ASTM D8311-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Impurities in Monoethylene Glycol by Gas Chromatography with Normalization
Standard Test Method for Impurities in Monoethylene Glycol by Gas Chromatography with Normalization
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
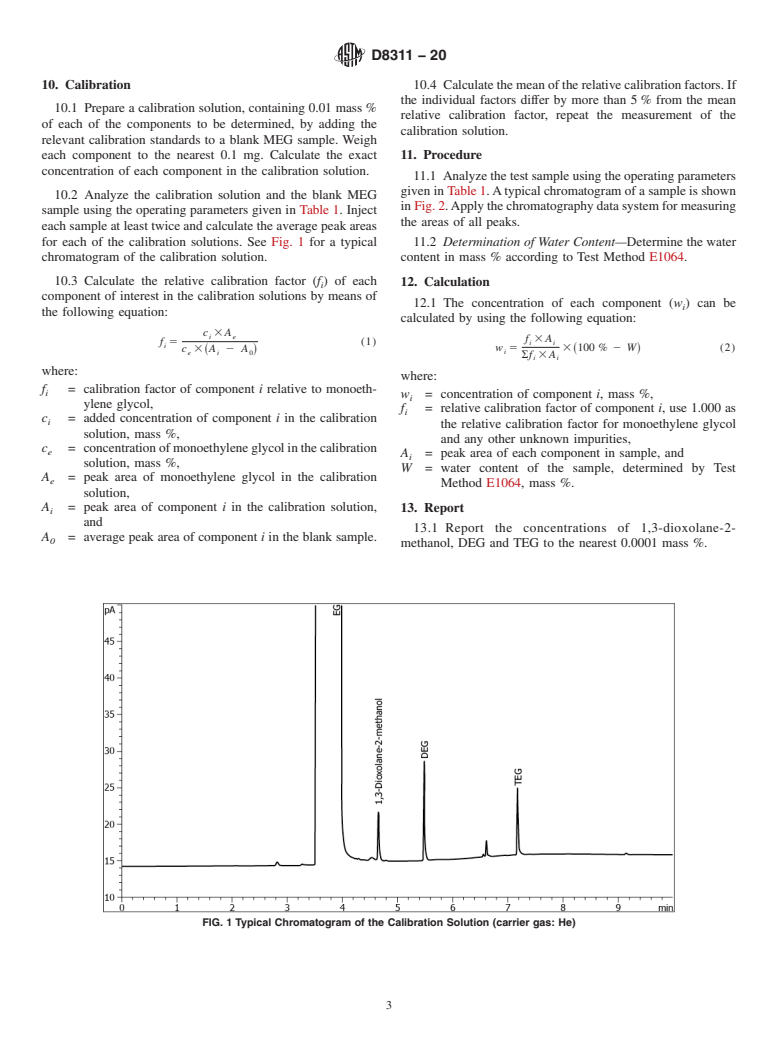
4.1 This test method is suitable for setting specifications and for use as an internal quality control tool where these products are produced or are used. Typical impurities are: 1,3-dioxolane-2-methanol, diethylene glycol, and triethylene glycol.
4.2 This method may not detect all components and there may be unknown components that would be assigned inappropriate relative calibration factors and thus, the results may not be absolute.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the gas chromatographic determination of impurities in monoethylene glycol including 1,3-dioxolane-2-methanol, diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethylene glycol (TEG). The purity of monoethylene glycol (MEG) is also calculated. A similar test method, using the internal standard calibration technique and the external standard calibration technique, is Test Method E2409.
1.2 This test method is applicable for monoethylene glycol purities of 98.0 mass % or higher.
1.3 The limit of detection (LOD) for 1,3-dioxolane-2-methanol, DEG and TEG is 0.0002 mass %.
1.4 In determining the conformance of the test results using this method to applicable specifications, results shall be rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D8311 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Impurities in Monoethylene Glycol by Gas Chromatography
1
with Normalization
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D8311; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers the gas chromatographic deter- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
mination of impurities in monoethylene glycol including 1,3- D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance
dioxolane-2-methanol, diethylene glycol (DEG) and triethyl- Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Ma-
ene glycol (TEG). The purity of monoethylene glycol (MEG) terials
is also calculated. A similar test method, using the internal E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
standard calibration technique and the external standard cali- Determine Conformance with Specifications
bration technique, is Test Method E2409. E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relation-
1.2 This test method is applicable for monoethylene glycol
ships
purities of 98.0 mass % or higher.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.3 The limit of detection (LOD) for 1,3-dioxolane-2-
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
methanol, DEG and TEG is 0.0002 mass %.
E1064 Test Method for Water in Organic Liquids by Coulo-
metric Karl Fischer Titration
1.4 In determining the conformance of the test results using
this method to applicable specifications, results shall be E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of
Practice E29. E2409 TestMethodforGlycolImpuritiesinMono-,Di-,Tri-
and Tetraethylene Glycol and in Mono- and Dipropylene
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Glycol(Gas Chromatographic Method)
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
2.2 Other Document:
standard.
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR paragraphs 1910.1000 and
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the 3
1910.1200
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 3. Summary of Test Method
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.1 The specimen to be analyzed is injected into a gas
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
chromatographequippedwithaflameionizationdetector(FID)
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
and a capillary column.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.2 The peak area of each component is measured and
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
adjustedusingrelativecalibrationfactors.Theconcentrationof
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
each component is calculated based on its relative percentages
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
of total adjusted peak area and normalized to 100.0000 %.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Aromatic, Industrial, Specialty and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsi- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
bility of Subcommittee D16.14 on Alcohols & Glycols. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved April 1, 2020. Published May 2020. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), 200
D8311-20. Constitution Ave., NW, Washington, DC 20210, http://www.osha.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D8311 − 20
4. Significance and Use 6. Reagents and Materials
4.1 Thistestmethodissuitableforsettingspecificationsand 6.1 Purity of Reagent—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
for use as an internal quality control tool where these products
are produced or are used. Typical impurities are: 1,3- all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
tee onAnalytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society,
dioxolane-2-methanol, diethylene glycol, an
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.