ASTM D5621-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sonic Shear Stability of Hydraulic Fluids
Standard Test Method for Sonic Shear Stability of Hydraulic Fluids
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method was developed using Test Method D2603–91.
4.2 This test method permits the evaluation of shear stability with minimum interference from thermal and oxidative factors that may be present in some applications. It has been found applicable to fluids containing both readily sheared and shear-resistant polymers. Correlation with performance in the case of hydraulic applications has been established.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the shear stability of hydraulic fluids in terms of the final viscosity that results from irradiating a sample of the hydraulic fluid in a sonic oscillator.
1.2 Evidence has been presented that a good correlation exists between the shear degradation that results from sonic oscillation and that obtained in a vane pump test procedure.2
1.3 This test method uses millimetres squared per second (mm2/s), an SI unit, as the unit of viscosity. For information, the equivalent unit, cSt, is shown in parentheses.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D5621 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Sonic Shear Stability of Hydraulic Fluids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5621; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D2603 Test Method for Sonic Shear Stability of Polymer-
Containing Oils
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the shear
D6022 Practice for Calculation of Permanent Shear Stability
stability of hydraulic fluids in terms of the final viscosity that
Index
results from irradiating a sample of the hydraulic fluid in a
sonic oscillator.
3. Summary of Test Method
1.2 Evidence has been presented that a good correlation
3.1 Aconvenient volume of hydraulic fluid is irradiated in a
exists between the shear degradation that results from sonic
sonic oscillator for a period of time and the viscosities before
2
oscillation and that obtained in a vane pump test procedure.
and after irradiation are determined by Test Method D445.A
1.3 This test method uses millimetres squared per second standardreferencefluidcontainingareadilyshearedpolymeris
2
(mm /s), an SI unit, as the unit of viscosity. For information,
run frequently to ensure that the equipment imparts a con-
the equivalent unit, cSt, is shown in parentheses. trolled amount of sonic energy to the sample.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.2 The conditions to obtain the data for the precision
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
statement were: 30 mL sample, 12.5 min calibration, and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
40 min sample irradiation at 0 °C jacket temperature.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4. Significance and Use
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
4.1 This test method was developed using Test Method
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
D2603–91.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.2 Thistestmethodpermitstheevaluationofshearstability
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
with minimum interference from thermal and oxidative factors
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
that may be present in some applications. It has been found
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
applicable to fluids containing both readily sheared and shear-
resistant polymers. Correlation with performance in the case of
2. Referenced Documents
3 hydraulic applications has been established.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
5. Apparatus
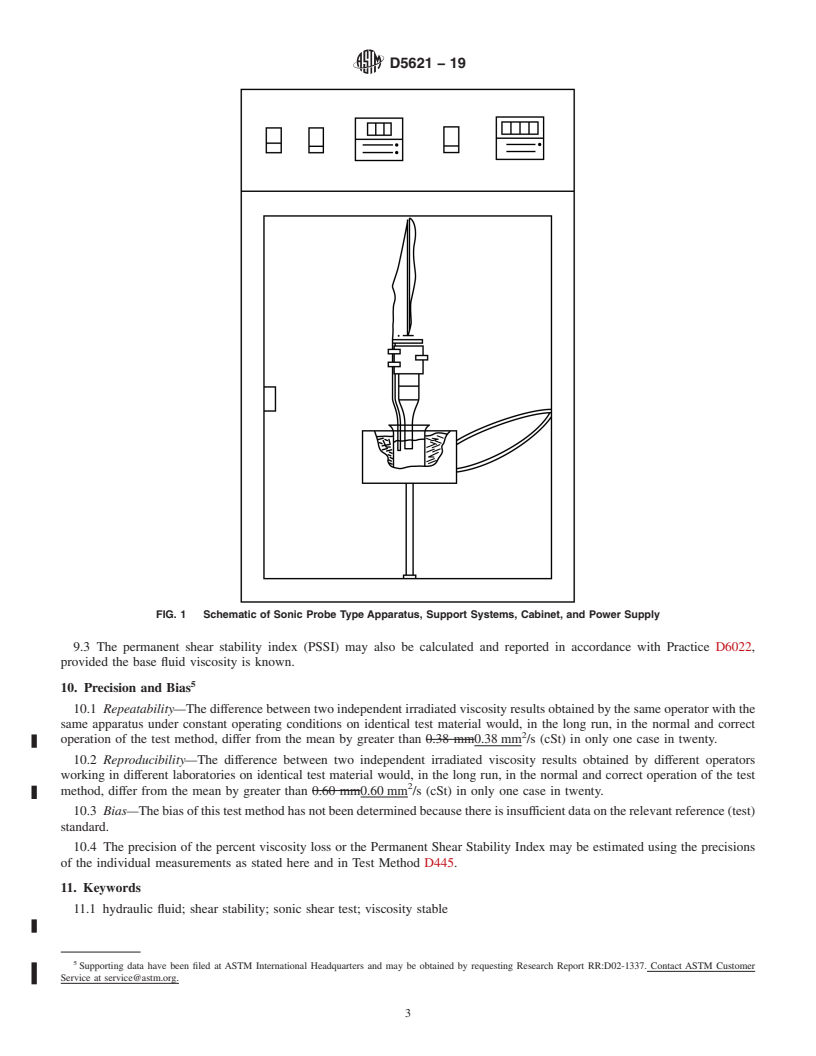
and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscos-
5.1 Sonic Shear Unit, fixed frequency oscillator and sonic
ity)
horn.
