SIST EN 1273:2021
(Main)Child care articles - Baby walking frames - Safety requirements and test methods
Child care articles - Baby walking frames - Safety requirements and test methods
This document specifies safety requirements and test methods for baby walking frames into which a child is placed, and intended to be used from when the child is able to sit up by itself until the child is able to walk by itself.
This document does not apply to baby walking frames for therapeutic and curative purposes and to those baby walking frames relying on inflatable parts to support the child.
Toys (e.g. ride on toys, push-along toys, usually intended for children able to walk unaided) are not covered by this document.
If a baby walking frame has several functions or can be converted into another function the relevant European standards apply to it.
Artikel für Säuglinge und Kleinkinder - Kinderlaufhilfen - Sicherheitstechnische Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren
Dieses Dokument legt die sicherheitstechnischen Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren für Kinderlaufhilfen fest, die von einem Alter an verwendbar sind, in dem das Kind schon selbstständig sitzen kann, bis zu dem Alter, in dem es selbstständig laufen kann.
Dieses Dokument gilt nicht für Kinderlaufhilfen zu therapeutischen Zwecken und Heilbehandlungen und für Kinderlaufhilfen, bei denen das Kind von aufblasbaren Teilen gestützt wird.
Spielzeuge (z. B. Aufsitzspielzeuge oder Rutschspielzeuge, die gewöhnlich für Kinder zum Laufen ohne Unterstützung vorgesehen sind) werden in diesem Dokument nicht behandelt.
Wenn eine Kinderlaufhilfe mehrere Funktionen hat oder zu einer anderen Funktion umgebaut werden kann, gelten dafür die zutreffenden Europäischen Normen.
Articles de puériculture - Trotteurs - Exigences de sécurité et méthodes d'essai
Le présent document spécifie les exigences de sécurité et les méthodes d’essai applicables aux trotteurs dans lesquels un enfant est installé, qui sont destinés à être utilisés à partir du moment où l’enfant est capable de se tenir assis tout seul jusqu’au moment où il sait marcher.
Le présent document ne s’applique ni aux trotteurs à fonction thérapeutique et curative, ni à ceux dans lesquels l’enfant est soutenu par des parties gonflables.
Les jouets (par exemple les jouets à enfourcher et les jouets à pousser, habituellement destinés aux enfants en mesure de marcher tout seuls) ne sont pas couverts par le présent document.
Si un trotteur offre plusieurs fonctions ou peut être converti en une autre fonction, les Normes européennes pertinentes s’appliquent.
Izdelki za otroke - Hojce - Varnostne zahteve in preskusne metode
General Information
- Status
- Withdrawn
- Public Enquiry End Date
- 04-May-2019
- Publication Date
- 21-Jan-2021
- Withdrawal Date
- 17-Jun-2024
- Technical Committee
- OTR - Child use and care article
- Current Stage
- 9900 - Withdrawal (Adopted Project)
- Start Date
- 18-Jun-2024
- Due Date
- 11-Jul-2024
- Completion Date
- 18-Jun-2024
Relations
- Effective Date
- 01-Feb-2021
- Effective Date
- 01-Jul-2024
- Effective Date
- 01-Mar-2023
SIST EN 1273:2021 - BARVE
Frequently Asked Questions
SIST EN 1273:2021 is a standard + national annex and/or foreword published by the Slovenian Institute for Standardization (SIST). Its full title is "Child care articles - Baby walking frames - Safety requirements and test methods". This standard covers: This document specifies safety requirements and test methods for baby walking frames into which a child is placed, and intended to be used from when the child is able to sit up by itself until the child is able to walk by itself. This document does not apply to baby walking frames for therapeutic and curative purposes and to those baby walking frames relying on inflatable parts to support the child. Toys (e.g. ride on toys, push-along toys, usually intended for children able to walk unaided) are not covered by this document. If a baby walking frame has several functions or can be converted into another function the relevant European standards apply to it.
This document specifies safety requirements and test methods for baby walking frames into which a child is placed, and intended to be used from when the child is able to sit up by itself until the child is able to walk by itself. This document does not apply to baby walking frames for therapeutic and curative purposes and to those baby walking frames relying on inflatable parts to support the child. Toys (e.g. ride on toys, push-along toys, usually intended for children able to walk unaided) are not covered by this document. If a baby walking frame has several functions or can be converted into another function the relevant European standards apply to it.
SIST EN 1273:2021 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 97.190 - Equipment for children. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
SIST EN 1273:2021 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to SIST EN 1273:2005, SIST EN 1273:2021+A1:2024, SIST EN 1273:2021/kFprA1:2023. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
SIST EN 1273:2021 is associated with the following European legislation: EU Directives/Regulations: 2001/95/EC; Standardization Mandates: M/264. When a standard is cited in the Official Journal of the European Union, products manufactured in conformity with it benefit from a presumption of conformity with the essential requirements of the corresponding EU directive or regulation.
You can purchase SIST EN 1273:2021 directly from iTeh Standards. The document is available in PDF format and is delivered instantly after payment. Add the standard to your cart and complete the secure checkout process. iTeh Standards is an authorized distributor of SIST standards.
Standards Content (Sample)
SLOVENSKI SIST EN 1273
STANDARD
februar 2021
Izdelki za otroke – Hojce – Varnostne zahteve in preskusne metode
Child care articles – Baby walking frames – Safety requirements and
test methods
Articles de puériculture – Trotteurs – Exigences de sécurité et
méthodes d'essai
Artikel für Säuglinge und Kleinkinder – Kinderlaufhilfen – Sicherheitstechnische
Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren
Referenčna oznaka
ICS 97.190 SIST EN 1273:2021 ((sl)en)
Nadaljevanje na straneh od II do IV in od 1 do 59
© 2021-02. Standard je založil in izdal Slovenski inštitut za standardizacijo. Razmnoževanje celote ali delov tega standarda ni dovoljeno.
