ASTM D3908-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Hydrogen Chemisorption on Supported Platinum Catalysts by Volumetric Vacuum Method
Standard Test Method for Hydrogen Chemisorption on Supported Platinum Catalysts by Volumetric Vacuum Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method sets forth a procedure by which duplicate catalyst samples can be compared either on an interlaboratory or intralaboratory basis. It is anticipated that catalyst producers and users will find this test method of value.
4.2 Discrimination of the samples for which this procedure is recommended must be exercised when considering carrier (support) materials that sorb appreciable quantities of hydrogen or could cause an alteration of the state of the catalyst during pretreatment, or both, (that is, sintering or metal occlusion). These materials must be identified by the user and experimented with to determine the most significant conditions of measurement.
4.3 This test method provides a measure of the total hydrogen uptake (volume of hydrogen at STP, cm3/g of catalyst) without specifying the nature of the hydrogen-platinum interaction. Persons interested in using hydrogen uptake data to calculate percent platinum dispersion in a specific catalyst should be aware of carrier (support) interactions, spillover effects, and other phenomena related to the hydrogen uptake capabilities of the catalyst in question.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the chemisorption of hydrogen at 298 K (25 °C) on supported platinum catalysts that have been reduced in flowing hydrogen at 723 K (450 °C). It incorporates a static volumetric vacuum technique at constant volume.
1.2 The test method is intended for use on unused supported platinum on alumina catalysts of loadings greater than 0.3 weight %. Data on other supports and lower platinum loadings were not tested.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D3908 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Hydrogen Chemisorption on Supported Platinum Catalysts
1
by Volumetric Vacuum Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3908; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—See Terminology D3766.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the
chemisorption of hydrogen at 298 K (25°C) on supported
3.2 Quality and Statistics—See Terminology E456.
platinum catalysts that have been reduced in flowing hydrogen
3.3 Precision and Bias—See Practice E177.
at 723K (450°C). It incorporates a static volumetric vacuum
technique at constant volume.
3.4 Symbols—The following symbols are used:
1.2 Thetestmethodisintendedforuseonunusedsupported
platinum on alumina catalysts of loadings greater than 0.3
P = pressure of gas in calibrated bulb, torr
c
weight %. Data on other supports and lower platinum loadings
P = pressure of gas in calibrated bulb and
mc
were not tested.
manifold, torr
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the P = pressure in manifold, torr
m
P = pressure in manifold and dead space, torr
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
md
P = pressure in manifold prior to expansion into
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
m
x
sample tube for X equilibration point, torr
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
P = equilibrium pressure after expansion for gen-
e
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
x
erating X equilibrium point, torr
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3
V = volume of calibrated bulb, cm
c
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
V = volume of manifold between stopcocks 12
m
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3
and 2 with only 4 and 1 open, cm
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
V = volume of dead space in sample cell contain-
d
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical 3
ing catalyst (volume between 2 and 3), cm
3
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
V (STP) = volume of gas adsorbed at STP, cm
ads x
V (STP) = cumulative volume of gas adsorbed through
ads cx
3
2. Referenced Documents
X,cm
V = monolayer volume of gas adsorbed at STP,
2
S
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
cm
D3766Terminology Relating to Catalysts and Catalysis
T = temperature representative of the manifold
m
Ax
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
prior to expansion into the sample cell, K
ASTM Test Methods
T = temperature representative of the entire sys-
m
Bx
E456Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
tem after equilibrium pressure (P ) has been
e
x
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
established, K
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
T = temperature of manifold prior to expansion
m
intosamplecellfordeadspacedetermination,
K
1
T = temperatureofentiresystemafterequilibrium
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on
m
D
Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.01 on Physical-
pressure has been established for dead space
Chemical Properties.
determination, K
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2020. Published November 2020. Originally
T = average manifold temperature for a given
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D3908–03(2015).
dose, K
DOI: 10.1520/D3908-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
=(T + T )/2
m m
Ax Bx
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
W = mass of catalyst, g
cat
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
X = weight percent of platinum
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3908 − 20
FIG. 1 Schematic: Static Vacuum System
manifold. One should make sure that the glass blowing is
%D = percent platinum atoms on the surface
sufficiently far removed from the calibrated volume to avoid
4. Significance and Use
distortion.