1
5.2 Auxiliary Equipment—To facilitate uniform
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
performance, the following auxiliary equipment is recom-
Subcommittee D02.07 on Flow Properties.
mended:
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2019.PublishedJuly2019.Originallyapproved
5.2.1 Cooling Bath or Ice Bath, to maintain a jacket
in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as D5621 – 07 (2013). DOI:
temperature of 0 °C.
10.1520/D5621-19.
2
Stambaugh, R. L., Kopko, R. J., and Roland, T. F., “Hydraulic Pump
5.2.2 Griffın 50 mL Beaker, borosilicate glass.
Performance—A Basis for Fluid Viscosity Classification,” SAE Paper No. 901633.
5.2.3 Sonic-Insulated Box, to enclose the sonic horn to
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr.,
reduce the ambient noise level produced by the sonic shear
Warrendale, PA 15096.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or unit.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.3 Viscometer, any viscometer and bath meeting the re-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. quirements of Test Method D445.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5621 − 19
6. Reference Fluids
4
6.1 The reference fluid is ASTM Reference Fluid B, a
petroleum oil containing a polymer capable of being broken
down by turbulence at high rates of shear. This oil has a
2
viscosity of about 13.6 mm /s (cSt) at 40 °C. The viscosity of
a specific lot is supplied by the provider
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5621 − 07 (Reapproved 2013) D5621 − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Sonic Shear Stability of Hydraulic Fluids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5621; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the shear stability of hydraulic fluids in terms of the final viscosity that results
from irradiating a sample of the hydraulic fluid in a sonic oscillator.
1.2 Evidence has been presented that a good correlation exists between the shear degradation that results from sonic oscillation
2
and that obtained in a vane pump test procedure.
2
1.3 This test method uses millimetres squared per second (mm /s), an SI unit, as the unit of viscosity. For information, the
equivalent unit, cSt, is shown in parentheses.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity)
D2603 Test Method for Sonic Shear Stability of Polymer-Containing Oils
D6022 Practice for Calculation of Permanent Shear Stability Index
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A convenient volume of hydraulic fluid is irradiated in a sonic oscillator for a period of time and the viscosities before and
after irradiation are determined by Test Method D445. A standard reference fluid containing a readily sheared polymer is run
frequently to ensure that the equipment imparts a controlled amount of sonic energy to the sample.
3.2 The conditions to obtain the data for the precision statement were: 30 mL sample, 12.5 min 30 mL sample, 12.5 min
calibration, and 40 min 40 min sample irradiation at 0°C0 °C jacket temperature.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method was developed using Test Method D2603–91.
4.2 This test method permits the evaluation of shear stability with minimum interference from thermal and oxidative factors that
may be present in some applications. It has been found applicable to fluids containing both readily sheared and shear-resistant
polymers. Correlation with performance in the case of hydraulic applications has been established.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Sonic Shear Unit, fixed frequency oscillator and sonic horn.
5.2 Auxiliary Equipment—To facilitate uniform performance, the following auxiliary equipment is recommended:
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.07 on Flow Properties.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013June 1, 2019. Published October 2013July 2019. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 20072013 as
D5621 – 07.D5621 – 07 (2013). DOI: 10.1520/D5621-07R13.10.1520/D5621-19.
2
Stambaugh, R. L., Kopko, R. J., and Roland, T. F., “Hydraulic Pump Performance—A Basis for Fluid Viscosity Classification”,Classification,” SAE Paper No. 901633.
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers, 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5621 − 19
5.2.1 Cooling Bath or Ice Bath, to maintain a jacket temperature of 0°C.0 °C.
5.2.2 Griffın 50–mL50 mL Beaker, borosilicate glass.
5.2.3 Sonic-Insulated Box, to enclose the sonic horn t
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.