SIST EN 1273 : 2021
NACIONALNI UVOD
Standard SIST EN 1273 ((sl)en), Izdelki za otroke – Hojce – Varnostne zahteve in preskusne metode,
2021, ima status slovenskega standarda in je po metodi ponatisa izvirnika z nacionalnim dodatkom
privzet evropski standard EN 1273 (en), Child care articles – Baby walking frames – Safety
requirements and test methods, 2020.
Ta slovenski standard nadomešča SIST EN 1273:2005.
NACIONALNI PREDGOVOR
Evropski standard EN 1273:2020 je pripravil tehnični odbor Evropskega komiteja za standardizacijo
CEN/TC 252 "Izdelki za otroke", katerega sekretariat vodi AFNOR.
Pripravo tega standarda sta Evropska komisija in Evropsko združenje za prosto trgovino poverila CEN z
mandatom M/264.
Odločitev za izdajo tega standarda je dne 16. decembra 2020 sprejel tehnični odbor SIST/TC OTR
Izdelki za otroke.
NACIONALNI DODATEK
Dodatek C
(normativen)
Opozorila
K preglednici C.1, ki navaja prevode opozoril, navedenih v točki 9, se dodajo slovenski prevodi:
Preglednica C.1: Prevodi opozoril
Slovenian
9.2 OPOZORILO!
[1] OPOZORILO!
[2] Preprečite otroku dostop do stopnišč, stopnic in neravnih površin
[3] Nikoli ne puščajte otroka brez nadzora
9.3 OPOZORILO!
[1] OPOZORILO!
[2] Nikoli ne puščajte otroka brez nadzora.
[3] Preprečite otroku dostop do stopnišč, stopnic in neravnih površin.
9.4 POMEMBNO! POZORNO PREBERITE NAVODILA IN JIH SHRANITE KOT
NAPOTEK ZA V PRIHODNJE.
[1] OPOZORILO!
[2] Nikoli ne puščajte otroka brez nadzora.
[3] S hojco se otrok lahko premika hitreje in tako pride dlje.
[4] Preprečite otroku dostop do stopnišč, stopnic in neravnih površin.
II
SIST EN 1273 : 2021
Slovenian
[5] Zavarujte dostop do ognja, grelnih in kuhalnih naprav.
[6] Odstranite vroče tekočine, električne kable in druge možne nevarnosti iz dosega
otroka.
[7] Preprečite, da bi otrok trčil v steklo v vratih, oknih in pohištvu.
ZVEZA Z NACIONALNIMI STANDARDI
S privzemom tega evropskega standarda veljajo za omejeni namen referenčnih standardov vsi
standardi, navedeni v izvirniku, razen standardov, ki so že sprejeti v nacionalno standardizacijo:
SIST EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014 Varnost igrač – 2. del: Vnetljivost (vključno z dopolnilom A1)
SIST EN 71-3 Varnost igrač – 3. del: Migracija določenih elementov
SIST EN 71-10:2006 Varnost igrač – 10. del: Organske kemijske spojine – Priprava
vzorcev in ekstrakcija
SIST EN 71-11 Varnost igrač – 11. del: Organske kemijske spojine – Analizne
metode
SIST EN 622-1 Vlaknene plošče – Specifikacije – 1. del Splošne zahteve
SIST EN 717-1 Lesne plošče – Ugotavljanje sproščanja formaldehida – 1. del:
Sproščanje formaldehida po komorni metodi
SIST EN ISO 105-A03 Tekstilije – Preskušanje barvne obstojnosti – Del A03: Siva skala za
ocenjevanje prehoda obarvanja spremljajočih tkanin (ISO 105-
A03:2019)
SIST EN ISO 14184-1 Tekstilije – Določevanje formaldehida – 1. del: Prosti in hidrolizirani
formaldehid (vodna ekstrakcija) (ISO 14184-1:2011)
SIST EN ISO 14362-1 Tekstilije – Metode za določevanje nekaterih aromatskih aminov,
izvirajočih iz azo barvil – 1. del: Zaznavanje prisotnosti določenih
azo barvil, dostopnih z ekstrahiranjem vlaken in brez njega (ISO
24362-1:2017)
SIST EN ISO 2813 Barve in laki – Ugotavljanje vrednosti sijaja pod koti 20, 60 in 85
stopinj (ISO 2813:2014)
SIST EN ISO 2439:2009 Penjeni polimerni materiali – Mehke pene – Ugotavljanje trdote
(odpornost proti vtiskovanju) (ISO 2439:2008)
OSNOVA ZA IZDAJO
– privzem standarda EN 1273:2020
PREDHODNE IZDAJE
– SIST EN 1273:2005
– SIST EN 1273:2002
III
SIST EN 1273 : 2021
OPOMBE
– Povsod, kjer se v besedilu standarda uporablja izraz “evropski standard”, v SIST EN 1273:2021
to pomeni “slovenski standard”.
– Nacionalni uvod in nacionalni predgovor nista sestavni del standarda.
