
mentation that measures the exposure imposed by the furnace
onto test specimens.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C1396/C1396M Specification for Gypsum Board
4.2 The standardized test specimen consists of two layers of
15.9 mm ( ⁄8 in.) thick Type X gypsum board on the surface
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E05 on Fire
facing the furnace chamber attached to steel channels and a
Standards and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.11 on Fire
single layer of structural panels (plywood or oriented strand
Resistance.
board) attached to the steel channels on the surface away from
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published June 2010. DOI:10.1520/
E2749-10.
the furnace chamber. The gypsum board provides a fire-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
resistive surface for the mounting of the instrumentation. The
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
structural panels provide stability for the steel support chan-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. nels.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E2749 − 10
4.3 Instrumentation to measure the thermal impact due to
exposure to the furnace upon the standardized test specimen is
installed at various locations on the exposed surface of the
standardized test specimen. Probes used to gather air samples
within the furnace chamber are also installed.
4.4 The standardized test specimen is exposed to the time-
temperature curve specified in referenced ASTM fire test
standards for a time period of 45 min during which time data
are recorded by the instrumentation mounted on the standard-
ized test specimen.
4.5 The data provide a record of the conditions and unifor-
mityofthefurnaceexposureuponstandardizedtestspecimens.
The area bounded by the instrumentation installed on the
standardizedtestspecimenisdesignatedastheeffectiveareaof
the furnace opening.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This practice describes a procedure to gather data
intended to measure the uniformity of exposure conditions
upon test specimens for the fire test methods described in Test
Methods E119, E814, E1529, E1725, E1966 and E2336. The
NOTE 1—Dimensions in millimetres.
collected data from furnaces are intended to form a basis for
FIG. 1 Horizontal Standardized Test Specimen, Location of
performance requirements for the furnaces described in the
Joists and Track Channels
referenced standards.
5.2 This practice does not include requirements for furnace
6.2.1.1 The gypsum board shall be minimum 15.9 mm ( ⁄8
performance.
in.) thick complying with the requirements of Type X as
5.3 In this procedure, the standardized test specimen is
defined in Specification C1396/C1396M.
subjected to one or more specific sets of laboratory test
6.2.1.2 The structural panels shall be minimum 18 mm ( ⁄4
conditions. If different test conditions are substituted or the
in.) thick. Typical materials include plywood and oriented
end-use conditions are changed, it is not always possible by or
strand boards.
from this procedure to predict changes in the fire-test-response
6.2.1.3 The cold-formed steel joists for horizontal speci-
characteristics measured. Therefore, the results are valid only
mens shall be fabricated from minimum 1.4 mm thick (0.055
for the fire-test-exposure conditions described in this proce-
in.) steel. The cold formed steel joists shall be “C” shaped
dure.
having a minimum depth of 240 mm (9 ⁄2 in.), a minimum
flange width of 40 mm (1 ⁄8 in.) and a minimum lip length of
5.4 The attention of all persons connected with the conduct
12 mm ( ⁄2 in.).
of this practice is drawn to the fact that fire testing is hazardous
6.2.1.4 The cold-formed steel wall studs for vertical speci-
and that there is a possibility that harmful smoke and gases are
mens shall be fabricated from minimum 0.9 mm thick (0.035
developed during the test. There is also a possibility that
in.) steel.The cold-formed steel wall studs shall be “C” shaped
mechanical and operational hazards develop during the con-
havingaminimumdepthof90mm(3 ⁄2in.),aminimumflange
struction of the test specimen and the disposal of the test
width of 30 mm (1 ⁄4 in.) and a minimum folded back return
residues. An assessment of all potential hazards and risks to
flange legs of 5 mm ( ⁄4 in.).
health shall be made and safety precautions shall be identified
6.2.1.5 The cold-formed steel track channels for the hori-
and provided. Written safety instructions shall be issued.
zontal and vertical specimens shall be “C” shaped having a
Appropriate training shall be provided to relevant personnel.
depth compatible with the joists or wall studs being used.
Laboratory personnel shall ensure that they follow written
6.2.1.6 Steel fasteners used to attach the gypsum board to
safety instructions at all times.
the studs shall be designed for the attachment of gypsum board
to steel supports. Typical screws have a thread diameter of 5
6. Apparatus
1 3
mm ( ⁄4 in.) and a head diameter of 8 mm ( ⁄8 in.). The steel
6.1 The furnace(s) and restraining frame(s) used to conduct
fasteners used to attach the inner layer shall have a minimum
tests in accordance with Test Methods E119, E814, E1529,
length of 25 mm (1 in.). The steel fasteners used to attach the
E1725, E1966 and E2336 shall be used.
exposed layer shall have a minimum length of 40 mm (1 ⁄8 in.).
