ASTM C411-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-Temperature Thermal Insulation
Standard Test Method for Hot-Surface Performance of High-Temperature Thermal Insulation
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Performance in service is the final measure of value for a thermal insulation, but simulative service tests give useful indications. One type involves application for a specified time to a surface heated at a temperature approximately that of intended service, and noting during the test and afterward, changes in the material and its properties. Measurement of these changes are used for predicting what occurs in service as a result of exposure to temperatures corresponding to those of the tests.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the performance of commercial sizes of both block and pipe forms of thermal insulating materials when exposed to simulated hot-surface application conditions. The term “hot-surface performance” has reference to a simulated use-temperature test in which the heated testing surface is in a horizontal position.
1.2 This test method refers primarily to high-temperature insulations that are applicable to hot-side temperatures in excess of 200°F (93°C). It is used for materials such as preformed insulations, insulating cements, blankets, and the like, by proper laboratory preparation of the samples.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C411 − 11
Standard Test Method for
Hot-Surface Performance of High-Temperature Thermal
1
Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C411; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the perfor-
3.1 Definitions—Terminology C168 shall apply to the terms
mance of commercial sizes of both block and pipe forms of used in this test method.
thermal insulating materials when exposed to simulated hot-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
surface application conditions. The term “hot-surface perfor-
3.2.1 sag, n—the extent of thickness loss of pipe insulation,
mance” has reference to a simulated use-temperature test in
at the top longitudinal center, due to material fatigue or
which the heated testing surface is in a horizontal position.
decomposition due to elevated temperature.
1.2 This test method refers primarily to high-temperature
insulations that are applicable to hot-side temperatures in
4. Significance and Use
excess of 200°F (93°C). It is used for materials such as
4.1 Performance in service is the final measure of value for
preformed insulations, insulating cements, blankets, and the
a thermal insulation, but simulative service tests give useful
like, by proper laboratory preparation of the samples.
indications. One type involves application for a specified time
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
to a surface heated at a temperature approximately that of
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
intended service, and noting during the test and afterward,
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
changes in the material and its properties. Measurement of
and are not considered standard.
these changes are used for predicting what occurs in service as
a result of exposure to temperatures corresponding to those of
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the tests.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
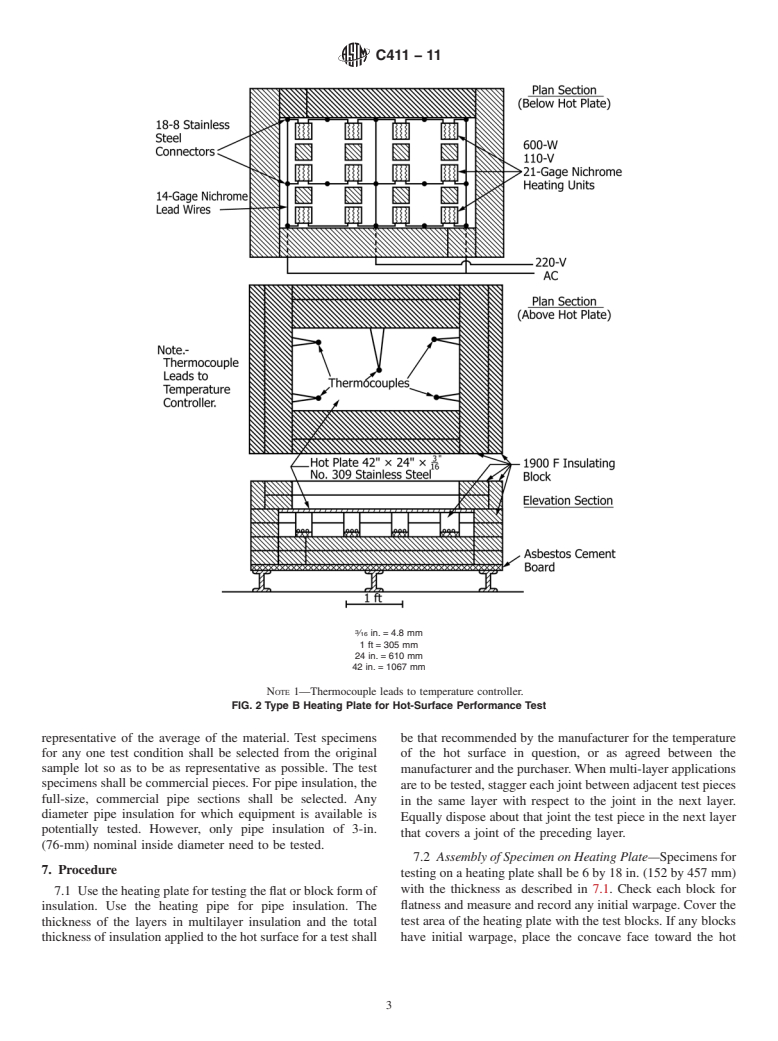
5.1 Heating Plate—The heating plate shall consist of a
corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant plate with a preferred
2. Referenced Documents
exposed test area of 36 by 18 in. (914 by 457 mm), but having
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
a minimum test area of 18 by 18 in. (457 by 457 mm). The
C167Test Methods forThickness and Density of Blanket or