– Ta nacionalni dokument je istoveten EN 1273:2020 in je objavljen z dovoljenjem
Upravni center
CEN-CENELEC
Rue de la Science 23
B-1040 Bruselj
This national document is identical with EN 1273:2020 and is published with the permission of
Upravni center
CEN-CENELEC
Rue de la Science 23
B-1040 Brussels
IV
EN 1273
EUROPEAN STANDARD
NORME EUROPÉENNE
July 2020
EUROPÄISCHE NORM
ICS 97.190 Supersedes EN 1273:2005
English Version
Child care articles - Baby walking frames - Safety
requirements and test methods
Articles de puériculture - Trotteurs - Exigences de Artikel für Säuglinge und Kleinkinder -
sécurité et méthodes d'essai Kinderlaufhilfen - Sicherheitstechnische
Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren
This European Standard was approved by CEN on 24 May 2020.
CEN members are bound to comply with the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations which stipulate the conditions for giving this
European Standard the status of a national standard without any alteration. Up-to-date lists and bibliographical references
concerning such national standards may be obtained on application to the CEN-CENELEC Management Centre or to any CEN
member.
This European Standard exists in three official versions (English, French, German). A version in any other language made by
translation under the responsibility of a CEN member into its own language and notified to the CEN-CENELEC Management
Centre has the same status as the official versions.
CEN members are the national standards bodies of Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia,
Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway,
Poland, Portugal, Republic of North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and
United Kingdom.
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION
COMITÉ EUROPÉEN DE NORMALISATION
EUROPÄISCHES KOMITEE FÜR NORMUNG
CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Rue de la Science 23, B-1040 Brussels
© 2020 CEN All rights of exploitation in any form and by any means reserved Ref. No. EN 1273:2020 E
worldwide for CEN national Members.
Contents Page
European foreword . 5
Introduction . 6
1 Scope . 7
2 Normative references . 7
3 Terms and definitions . 8
4 Test equipment . 8
4.1 Test masses . 8
4.1.1 Test mass A . 8
4.1.2 Test mass B . 8
4.1.3 Test mass C . 8
4.1.4 Test mass D . 9
4.2 Small parts cylinder . 10
4.3 Feeler gauge . 10
4.4 Test probes for finger entrapment . 11
4.4.1 Test probes with hemispherical end . 11
4.4.2 Shape assessment probe . 12
4.5 Test platform for stability test . 12
4.6 Test equipment for dynamic stability . 13
4.6.1 Test platform . 13
4.6.2 Spacer . 13
4.7 Test equipment for prevention of fall down steps test . 13
4.7.1 Test platform . 13
4.7.2 Steel cable . 14
4.7.3 Pulley . 14
4.7.4 Aluminium angle . 14
4.7.5 Rigid plate . 14
4.7.6 Structural characteristics for the test equipment . 14
4.8 Foam. 15
5 General requirements and test conditions . 15
5.1 Product conditioning . 15
5.2 Test conditions . 15
5.3 Application of forces . 15
5.4 Tolerances . 16
5.5 Order of tests . 16
6 Chemical hazards (see A.2) . 16
6.1 General . 16
6.2 Migration of certain elements (see A.2) . 16
6.3 Formaldehyde (see A.2) . 17
6.4 Colourants (see A.2) . 17
6.5 Aniline (see A.2). 17
7 Thermal hazards (see A.3) . 18
7.1 Requirement . 18
7.2 Test method . 18
8 Mechanical hazards (see A.4) . 18
8.1 Entrapment hazards (see A.4.1) . 18
8.1.1 Requirements . 18
8.1.2 Test methods . 19
8.2 Hazards due to moving parts (see A.4.2) . 19
8.2.1 General . 19
8.2.2 Requirements for compression points . 19
8.2.3 Requirements for shear points . 19
8.3 Protective function of the seat . 19
8.3.1 General . 19
8.3.2 Crotch strap . 19
8.3.3 Removable seats . 19
8.3.4 Seat height . 20
8.4 Hazards due to height adjustment and folding of the product . 20
8.4.1 Requirements . 20
8.4.2 Test methods for height adjustment and folding mechanisms . 21
8.5 Strangulation hazards due to cords, ribbons and similar parts (see A.4.3) . 21
8.5.1 Requirements . 21
8.5.2 Test method . 22
8.6 Choking and ingestion hazard (see A.4.4) . 22
8.6.1 Requirements . 22
8.6.2 Test methods . 22
8.7 Suffocation hazards from plastic packaging (see A.4.5) . 23
8.7.1 Plastic packaging . 23
8.7.2 Plastic decals . 24
8.8 Hazards from edges, corners and protruding parts (see A.4.6). 24
8.9 Hazards from inadequate structural integrity (see A.4.7) . 24
8.9.1 Static strength . 24
8.9.2 Dynamic strength . 25
8.10 Hazards from inadequate stability (see A.4.8). 25
8.10.1 Static stability . 25
8.10.2 Dynamic stability . 25
8.11 Hazards due to falling down stairs (see A.4.9) . 26
8.11.1 Requirements . 26
8.11.2 Test method . 26
8.11.3 Tip over test . 30
8.12 Parking devices . 31
8.12.1 Requirements . 31
8.12.2 Test method . 31
9 Product information . 32
9.1 General . 32
9.2 Marking of the product . 33
9.3 Purchase information . 33
9.4 Instructions for use . 34
Annex A (informative) Rationales . 35
A.1 Introduction. 35
A.2 Chemical hazards (see Clause 6) . 35
A.3 Thermal hazards (see Clause 7) . 35
A.4 Mechanical hazards (see Clause 8) . 35
A.4.1 Entrapment hazards (see 8.1) . 35
A.4.2 Hazards due to moving parts (see 8.2) . 35
A.4.3 Strangulation hazards (see 8.5) . 36
A.4.4 Choking and ingestion hazards (see 8.6) . 36
A.4.5 Suffocation hazards (see 8.7) . 36
A.4.6 Hazardous edges, corners and protruding parts (see 8.8). 36
A.4.7 Hazards from inadequate structural integrity (see 8.9) . 36
A.4.8 Hazards from inadequate stability (see 8.10) . 36
A.4.9 Hazards due to falling down stairs (see 8.11). 36
Annex B (normative) Test platform for tip over test . 37
Annex C (normative) Warnings . 38
Annex D (informative) A–deviations . 59
European foreword
This document (EN 1273:2020) has been prepared by Technical Committee CEN/TC 252 “Child care
articles”, the secretariat of which is held by AFNOR.