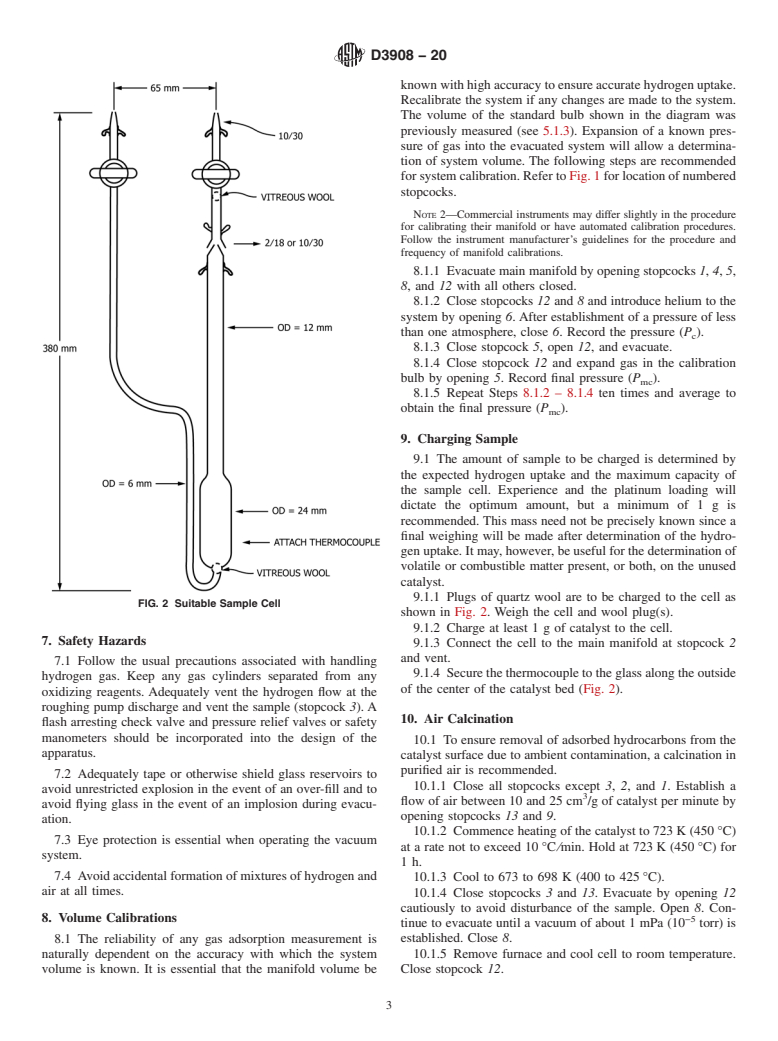
5.1.4 Flow-Through Cell,thatcanbeevacuatedandthatcan
4.1 This test method sets forth a procedure by which
be detached from the main manifold; for example, see Fig. 2.
duplicate catalyst samples can be compared either on an
This is accomplished by including a remova
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D3908 − 03 (Reapproved 2015) D3908 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Hydrogen Chemisorption on Supported Platinum Catalysts
1
by Volumetric Vacuum Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3908; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the chemisorption of hydrogen at 298 K (25°C)(25 °C) on supported platinum
catalysts that have been reduced in flowing hydrogen at 723 K (450°C).(450 °C). It incorporates a static volumetric vacuum
technique at constant volume.
1.2 The test method is intended for use on unused supported platinum on alumina catalysts of loadings greater than 0.3 weight
%. Data on other supports and lower platinum loadings were not tested.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D3766 Terminology Relating to Catalysts and Catalysis
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—See Terminology D3766.
3.2 Quality and Statistics—See Terminology E456.
3.3 Precision and Bias—See Practice E177.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D32 on Catalysts and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D32.01 on Physical-Chemical
Properties.
Current edition approved April 1, 2015Oct. 1, 2020. Published June 2015November 2020. Originally approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 20082015 as
D3908 – 03 (2008).(2015). DOI: 10.1520/D3908-03R15.10.1520/D3908-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3908 − 20
FIG. 1 Schematic: Static Vacuum System
3.4 Symbols—The following symbols are used:
P = pressure of gas in calibrated bulb, torr
c
P = pressure of gas in calibrated bulb and manifold, torr
mc
P = pressure in manifold, torr
m
P = pressure in manifold and dead space, torr
md
P = pressure in manifold prior to expansion into sample tube for X equilibration point, torr
m
x
P = equilibrium pressure after expansion for generating X equilibrium point, torr
e
x
3
V = volume of calibrated bulb, cm
c
3
V = volume of manifold between stopcocks 12 and 2 with only 4 and 1 open, cm
m
3
V = volume of dead space in sample cell containing catalyst (volume between 2 and 3), cm
d
3
V (STP) = volume of gas adsorbed at STP, cm
ads x
3
V (STP) = cumulative volume of gas adsorbed through X, cm
ads cx
3
V = monolayer volume of gas adsorbed at STP, cm
S
T = temperature representative of the manifold prior to expansion into the sample cell, K
m
Ax
T = temperature representative of the entire system after equilibrium pressure (P ) has been established, K
m e
Bx x
T = temperature of manifold prior to expansion into sample cell for dead space determination, K
m
T = temperature of entire system after equilibrium pressure has been established for dead space determination, K
m
D
T = average manifold temperature for a given dose, K
= (T + T )/2
m m
Ax Bx
W = mass of catalyst, g
cat
X = weight percent of platinum
%D = percent platinum atoms on the surface
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method sets forth a procedure by which duplicate catalyst samples can be compared either on an interlaboratory or
intralaboratory ba
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.