ASTM D3385-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Infiltration Rate of Soils in Field Using Double-Ring Infiltrometer
Standard Test Method for Infiltration Rate of Soils in Field Using Double-Ring Infiltrometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is useful for field measurement of the infiltration rate of soils. Infiltration rates have application to such studies as liquid waste disposal, evaluation of potential septic-tank disposal fields, leaching and drainage efficiencies, irrigation requirements, water spreading and recharge, and canal or reservoir leakage, among other applications.
Although the units of infiltration rate and hydraulic conductivity of soils are similar, there is a distinct difference between these two quantities. They cannot be directly related unless the hydraulic boundary conditions are known, such as hydraulic gradient and the extent of lateral flow of water, or can be reliably estimated.
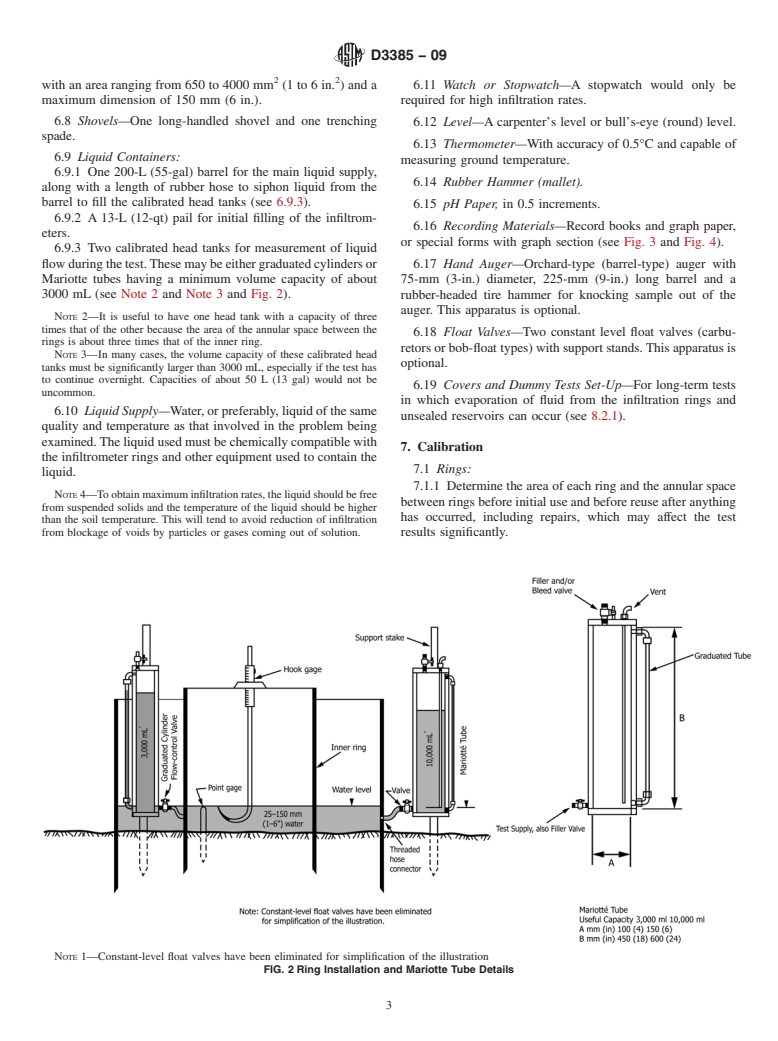
The purpose of the outer ring is to promote one-dimensional, vertical flow beneath the inner ring.
Many factors affect the infiltration rate, for example the soil structure, soil layering, condition of the soil surface, degree of saturation of the soil, chemical and physical nature of the soil and of the applied liquid, head of the applied liquid, temperature of the liquid, and diameter and depth of embedment of rings. Thus, tests made at the same site are not likely to give identical results and the rate measured by the test method described in this standard is primarily for comparative use.
Some aspects of the test, such as the length of time the tests should be conducted and the head of liquid to be applied, must depend upon the experience of the user, the purpose for testing, and the kind of information that is sought.
Note 1—The quality of the result produced by this standard is dependent on the competence of the personnel performing it, and the suitability of the equipment and facilities used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice D3740 are generally considered capable of competent and objective testing/sampling/inspection/etc. Users of this standard are cautioned that compliance with Practice D3740 does not in itself assure reliable results. Reliable results d...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for field measurement of the rate of infiltration of liquid (typically water) into soils using double-ring infiltrometer.
1.2 Soils should be regarded as natural occurring fine or coarse-grained soils or processed materials or mixtures of natural soils and processed materials, or other porous materials, and which are basically insoluble and are in accordance with requirements of 1.5.
1.3 This test method is particularly applicable to relatively uniform fine-grained soils, with an absence of very plastic (fat) clays and gravel-size particles and with moderate to low resistance to ring penetration.