This European standard shall be given the status of a national standard, either by publication of an
identical text or by endorsement, at the latest by January 2021, and conflicting national standards shall
be withdrawn at the latest by July 2021.
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of
patent rights. CEN shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
This document supersedes EN 1273:2005.
In comparison with the previous edition EN 1273:2005, the following major technical modifications have
been made:
— general redraft in hazard based format;
— addition of new chemical requirements based on CEN/TR 13387-2;
— general update of some mechanical requirements and test methods to the state of the art of
CEN/TR 13387-3;
— improvement of the requirements and test methods for static and dynamic strength;
— modification of the test method for prevention of falls down stairs to improve reproducibility of
results;
— update of product information section and addition of a new symbol from CEN/TR 13387-5.
This document has been prepared under Mandate M/264 given to CEN by the European Commission and
the European Free Trade Association.
According to the CEN-CENELEC Internal Regulations, the national standards organisations of the
following countries are bound to implement this European standard: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia,
Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland,
Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Republic of North
Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and the United
Kingdom.
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to reduce the risk of accidents.
It is stressed that this document cannot eliminate all possible risks to children using such a product and
that carer control is of paramount importance. Accidents are mainly due to carer(s) not anticipating the
extra reach and speed that children can achieve in the baby walking frame.
It is essential that all warnings and instructions specified in this standard are clearly given by the
manufacturer, to ensure that the baby walking frame can be used safely and correctly.
1 Scope
This document specifies safety requirements and test methods for baby walking frames into which a child
is placed, and intended to be used from when the child is able to sit up by itself until the child is able to
walk by itself.
This document does not apply to baby walking frames for therapeutic and curative purposes and to those
baby walking frames relying on inflatable parts to support the child.
Toys (e.g. ride on toys, push-along toys, usually intended for children able to walk unaided) are not
covered by this document.
If a baby walking frame has several functions or can be converted into another function, the relevant
European standards apply to it.
2 Normative references
The following documents are referred to in the text in such a way that some or all of their content
constitutes requirements of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For
undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014, Safety of toys - Part 2: Flammability
EN 71-3, Safety of toys - Part 3: Migration of certain elements
EN 71-10:2005, Safety of toys - Part 10: Organic chemical compounds - Sample preparation and extraction
EN 71-11, Safety of toys - Part 11: Organic chemical compounds - Methods of analysis
EN 622-1, Fibreboards - Specifications - Part 1: General requirements
EN 717-1, Wood-based panels - Determination of formaldehyde release - Part 1: Formaldehyde emission by
the chamber method
EN ISO 105-A03, Textiles - Tests for colour fastness - Part A03: Grey scale for assessing staining (ISO 105-
A03
EN ISO 14184-1, Textiles - Determination of formaldehyde - Part 1: Free and hydrolysed formaldehyde
(water extraction method) (ISO 14184-1)
EN ISO 14362-1, Textiles - Methods for determination of certain aromatic amines derived from azo
colorants - Part 1: Detection of the use of certain azo colorants accessible with and without extracting the
fibres (ISO 14362-1)
EN ISO 2813, Paints and varnishes - Determination of gloss value at 20°, 60° and 85° (ISO 2813)
EN ISO 2439:2008, Flexible cellular polymeric materials - Determination of hardness (indentation
technique) (ISO 2439:2008)
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
ISO and IEC maintain terminological databases for use in standardization at the following addresses:
— IEC Electropedia: available at http://www.electropedia.org/
— ISO Online browsing platform: available at https://www.iso.org/obp
3.1
baby walking frame
structure with a seat in which a child is placed in a sitting or standing position, which allows a child to
move around with the aid of the support offered by the frame
3.2
crotch strap
device which passes between the child’s legs to prevent the child slipping out of the seat
3.3
base
lower part of the frame where castors or wheels may be attached
3.4
parking device
device to maintain the baby walking frame in a stationary position
4 Test equipment
4.1 Test masses
4.1.1 Test mass A
Test mass A is a rigid cylinder (160 ± 5) mm in diameter and (280 ± 5) mm in height, having a mass of
+01,
12 kg and with its centre of gravity in the centre of the cylinder. All edges shall have a radius of
(20 ± 1) mm. See Figure 1.
4.1.2 Test mass B
Test mass B is a rigid cylinder (160 ± 5) mm in diameter and (280 ± 5) mm in height, having a mass of
+01,
7,65 kg and with its centre of gravity in the centre of the cylinder. All edges shall have a radius of
(20 ± 1) mm. See Figure 1.
4.1.3 Test mass C
Test mass C is a rigid cylinder (160 ± 5) mm in diameter and (280 ± 5) mm in height, having a mass of
+01,
12,6 kg and with its centre of gravity in the centre of the cylinder. All edges shall have a radius of
(20 ± 1) mm. See Figure 1.
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
1 Radius: (20 ± 1) mm
Test Mass A
+01,
Mass 12 kg
Test Mass B +01,
Mass 7,65 kg
Test Mass C
+01,
Mass 12,6 kg
Figure 1 — Test mass A, B and C
4.1.4 Test mass D
+01,
Test mass D is a mass of kg with a flat circular bottom surface. See Figure 2.