heated area shall have an insulated, heated guard area having a
Batt Thermal Insulations
minimumwidthof3in.(76mm)aroundtheentireperipheryof
C168Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
the test area.The plate shall be supported in a horizontal plane
C356Test Method for Linear Shrinkage of Preformed High-
at a sufficient number of points to prevent sagging. It shall be
Temperature Thermal Insulation Subjected to Soaking
heated on the under side by gas or electricity. The surface
Heat temperatureoftheplateshallbemeasuredbynotlessthanfive
thermocouples. Four of the thermocouples shall be located
alongthediagonalsthatextendfromthecornersoftheexposed
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeC16onThermal
area of the plate and at a distance of 6 in. (152 mm) in from
InsulationandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeC16.31onChemicaland
each corner. A fifth thermocouple shall be located near the
Physical Properties.
center of the test plate area. The temperature at no point of
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published August 2011. Originally
measurement shall vary more than 65%or 625°F (614°C),
approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as C411–05. DOI:
10.1520/C0411-11.
whichever is less, from the desired temperature. A heating
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
chamber beneaththe heatingplate shall be formedtoretainthe
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
heat generated by the heating means. A 6-in. thickness of
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. insulation shall form the bottom and the sides, and the heating
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C411 − 11
plate shall form the top of the c
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:C411–05 Designation:C411–11
Standard Test Method for
Hot-Surface Performance of High-Temperature Thermal
1
Insulation
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C411; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the performance of commercial sizes of both block and pipe forms of thermal
insulating materials when exposed to simulated hot-surface application conditions. The term “hot-surface performance” has
reference to a simulated use-temperature test in which the heated testing surface is in a horizontal position.
1.2 This test method refers primarily to high-temperature insulations that are applicable to hot-side temperatures in excess of
200°F(93°C).Itisusedformaterialssuchaspreformedinsulations,insulatingcements,blankets,andthelike,byproperlaboratory
preparation of the samples.
1.3The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C167 Test Methods for Thickness and Density of Blanket or Batt Thermal Insulations
C168 Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation Terminology Relating to Thermal Insulation
C356 Test Method for Linear Shrinkage of Preformed High-Temperature Thermal Insulation Subjected to Soaking Heat
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Terminology C168 shall apply to the terms used in this test method.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 sag, n—the extent of thickness loss of pipe insulation, at the top longitudinal center, due to material fatigue or
decomposition due to elevated temperature.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Performance in service is the final measure of value for a thermal insulation, but simulative service tests give useful
indications. One type involves application for a specified time to a surface heated at a temperature approximately that of intended
service,andnotingduringthetestandafterward,changesinthematerialanditsproperties.Measurementofthesechangesareused
for predicting what occurs in service as a result of exposure to temperatures corresponding to those of the tests.
