ASTM D1384-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants in Glassware
Standard Test Method for Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants in Glassware
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a simple beaker-type procedure for evaluating the effects of engine coolants on metal specimens under controlled laboratory conditions (see Appendix X1).
Note 1—For more information on engine coolants, see (Refs 1-8)².
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards statements are given in 10.1.7.2, 10.1.7.3, and 10.1.7.4.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1384–05
Standard Test Method for
1
Corrosion Test for Engine Coolants in Glassware
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1384; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
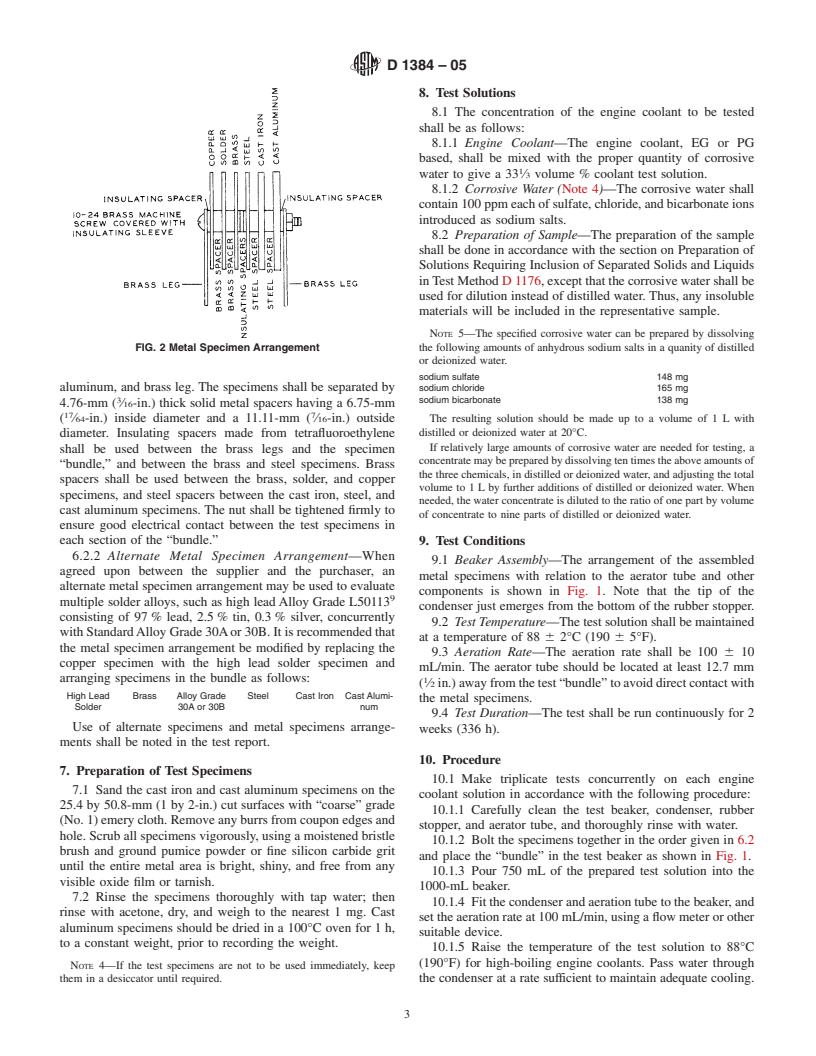
1. Scope 3. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers a simple beaker-type procedure 3.1 Inthistestmethod,specimensofmetalstypicalofthose
for evaluating the effects of engine coolants on metal speci- present in engine cooling systems are totally immersed in
mens under controlled laboratory conditions (see Appendix aeratedenginecoolantsolutionsfor336hat88°C(190°F).The
X1). corrosion-inhibitivepropertiesofthetestsolutionareevaluated
on the basis of the weight changes incurred by the specimens.
2
NOTE 1—For more information on engine coolants, see (Refs 1-8).
Each test is run in triplicate, and the average weight change is
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
determined for each metal. A single test may occasionally be
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
completely out of line (see 11.2).
only.
4. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 This test method will generally distinguish between
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
coolants that are definitely deleterious from the corrosion
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
standpoint and those that are suitable for further evaluation.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazards
However, the results of this test method cannot stand alone as
statements are given in 10.1.7.2, 10.1.7.3, and 10.1.7.4.
evidence of satisfactory corrosion inhibition. The actual ser-
vice value of an engine coolant formulation can be determined
2. Referenced Documents
only by more comprehensive bench, dynamometer, and field
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tests.
B32 Specification for Solder Metal
B36/B36M Specification for Brass Plate, Sheet, Strip, and 5. Apparatus
Rolled Bar
5.1 Container—A 1000-mL, tall-form, spoutless beaker,
D1176 Test Method for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous
made of heat-resistant glass, for containing the engine coolant
Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing
solution and test specimens. The beaker shall be tightly closed
Purposes
with a No. 15 rubber stopper, having drill holes to accommo-
E1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
date a water condenser, an aerator tube, and a thermometer as
4
E178 Practice for Dealing with Outlying Observations
shown in Fig. 1.
E230 Specification and Temperature-Electromotive Force
5.2 Condenser—Awatercondenserofthereflux,glass-tube
(EMF) Tables for Standardized Thermocouples
type, having a 400-mm (16-in.) condenser jacket.
G31 Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing
5.3 Aerator Tube— A gas-dispersion tube, porosity size
5
of Metals
12-C, to ensure continuous aeration without plugging.
4
Optionally, an all-glass apparatus may be used. Contact ASTM Headquarters
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D15 on Engine for details. Request Adjunct ADJD1384.
5
Coolants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.06 on Glassware The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
Performance Tests. is the Corning Glass Works. Gas-dispersion tube No. 39533, manufactured by the
Current edition approved June 1, 2005. Published June 2005. Originally Corning Glass Works, 44-5 Crystal St., Corning, NY, has generally has been found
approved in 1955. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D1384–04. satisfactory for this purpose. Optionally, a capillary tip bleed tube with 0.28-in.
2
Theboldfacenumbersinparenthesesrefertothelistofreferencesattheendof (7-mm) bore and 11.2-in. (280-mm) length may be used when consistent early
this standard. plugging of gas dispersion tubes occurs. The tube, catalog No. 7815-19, may be
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or obtained from the Corning Glass Works, Corning, NY14830. If you are aware of
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
5
the ASTM website. responsible technical committee , which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, Unit
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.