3,6
Figure 2 — Test mass D
4.2 Small parts cylinder
Small parts cylinder for the assessment of small components, having dimensions in accordance with
Figure 3.
Dimension in millimetres
Figure 3 — Small parts cylinder
4.3 Feeler gauge
Gauge with a thickness of (0,4 ± 0,02) mm and an insertion edge radius of (3 ± 0,5) mm (see Figure 4).
Dimensions in millimetres
Figure 4 — Feeler gauge
4.4 Test probes for finger entrapment
4.4.1 Test probes with hemispherical end
0 +01,
Probes made from plastic or other hard, smooth material of diameters 7 mm and 12 mm with a
−01,
full hemispherical end that can be mounted on a force-measuring device, see Figure 5.
Mesh probe made from plastic or other hard, smooth material as shown in Figure 6.
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
Probe type 7 mm probe 12 mm probe
Diameter A 0
+01,
−01,
Radius RB half of diameter A half of diameter A
1 Line scribed around circumference showing depth of penetration
Figure 5 — Test probes with hemispherical end
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
Probe type Mesh probe
Diameter A 0
−01,
Diameter B 0
5,6
−01,
Radius RB half of diameter B
Figure 6 — Test probe for mesh
4.4.2 Shape assessment probe
Probe made from plastics or other hard, smooth material, which can be mounted on a force-measuring
device, with the dimensions shown in Figure 7.
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
A front view
B top view
C side view
D 3D view
Figure 7 — Shape assessment probe
4.5 Test platform for stability test
A sloping platform inclined at an angle of 30° to the horizontal with a 100 mm stop fitted to the lower
edge of the slope (Figure 8).
Key
1 stop
2 platform
Figure 8 — Test platform for stability test
4.6 Test equipment for dynamic stability
4.6.1 Test platform
The test platform of 4.7.1 with an aluminium stop with a height of 40 mm and thickness of at least 10 mm
at its front edge.
4.6.2 Spacer
A squared sectioned piece of aluminium 40 mm by 40 mm with a minimum length of 200 mm.
4.7 Test equipment for prevention of fall down steps test
4.7.1 Test platform
A horizontal test platform as shown in Figure B.1 of Annex B with a flat smooth surface made of beech
wood with a minimum thickness of 18 mm.
The front edge shall be straight cut, without any radius (Figure 9).
Figure 9 — Front edge of the test platform
The grain of the wooden surface shall be orientated in line with the longitudinal axis of the test platform
and there shall be no joints perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the test platform (see Figure 10).
The top shall be pre-finished with wood floor polyurethane varnish with a nominal gloss of (75 ± 5) gloss
units measured with an angle of 60° according to EN ISO 2813.
The wooden surface shall be fixed to the frame to avoid deformation of the wooden surface during the
tests. If variations in temperature and/or humidity in the laboratory cause the wooden surface to deform,
the fixing shall be adjusted to ensure the wooden surface is flat.
Key
1 direction of the baby walking frame movement
Figure 10 — Orientation of the wooden surface
4.7.2 Steel cable
A galvanised steel cable with a nominal diameter of 2 mm ± 0,1 mm.
4.7.3 Pulley
A stainless steel ball bearing pulley with the functional diameter of 80 mm with a rounded groove suitable
for the cable. The centre of the pulley is positioned at a minimum distance of 510 mm from the platform
edge. The height of the pulley shall be adjustable.
4.7.4 Aluminium angle
A 25 mm by 25 mm rigid aluminium angle with a thickness of (2 ± 0,5) mm and a length of (1,5 ± 0,1) m.
4.7.5 Rigid plate
A rigid plate of a dimensions of (50 ± 2) mm × (50 ± 2) mm.
4.7.6 Structural characteristics for the test equipment
The different parts of the test equipment shall fulfil the following (see Figure 11):
i. have a maximum vertical displacement of 1 mm when a force of 400 N is applied over a diameter of
100 mm flush on the centre of the front edge of the platform (point a);
ii. have a maximum horizontal displacement of 1 mm when a force of 200 N is applied over a diameter
of 100 mm on the edge parallel to the longitudinal axis of the platform at the following points: (b)
front edge, (c) middle point, (d) rear edge;
iii. have a maximum horizontal displacement of 1 mm when a force of 200 N is applied over a diameter
of 100 mm in the middle of the front or rear edge along the longitudinal axis of the platform (point
e);
iv. have a maximum vertical displacement of 1 mm when a 20 kg mass is hung on the pulley.
Key
a the centre of the front edge of the platform d rear edge
b front edge e the longitudinal axis of the platform
c middle point
Figure 11 — Application of forces on the platform
4.8 Foam
A polyurethane foam sheet with a thickness of (60 ± 5) mm, a bulk density of 35 kg/m with a tolerance
of 10 % or an indentation hardness index of (170 ± 40) N in accordance with EN ISO 2439:2008, A.40.
5 General requirements and test conditions
5.1 Product conditioning
Before testing, any fabrics used shall be cleaned or washed and dried twice in accordance with the
manufacturer's instructions.
5.2 Test conditions
The tests shall be carried out in ambient conditions of (20 ± 5) °C.
The tests are designed to be applied to baby walking frames that are fully assembled and ready for use in
accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. If the baby walking frame can be assembled or adjusted
in different ways in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, the most onerous combinations
shall be used for each test, unless otherwise specified in the test method.
5.3 Application of forces
The forces in the static load tests shall be applied sufficiently slowly to ensure that negligible dynamic
effect is applied.