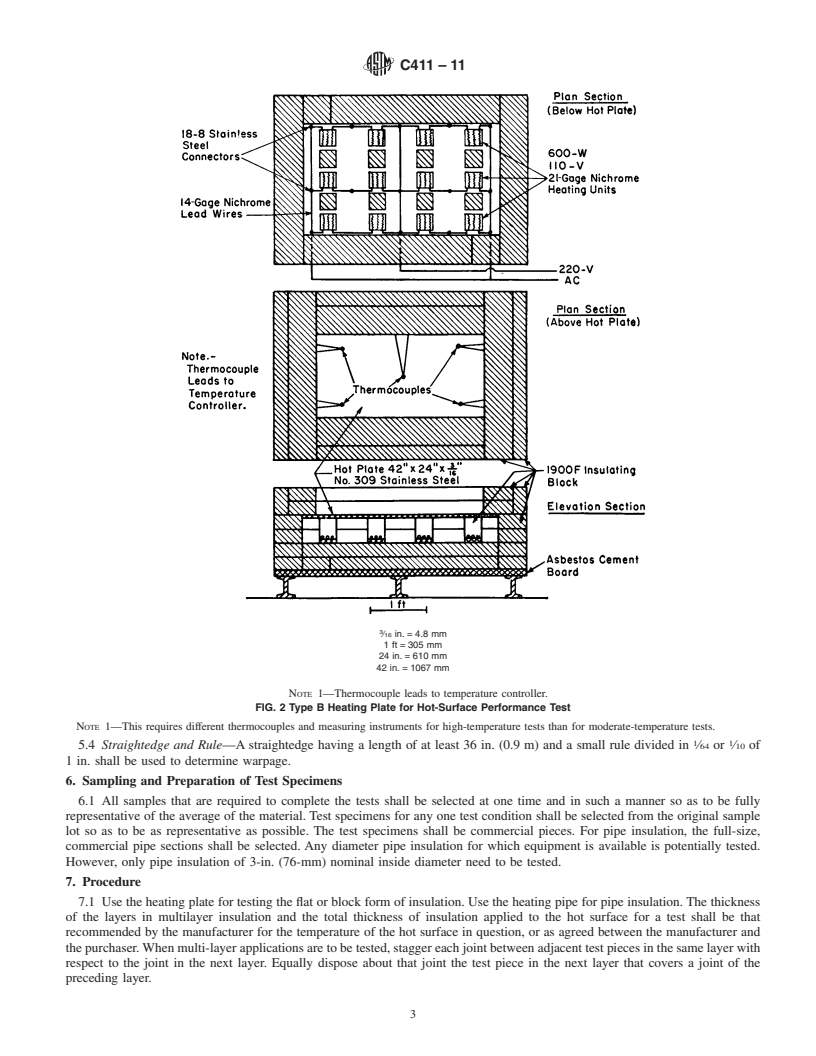
5. Apparatus
5.1 Heating Plate—The heating plate shall consist of a corrosion-resistant and heat-resistant plate with a preferred exposed test
area of 36 by 18 in. (914 by 457 mm), but having a minimum test area of 18 by 18 in. (457 by 457 mm). The heated area shall
have an insulated, heated guard area having a minimum width of 3 in. (76 mm) around the entire periphery of the test area. The
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C16 on Thermal Insulation and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C16.31 on Chemical and
Physical Properties.
Current edition approved Nov.May 1, 2005.2011. Published December 2005.August 2011. Originally approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 20042005 as
C411 – 045. DOI: 10.1520/C0411-05.10.1520/C0411-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C411–11
plate shall be supported in a horizontal plane at a sufficient number of points to prevent sagging. It shall be heated on the under
side by gas or electricity. The surface temperature of the plate shall be measured by not less than five thermocouples. Four of the
thermocouples shall be located along the diagonals that extend from the corners
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.