ASTM D2712-18
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in High Purity Propylene by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in High Purity Propylene by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 High-purity propylene is required as a feedstock for various manufacturing processes, and the presence of trace amounts of certain hydrocarbon impurities may have adverse effects on yield or catalyst life. This test method is suitable for use as a benchmark in setting commercial specifications, for use as an internal quality control tool, and for use in development or research work.
SCOPE
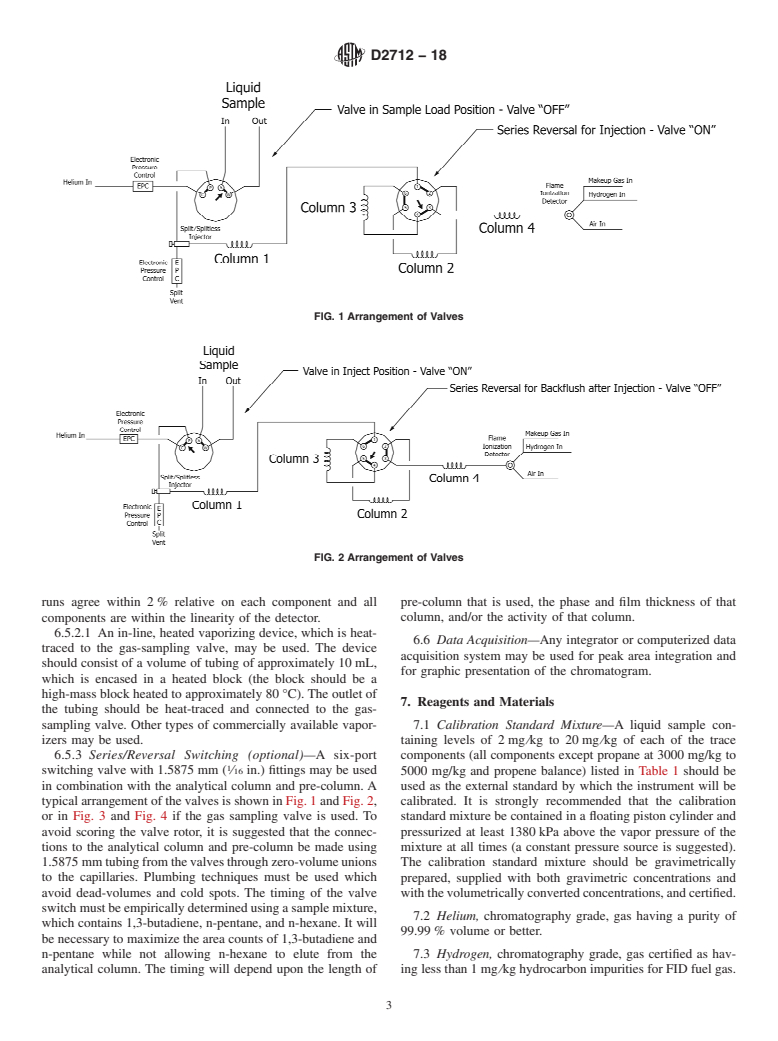
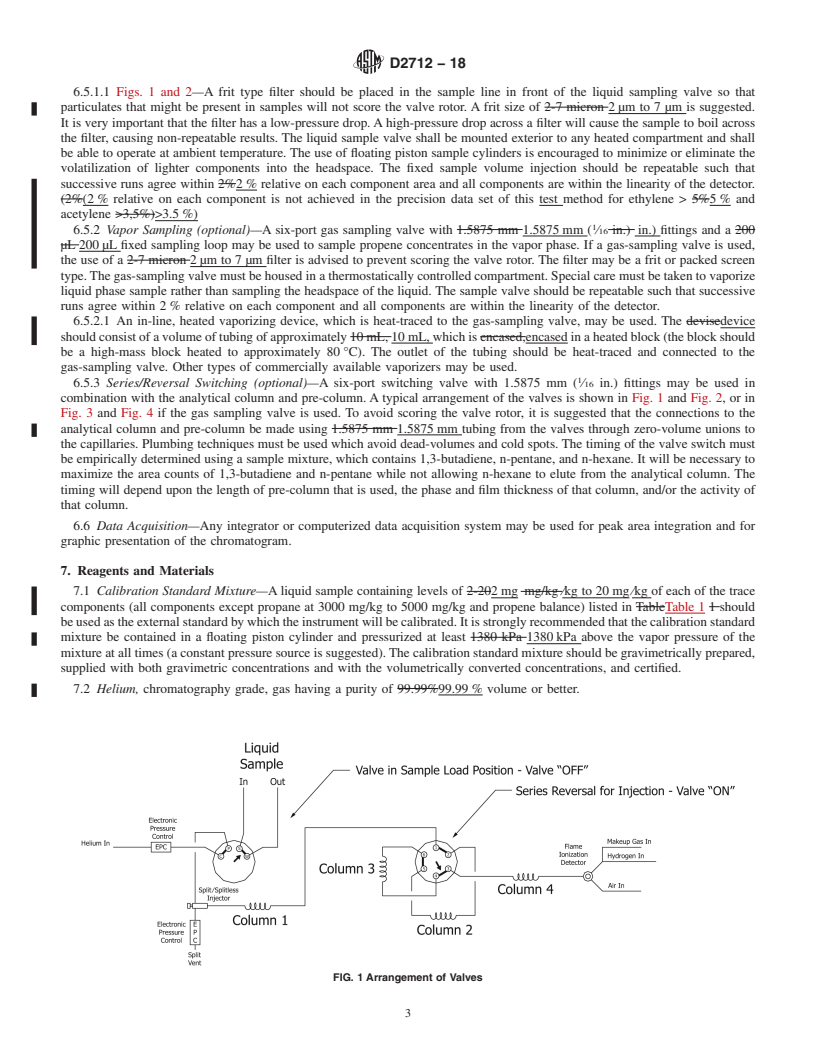
1.1 This test method is used for the determination of hydrocarbon impurities in propylene (propene) material of 97 % by mass or greater purity (concentrates). These impurities are determined in the concentration range of 0.35 mg/kg to 8575 mg/kg and includes the following components: methane, ethane, ethylene, propane, acetylene, isobutane, propadiene, normal butane, trans-2-butene, butene-1, isobutylene, cis-2-butene, isopentane, methylacetylene, normal pentane, and 1,3-butadiene.
Note 1: Optionally, the analysis may include the determination of pentenes/hexanes and heavier components, see 6.3.
1.2 This test method does not determine non-hydrocarbon impurities, and additional tests may be necessary to fully characterize the propylene sample. However, for the purposes of this test, the purity of propylene is determined as the difference between the total of the determined analytes and 100 % (by difference).
1.3 When this test method is being used for the determination of trace level impurities in high-purity propylene, the use of this test method for the analysis of propylene samples at lower purities is not recommended due to the potential for cross contamination between samples.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2712 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in High Purity
1
Propylene by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2712; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
NOTE—Previously balloted and approved material was included and the year date changed on January 19, 2018.
1. Scope* 1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method is used for the determination of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
hydrocarbon impurities in propylene (propene) material of
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
97 %bymassorgreaterpurity(concentrates).Theseimpurities
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
are determined in the concentration range of 0.35 mg⁄kg to
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
8575 mg/kg and includes the following components: methane,
ethane, ethylene, propane, acetylene, isobutane, propadiene,
2. Referenced Documents
normal butane, trans-2-butene, butene-1, isobutylene, cis-2-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
butene, isopentane, methylacetylene, normal pentane, and
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP)
1,3-butadiene.
Gases, Manual Method
NOTE 1—Optionally, the analysis may include the determination of
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Float-
pentenes/hexanes and heavier components, see 6.3.
ing Piston Cylinder
1.2 This test method does not determine non-hydrocarbon
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analy-
impurities, and additional tests may be necessary to fully
sis
characterize the propylene sample. However, for the purposes
3. Terminology
of this test, the purity of propylene is determined as the
difference between the total of the determined analytes and
3.1 Definitions:
100 % (by difference).