5.4 Tolerances
Unless otherwise stated, the accuracy of the test equipment shall be:
— Forces: ± 5 % of the nominal force;
— Masses: ± 0,5 % of the nominal mass;
— Dimensions: ± 0,5 mm of the nominal dimension;
— Angles: ± 0,5° of the nominal angle;
— Duration: ± 1 s of the nominal duration.
The tests are described in terms of the application of forces. Masses can however be used. The
relationship 10 N = 1 kg may be used for this purpose.
Unless otherwise specified, the test forces may be applied by any suitable device which does not adversely
affect the results.
5.5 Order of tests
Unless otherwise stated in the test methods, the tests shall be carried out on the same baby walking frame
in the order listed in this standard.
6 Chemical hazards (see A.2)
6.1 General
If testing is required, a separate unconditioned sample shall be used for the tests in Clause 6.
6.2 Migration of certain elements (see A.2)
The migration of elements from materials on exterior surfaces shall not exceed the limits listed in Table 1.
Table 1 — Limits for migration of certain elements
Element mg/kg Element mg/kg
Aluminium 70 000 Lead 23
Antimony 560 Manganese 15 000
Arsenic 47 Mercury 94
Barium 18 750 Nickel 930
Boron 15 000 Selenium 460
Cadmium 17 Strontium 56 000
Chromium (III) 460 Tin 180 000
Chromium (VI) 0,2 Organic tin 12
Cobalt 130 Zinc 46 000
Copper 7 700
When testing is performed, the method described in EN 71-3 shall be used.
Components under the base (e.g. castors or wheels, braking pads, …) are excluded from these
requirements.
6.3 Formaldehyde (see A.2)
Accessible textile components shall not contain free and hydrolysed formaldehyde in excess of 30 mg/kg.
When testing is performed, the method described in EN ISO 14184-1 shall be used.
Resin-bonded wood components shall not release formaldehyde in excess of 0,124 mg/m (class E1
according to EN 622-1).
When testing is performed, the method described in EN 717-1 shall be used.
6.4 Colourants (see A.2)
When tested in accordance with EN 71-10:2005, Annex A, if the colour fastness to sweat of accessible
textile components is lower than 3-4 on the grey scale as defined in EN ISO 105-A03, the part shall be
tested for colourants with the methods described in EN 71-10 and EN 71-11 and the limits in Table 2 shall
be fulfilled.
Table 2 — Colourants limits
CoIour Index Colour Index CAS Number Limit
Generic Name Constitution Number
(CIGN) (CICN)
Disperse Blue 1 64500 2475–45–8 Action limit
Disperse Blue 3 61505 2475–46–9 Action limit
Disperse Blue 106 111935 12223–01–7 Action limit
Disperse Blue 124 111938 61951–51–7 Action limit
Disperse Yellow 3 11855 2832–40–8 Action limit
Disperse Orange 3 11855 730–40–5 Action limit
Disperse Orange 37/76/59 11132 12223–33–5 Action limit
13301–61–6
Disperse Red 1 11110 2872–52–8 Action limit
Solvent Yellow 1 11000 60–09–3 Action limit
Solvent Yellow 2 11020 60–11–7 Action limit
Solvent Yellow 3 11160 97–56–3 Action limit
Basic Red 9 42500 569–61–9 Action limit
Basic Violet 1 42535 8004–87–3 Action limit
Basic Violet 3 42555 548–62–9 Action limit
Acid Red 26 16150 3761–53–3 Action limit
Acid Violet 49 42640 1694–09–3 Action limit
6.5 Aniline (see A.2)
Aniline shall not exceed the limit of 30 mg/kg after reductive cleavage from accessible textile
components.
When testing is performed the method of EN ISO 14362-1, adapted as appropriate to measure aniline,
shall be used.
7 Thermal hazards (see A.3)
7.1 Requirement
When tested in accordance with 7.2, there shall be no surface flash and the rate of spread of flame on
textile materials shall not exceed 50 mm/s.
These tests can be performed on a separate sample, conditioned according to 5.1, or at the end of the test
sequence.
NOTE Refer to Annex D for A-deviations on flammability requirements.
7.2 Test method
To verify the surface flash effect apply the test flame defined in EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014, 5.5 for (3 ± 0,5)
s to the baby walking frame in different places likely to cause surface flash.
To verify rate of spread of flame apply the test flame defined in EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014, 5.4.
8 Mechanical hazards (see A.4)
8.1 Entrapment hazards (see A.4.1)
8.1.1 Requirements
When tested in accordance with 8.1.2, there shall be no completely bounded openings between 7 mm and
12 mm unless the depth is less than 10 mm or unless the shape assessment probe (see 4.4.2) enters when
tested in accordance with 8.1.2.
When tested in accordance with 8.1.2, there shall be no openings in mesh that allow the test probe for
mesh (see 4.4.1) to penetrate to the 7 mm diameter section.
The test shall be carried out with the product in any intended position of use.
This requirement does not apply to the castors, wheels, the whole base of the baby walking frame, and to
any other part of the underside of the tray more than 100 mm from the vertical projection of the outer
edge (see Figure 12).
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
100 mm distance from the edge
Figure 12 — Underside of the tray
8.1.2 Test methods
Check whether the 7 mm probe (see 4.4.1), with an applied force of up to 30 N, enters 10 mm or more
into any accessible completely bounded opening in any possible orientation.
If the 7 mm probe enters 10 mm or more, then the 12 mm probe (see 4.4.1) shall also enter 10 mm or
more with an applied force of up to 5 N.