6.2 Standardized Test Specimen: 6.2.1.7 Fasteners used to attach the structural panels to the
6.2.1 Materials—The materials used to construct the stan- studs shall be designed for the attachment of the panels to steel
dardized test specimen shall consist of the following: gypsum supports.
board, structural panels, cold-formed steel supports and fasten- 6.2.2 Construction Method—Standardized horizontal test
ers. specimen.
E2749 − 10
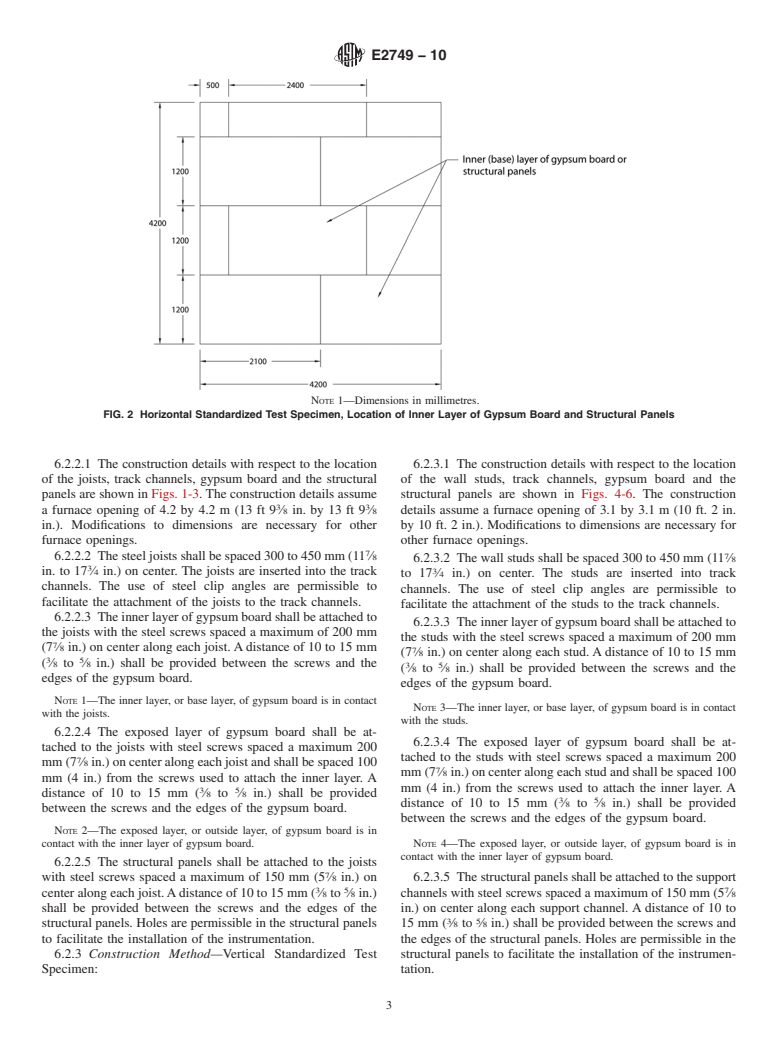
NOTE 1—Dimensions in millimetres.
FIG. 2 Horizontal Standardized Test Specimen, Location of Inner Layer of Gypsum Board and Structural Panels
6.2.2.1 The construction details with respect to the location 6.2.3.1 The construction details with respect to the location
of the joists, track channels, gypsum board and the structural of the wall studs, track channels, gypsum board and the
panels are shown in Figs. 1-3. The construction details assume structural panels are shown in Figs. 4-6. The construction
3 3
a furnace opening of 4.2 by 4.2 m (13 ft 9 ⁄8 in. by 13 ft 9 ⁄8 details assume a furnace opening of 3.1 by 3.1 m (10 ft. 2 in.
in.). Modifications to dimensions are necessary for other by 10 ft. 2 in.). Modifications to dimensions are necessary for
furnace openings. other furnace openings.
6.2.2.2 The steel joists shall be spaced 300 to 450 mm (11 ⁄8
6.2.3.2 The wall studs shall be spaced 300 to 450 mm (11 ⁄8
in. to 17 ⁄4 in.) on center. The joists are inserted into the track
to 17 ⁄4 in.) on center. The studs are inserted into track
channels. The use of steel clip angles are permissible to
channels. The use of steel clip angles are permissible to
facilitate the attachment of the joists to the track channels.
facilitate the attachment of the studs to the track channels.