1.4 This test method may be conducted at the ground surface or at given depths in pits, and on bare soil or with vegetation in place, depending on the conditions for which infiltration rates are desired. However, this test method cannot be conducted where the test surface is below the groundwater table or perched water table.
1.5 This test method is difficult to use or the resultant data may be unreliable, or both, in very pervious or impervious soils (soils with a hydraulic conductivity greater than about 10−2 cm/s or less than about 1 × 10−6 cm/s) or in dry or stiff soils that most likely will fracture when the rings are installed. For soils with hydraulic conductivity less than 1 × 10−6 cm/s refer to Test Method D5093.
1.6 This test method cannot be used directly to determine the hydraulic conductivity (coefficient of permeability) of the soil (see 5.2).
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D3385 −09
Standard Test Method for
Infiltration Rate of Soils in Field Using Double-Ring
1
Infiltrometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3385; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for field mea-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
surement of the rate of infiltration of liquid (typically water)
into soils using double-ring infiltrometer.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 Soils should be regarded as natural occurring fine or
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
coarse-grained soils or processed materials or mixtures of
D653Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
naturalsoilsandprocessedmaterials,orotherporousmaterials,
Fluids
and which are basically insoluble and are in accordance with
D1452Practice for Soil Exploration and Sampling byAuger
requirements of 1.5.
Borings
1.3 This test method is particularly applicable to relatively
D2216Test Methods for Laboratory Determination ofWater
uniformfine-grainedsoils,withanabsenceofveryplastic(fat)
(Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass
clays and gravel-size particles and with moderate to low
D2488Practice for Description and Identification of Soils
resistance to ring penetration.
(Visual-Manual Procedure)
D3740Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies
1.4 This test method may be conducted at the ground
Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as
surface or at given depths in pits, and on bare soil or with
Used in Engineering Design and Construction
vegetation in place, depending on the conditions for which
D5093Test Method for Field Measurement of Infiltration
infiltration rates are desired. However, this test method cannot
Rate Using Double-Ring Infiltrometer with Sealed-Inner
be conducted where the test surface is below the groundwater
Ring
table or perched water table.
1.5 This test method is difficult to use or the resultant data
3. Terminology
maybeunreliable,orboth,inveryperviousorimpervioussoils
−2
3.1 Definitions—For common definitions of terms in this
(soils with a hydraulic conductivity greater than about 10
−6
standard, refer to Terminology D653.
cm/s or less than about 1×10 cm/s) or in dry or stiff soils
that most likely will fracture when the rings are installed. For
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
−6
soils with hydraulic conductivity less than 1×10 cm/s refer
3.2.1 incremental infiltration velocity—the quantity of flow
to Test Method D5093.
per unit area over an increment of time. It has the same units
as the infiltration rate.
1.6 This test method cannot be used directly to determine
the hydraulic conductivity (coefficient of permeability) of the 3.2.2 infiltration—the downward entry of liquid into the
soil (see 5.2). soil.
3.2.3 infiltration rate—a selected rate, based on measured
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
incremental infiltration velocities, at which liquid can enter the
standard.
soil under specified conditions, including the presence of an
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
excess of liquid. It has the dimensions of velocity (that is,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3 −2 −1 −1
cm cm h =cmh ).
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD18onSoiland
Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.04 on Hydrologic
2
Properties and Hydraulic Barriers. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved March 1, 2009. Published March 2009. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D3385–03. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D3385-09. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3385−09
3.2.4 infiltrometer—a device for measuring the rate of entry 6. Apparatus
of liquid into a porous body, for example, water into soil.