If the 7 mm probe enters with an applied force of up to 30 N but the 12 mm probe does not enter 10 mm
or more with an applied force of up to 5 N, check whether the 12 mm shape assessment probe (see 4.4.2)
enters 10 mm or more with an applied force of up to 5 N.
Check whether the test probe for mesh (see 4.4.1), with an applied force of up to 30 N, penetrates
accessible openings in mesh up to the 7 mm diameter section.
8.2 Hazards due to moving parts (see A.4.2)
8.2.1 General
Shear and compression points which are created only when setting up or folding are acceptable as the
carer can be assumed to be in control of these actions.
The castors, wheels, whole base of the baby walking frame and the underside of the tray, more than
100 mm from the vertical projection of the outer edge of the tray, are excluded from the requirements of
8.2.
8.2.2 Requirements for compression points
After the baby walking frame is set up for normal use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions,
there shall be no compression points which can close to less than 12 mm unless they are always less than
5 mm, through the whole range of movement.
Movement due to elasticity of materials shall not be considered as a compression hazard.
8.2.3 Requirements for shear points
After the baby walking frame is set up for normal use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions
there shall be no shear points which can close to less than 12 mm.
Movement due to play and/or elasticity of materials shall not be considered as a shearing hazard.
8.3 Protective function of the seat
8.3.1 General
There shall be no harness-based restraint system.
8.3.2 Crotch strap
The baby walking frame shall be fitted with a crotch strap.
Where a crotch strap is made of flexible material, the width shall be at least 50 mm.
Where a crotch strap is made of rigid material, the width shall be at least 20 mm.
8.3.3 Removable seats
If the seat is remo
...
SLOVENSKI STANDARD
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
01-april-2019
Izdelki za otroke - Hojce - Varnostne zahteve in preskusne metode
Child use and care articles - Baby walking frames - Safety requirements and test
methods
Artikel für Säuglinge und Kleinkinder - Kinderlaufhilfen - Sicherheitstechnische
Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren
Articles de puériculture - Trotteurs - Exigences de sécurité et méthodes d'essai
Ta slovenski standard je istoveten z: prEN 1273
ICS:
97.190 Otroška oprema Equipment for children
oSIST prEN 1273:2019 en,fr,de
2003-01.Slovenski inštitut za standardizacijo. Razmnoževanje celote ali delov tega standarda ni dovoljeno.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
DRAFT
EUROPEAN STANDARD
prEN 1273
NORME EUROPÉENNE
EUROPÄISCHE NORM
March 2019
ICS 97.190 Will supersede EN 1273:2005
English Version
Child use and care articles - Baby walking frames - Safety
requirements and test methods
Articles de puériculture - Trotteurs - Exigences de Artikel für Säuglinge und Kleinkinder -
sécurité et méthodes d'essai Kinderlaufhilfen - Sicherheitstechnische
Anforderungen und Prüfverfahren
This draft European Standard is submitted to CEN members for enquiry. It has been drawn up by the Technical Committee
CEN/TC 252.
If this draft becomes a European Standard, CEN members are bound to comply with the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations
which stipulate the conditions for giving this European Standard the status of a national standard without any alteration.
This draft European Standard was established by CEN in three official versions (English, French, German). A version in any other
language made by translation under the responsibility of a CEN member into its own language and notified to the CEN-CENELEC
Management Centre has the same status as the official versions.
CEN members are the national standards bodies of Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia,
Finland, Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania,
Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland,
Turkey and United Kingdom.
Recipients of this draft are invited to submit, with their comments, notification of any relevant patent rights of which they are
aware and to provide supporting documentation.
Warning : This document is not a European Standard. It is distributed for review and comments. It is subject to change without
notice and shall not be referred to as a European Standard.
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE FOR STANDARDIZATION
COMITÉ EUROPÉEN DE NORMALISATION
EUROPÄISCHES KOMITEE FÜR NORMUNG
CEN-CENELEC Management Centre: Rue de la Science 23, B-1040 Brussels
© 2019 CEN All rights of exploitation in any form and by any means reserved Ref. No. prEN 1273:2019 E
worldwide for CEN national Members.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
Contents Page
European foreword . 3
Introduction . 4
1 Scope . 5
2 Normative references . 5
3 Terms and definitions . 5
4 Test equipment . 6
5 General requirements and test conditions . 12
6 Chemical hazards (see A.2) . 12
7 Thermal hazards (see A.3) . 14
8 Mechanical hazards (see A.4) . 15
9 Product information . 29
Annex A (informative) Rationales . 32
A.1 Introduction . 32
A.2 Chemical hazards (see Clause 6) . 32
A.3 Thermal hazards (see Clause 7) . 32
A.4 Mechanical hazards (see Clause 8) . 32
Annex B (normative) Test platform for tip over test . 34
Annex C (normative) Warnings . 35
Annex D (informative) A-Deviation . 36
Bibliography. 37
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
European foreword
This document (prEN 1273:2019) has been prepared by Technical Committee CEN/TC 252 “Child care
articles”, the secretariat of which is held by AFNOR.
This document is currently submitted to the CEN Enquiry.
This document will supersede EN 1273:2005.
In comparison with the previous edition EN 1273:2005, the following major technical modifications have
been made:
— general redraft in hazard based format;
— addition of new chemical requirements based on CEN/TR 13387-2;
— general update of some mechanical requirements and test methods to the state of the art of
CEN/TR 13387-3;
— improvement of the requirements and test methods for static and dynamic strength;
— modification of the test method for prevention of falls down stairs to improve reproducibility of
results;
— update of product information section and addition of a new symbol from CEN/TR 13387-5.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
Introduction
The purpose of this European Standard is to reduce the risk of accidents.