6.2.2.3 The inner layer of gypsum board shall be attached to
6.2.3.3 The inner layer of gypsum board shall be attached to
the joists with the steel screws spaced a maximum of 200 mm
the studs with the steel screws spaced a maximum of 200 mm
(7 ⁄8 in.) on center along each joist.Adistance of 10 to 15 mm
(7 ⁄8 in.) on center along each stud.Adistance of 10 to 15 mm
3 5
( ⁄8 to ⁄8 in.) shall be provided between the screws and the
3 5
( ⁄8 to ⁄8 in.) shall be provided between the screws and the
edges of the gypsum board.
edges of the gypsum board.
NOTE 1—The inner layer, or base layer, of gypsum board is in contact
NOTE 3—The inner layer, or base layer, of gypsum board is in contact
with the joists.
with the studs.
6.2.2.4 The exposed layer of gypsum board shall be at-
6.2.3.4 The exposed layer of gypsum board shall be at-
tached to the joists with steel screws spaced a maximum 200
tached to the studs with steel screws spaced a maximum 200
mm (7 ⁄8 in.) on center along each joist and shall be spaced 100
mm (7 ⁄8 in.) on center along each stud and shall be spaced 100
mm (4 in.) from the screws used to attach the inner layer. A
mm (4 in.) from the screws used to attach the inner layer. A
3 5
distance of 10 to 15 mm ( ⁄8 to ⁄8 in.) shall be provided
3 5
distance of 10 to 15 mm ( ⁄8 to ⁄8 in.) shall be provided
between the screws and the edges of the gypsum board.
between the screws and the edges of the gypsum board.
NOTE 2—The exposed layer, or outside layer, of gypsum board is in
contact with the inner layer of gypsum board. NOTE 4—The exposed layer, or outside layer, of gypsum board is in
contact with the inner layer of gypsum board.
6.2.2.5 The structural panels shall be attached to the joists
with steel screws spaced a maximum of 150 mm (5 ⁄8 in.) on 6.2.3.5 The structural panels shall be attached to the support
3 5 7
center along each joist.Adistance of 10 to 15 mm ( ⁄8 to ⁄8 in.) channels with steel screws spaced a maximum of 150 mm (5 ⁄8
shall be provided between the screws and the edges of the in.) on center along each support channel. A distance of 10 to
3 5
structural panels. Holes are permissible in the structural panels 15 mm ( ⁄8 to ⁄8 in.) shall be provided between the screws and
to facilitate the installation of the instrumentation. the edges of the structural panels. Holes are permissible in the
6.2.3 Construction Method—Vertical Standardized Test structural panels to facilitate the installation of the instrumen-
Specimen: tation.
E2749 − 10
NOTE 1—Dimensions in millimetres.
FIG. 3 Horizontal Standardized Test Specimen, Location of Outer Layer of Gypsum Board
directional flame thermometer, bi-directional probes, Type K
thermocouples and air sampling probes.
6.4.1 The plate thermometers (1) shall be constructed as
shown in Fig. 7.
6.4.1.1 The plate part of the plate thermometer shall be
constructedfrom150 61mmlongby100 61mmwideby0.7
6 0.1 mm thick nickel alloy plate strips folded to the design
shown in Fig. 7.
6.4.1.2 A Type K ungrounded Inconel sheathed thermo-
couple having a maximum diameter of 1 mm shall be fixed to
the geometric center of the plate in the position shown in Fig.
7 by a steel strip made from the same material as the plate.The
steel strip shall be welded or screwed to the plate. The strip
shall be 18 61mmby6 6 1 mm when it is spot welded to the
plate (Fig. 7) and 25 61mmby6 6 1 mm when it is to be
screwed to the plate. The screw shall be a maximum 2 mm in
diameter.
6.4.1.3 The assembly of the plate and thermocouple shall be
fittedwithapadofinorganicinsulationmaterial97 61mmby
97 61mmby10 6 1 mm thick. The density of the insulation
NOTE 1—Dimensions in millimetres material shall be 280 6 30 kg/m .
.
6.4.1.4 The plate thermometers shall be aged by immersing
FIG. 4 Vertical Standarized Test Specimen, Location of Wall
in a pre-heated oven at 1000°C for 1 h before their first use or
Studs and Track Channels
exposed in a furnace following the time-temperature curve
specified in Test Methods E119 for a minimum of 90 min.
6.4.2 The directional flame thermometers(2) shall be con-
structed as shown in Fig. 8.
6.3 Furnace Limitations—Furnaces with dedicated
6.4.2.1 The plate parts of the directional flame thermom-
applications, such a
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.