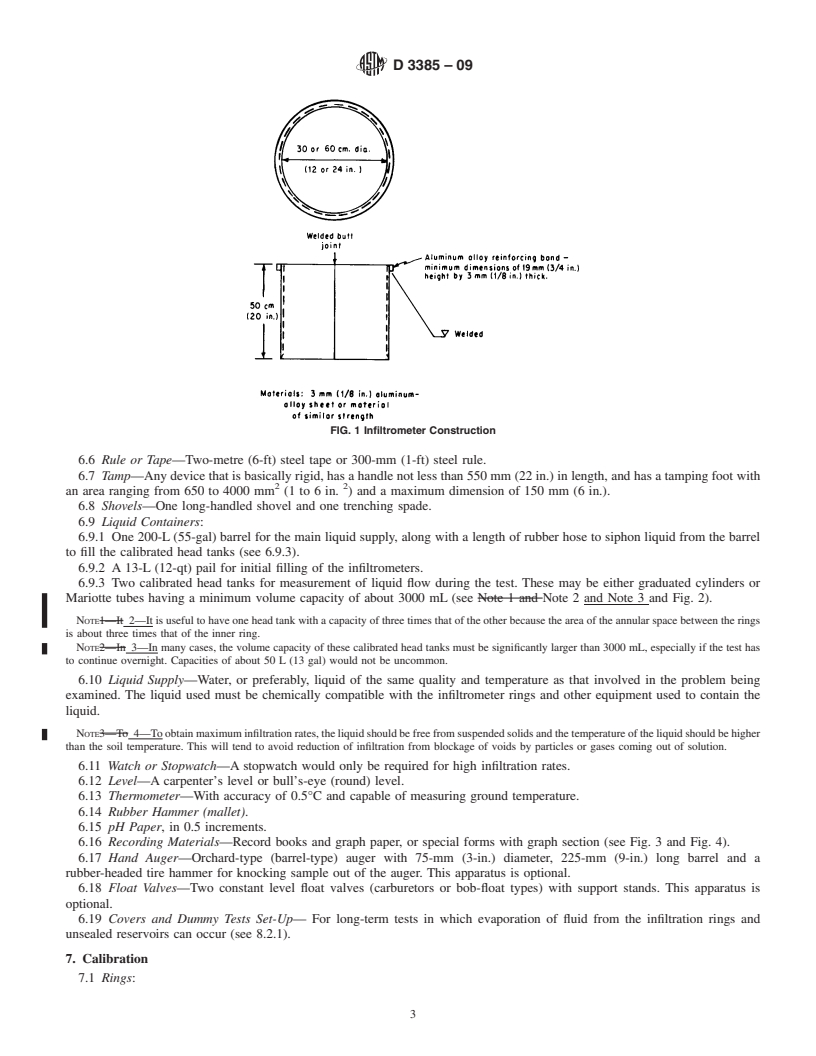
6.1 Infiltrometer Rings—Cylinders approximately 500 mm
(20 in.) high and having diameters of about 300 and 600 mm
4. Summary of Test Method
(12 and 24 in.). Larger cylinders may be used, providing the
4.1 Thedouble-ringinfiltrometermethodconsistsofdriving ratio
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D3385–03 Designation: D 3385 – 09
Standard Test Method for
Infiltration Rate of Soils in Field Using Double-Ring
1
Infiltrometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3385; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method describes a procedure for field measurement of the rate of infiltration of liquid (typically water) into soils
using double-ring infiltrometer.
1.2 Soils should be regarded as natural occurring fine or coarse-grained soils or processed materials or mixtures of natural soils
and processed materials, or other porous materials, and which are basically insoluble and are in accordance with requirements of
1.5.
1.3 Thistestmethodisparticularlyapplicabletorelativelyuniformfine-grainedsoils,withanabsenceofveryplastic(fat)clays
and gravel-size particles and with moderate to low resistance to ring penetration.
1.4 This test method may be conducted at the ground surface or at given depths in pits, and on bare soil or with vegetation in
place, depending on the conditions for which infiltration rates are desired. However, this test method cannot be conducted where
the test surface is below the ground water table or perched water table.
1.5 Thistestmethodisdifficulttouseortheresultantdatamaybeunreliable,orboth,inveryperviousorimpervioussoils(soils
−2 −6
withahydraulicconductivitygreaterthanabout10 cm/sorlessthanabout1 310 cm/s)orindryorstiffsoilsthatmostlikely
−6
will fracture when the rings are installed. For soils with hydraulic conductivity less than 1 310 cm/s refer to Test Method
D5093.
1.6 Thistestmethodcannotbeuseddirectlytodeterminethehydraulicconductivity(coefficientofpermeability)ofthesoil(see
5.2).
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids
D1452 Practice for Soil Investigation and Sampling by Auger Borings
2
D2216 Method for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil, Rock, and Soil-Aggregate Mixtures Test
Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass
D2488 Practice for Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure)
D3740 Practice for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Engaged in Testing and/or Inspection of Soil and Rock as Used in
Engineering Design and Construction
D5093 Test Method for Field Measurement of Infiltration Rate Using a Double-Ring Infiltrometer With a Sealed Inner with
Sealed-Inner Ring
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1For common definitions of terms in this standard, refer to Terminology D 653.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.04 on Hydrologic Properties
of Soil and Rock. Hydraulic Barriers.
Current edition approved June 10, 2003.March 1, 2009. Published August 2003.March 2009. Originally approved in 1975. Discontinued December 2002 and reinstated
Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D3385–03.
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 04.08.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3385–09
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 incremental infiltration velocity—the quantity of flow per unit area over an increment of time. It has the same units as the
infiltration rate.
3.1.2
3.2.2 infiltration—the downward entry of liquid into the soil.
3.1.3
3.2.3 infiltration rate—a selected rate, based on measured incremental infiltration velocities, at which liquid can enter the soil
3 −2
under specified conditions, including the presence of an excess
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.