3.1.1 liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)—hydrocarbon gases
that can be stored or handled in the liquid phase under
1.3 When this test method is being used for the determina-
moderate conditions of pressure and at ambient temperature;
tion of trace level impurities in high-purity propylene, the use
they consist essentially of C and C alkanes and alkenes, or
of this test method for the analysis of propylene samples at
3 4
mixtures of these, and contain generally less than 0.5 % by
lower purities is not recommended due to the potential for
liquid volume of material of higher carbon number, and have a
cross contamination between samples.
vapor pressure not exceeding 2000 kPa at 40 °C.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.2 propylene concentrate—material-containing propyl-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
ene at or above concentrations of 97 % by mass.
standard.
1.5 This standard may involve hazardous materials,
4. Summary of Test Method
operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
4.1 An LPG phase sample is analyzed as received via either
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
gas or liquid sampling valves into a gas chromatograph. The
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
gas chromatograph is provided with a liquid sampling valve
establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental prac-
and optionally with a 6-port gas sampling valve and/or a 6-port
tices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations
switching valve. If the user chooses to use a 6-port switching
prior to use.
valve to provide an initial composite backflush of C olefins
5
and C + components, a small length of pre-column should be
6
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
2
Subcommittee D02.D0.03 on Propylene. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Jan. 19, 2018. Published January 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ɛ1
approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 2017 as D2712 – 17 . DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D2712-18. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2712 − 18
used to provide separation of the components of interest, as temperatures up to
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D2712 − 17 D2712 − 18
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Hydrocarbon Impurities in High Purity
1
Propylene by Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2712; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
NOTE—Added Summary of Changes section editorially in January Previously balloted and approved material was included and the year
date changed on January 19, 2018.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method is used for the determination of hydrocarbon impurities in Propylenepropylene (propene) material of 97 %
by mass or greater purity (concentrates). These impurities are determined in the concentration range of 0.350.35 mg mg/kg ⁄kg to
8575 mg/kg and includes the following components,components: methane, ethane, ethylene, propane, acetylene, isobutane,
propadiene, normal butane, trans-2-butene, butene-1, isobutylene, cis-2-butene, isopentane, methylacetylene, normal pentane, and
1,3-butadiene.
NOTE 1—Optionally, the analysis may include the determination of pentenes/hexanes and heavier components, see 6.3.
1.2 This test method does not determine non-hydrocarbon impurities, and additional tests may be necessary to fully characterize
the propylene sample. However, for the purposes of this test, the purity of propylene is determined as the difference between the
total of the determined analytes and 100 % (by difference).
1.3 When this test method is being used for the determination of trace level impurities in high-purity propylene, the use of this
test method for the analysis of propylene samples at lower purities is not recommended due to the potential for cross contamination
between samples.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all
of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate
safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases, Manual Method
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Floating Piston Cylinder
F307 Practice for Sampling Pressurized Gas for Gas Analysis
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 propylene concentrate—material-containing propylene at or above concentrations of 97% by mass.
3.1.1 liquefied petroleum gas (LPG)—hydrocarbon gases that can be stored or handled in the liquid phase under moderate
conditions of pressure and at ambient temperature. Theytemperature; they consist essentially of C and C alkanes and alkenes,
3 4
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.D0.03 on Propylene.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2017Jan. 19, 2018. Published December 2017January 2018. Originally approved in 1968. Last previous edition approved in 20162017
ɛ1
as D2712 – 9117 (2016). . DOI: 10.1520/D2712-17E01.10.1520/D2712-18.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2712 − 18
or mixtures of these, and contain generally less than 0.5 % by liquid volume of material of higher carbon number, and have a vapor
pressure not exceeding 2000 kPa 2000 kPa at 40 °C.
3.1.2 propylene concentrate—material-containing propylene at or above concentr
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.