It is stressed that this European Standard cannot eliminate all possible risks to children using such a
product and that carer control is of paramount importance. Accidents are mainly due to carer(s) not
anticipating the extra reach and speed that children can achieve in the baby walking frame.
It is essential that all warnings and instructions specified in this standard are clearly given by the
manufacturer, to ensure that the baby walking frame can be used safely and correctly.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
1 Scope
This document specifies safety requirements and test methods for baby walking frames into which a child
is placed, and intended to be used from when the child is able to sit up by itself until the child is able to
walk by itself.
This document does not apply to baby walking frames for therapeutic and curative purposes and to those
baby walking frames relying on inflatable parts to support the child.
Toys (e.g. ride on toys, push-along toys, usually intended for children able to walk unaided) are not
covered by this document.
If a baby walking frame has several functions or can be converted into another function the relevant
European standards apply to it.
2 Normative references
The following documents are referred to in the text in such a way that some or all of their content
constitutes requirements of this document. For dated references, only the edition cited applies. For
undated references, the latest edition of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014, Safety of toys — Part 2: Flammability
EN 71-3, Safety of toys — Part 3: Migration of certain elements
EN 71-10:2005, Safety of toys — Part 10: Organic chemical compounds — Sample preparation and
extraction
EN 71-11, Safety of toys — Part 11: Organic chemical compounds — Methods of analysis
EN 622-1, Fibreboards — Specifications — Part 1: General requirements
EN 717-1, Wood-based panels — Determination of formaldehyde release — Part 1: Formaldehyde emission
by the chamber method
EN ISO 14184-1, Textiles — Determination of formaldehyde — Part 1: Free and hydrolysed formaldehyde
(water extraction method) (ISO 14184-1:2011)
EN ISO 14362-1, Textiles — Methods for determination of certain aromatic amines derived from azo
colorants — Part 1: Detection of the use of certain azo colorants accessible with and without extracting the
fibres (ISO 14362-1:2017)
EN ISO 17234-1, Leather — Chemical tests for the determination of certain azo colorants in dyed leathers
— Part 1: Determination of certain aromatic amines derived from azo colorants (ISO 17234-1:2015)
ISO 2813, Paints and varnishes — Determination of gloss value at 20 degrees, 60 degrees and 85 degrees
3 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply.
ISO and IEC maintain terminological databases for use in standardization at the following addresses:
— IEC Electropedia: available at http://www.electropedia.org/
— ISO Online browsing platform: available at http://www.iso.org/obp
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
3.1
baby walking frame
structure with a seat in which a child is placed in a sitting or standing position, which allows a child to
move around with the aid of the support offered by the frame
3.2
crotch strap
device which passes between the child’s legs to prevent the child slipping out of the seat
3.3
base
lower part of the frame where castors or wheels may be attached
3.4
parking device
device to maintain the baby walking frame in a stationary position
4 Test equipment
4.1 Test masses
4.1.1 Test mass A
Test mass A is a rigid cylinder (160 ± 5) mm in diameter and (280 ± 5) mm in height, having a mass
+01,
of 12 kg and with its centre of gravity in the centre of the cylinder. All edges shall have a radius of
(20 ± 1) mm.
4.1.2 Test mass B
Test mass B is a rigid cylinder (160 ± 5) mm in diameter and (280 ± 5) mm in height, having a mass
+01,
of 7,65 kg and with its centre of gravity in the centre of the cylinder. All edges shall have a radius of
(20 ± 1) mm.
4.1.3 Test mass C
Test mass C is a rigid cylinder (160 ± 5) mm in diameter and (280 ± 5) mm in height, having a mass
+01,
of 12,6 kg and with its centre of gravity in the centre of the cylinder. All edges shall have a radius of
(20 ± 1) mm.
4.1.4 Test mass D
Test mass D is a mass of 3,6 kg with a flat circular bottom surface.
4.2 Small parts cylinder
Small parts cylinder for the assessment of small components, having dimensions in accordance with
Figure 1.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
Dimension in millimetres
Figure 1 — Small parts cylinder
4.3 Feeler gauge
Gauge with a thickness of (0,4 ± 0,02) mm and an insertion edge radius of (3 ± 0,5) mm (see Figure 2).
Dimensions in millimetres
Figure 2 — Feeler gauge
4.4 Test probes for finger entrapment
4.4.1 Test probes with hemispherical end
0 +01,
Probes made from plastic or other hard, smooth material of diameters mm and 12 mm with a
−01, 0
full hemispherical end that can be mounted on a force-measuring device, see Figure 3.
Mesh probe made from plastic or other hard, smooth material as shown in Figure 4.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
Probe type 7 mm probe 12 mm probe
Diameter A
0 +01,
-0,1
Radius RB half of diameter A half of diameter A
1 Line scribed around circumference showing depth of penetration
Figure 3 — Test probes with hemispherical end
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
Probe type Mesh probe
Diameter A 7
−01,
Diameter B 5,6
−01,
Radius RB half of diameter B
Figure 4 — Test probe for mesh
4.4.2 Shape assessment probe
Probe made from plastics or other hard, smooth material with the dimensions shown in Figure 5.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
A front view
B top view
C side view
D 3D view
Figure 5 — Shape assessment probe
4.5 Test platform for stability test
A sloping platform inclined at an angle of 30° to the horizontal with a 100 mm stop fitted to the lower
edge of the slope (Figure 6).
Key
1 stop
2 platform
Figure 6— Static stability test
4.6 Test equipment for dynamic stability
4.6.1 Test platform
The test platform of 4.7.1 with an aluminium stop with a height of 40 mm and thickness of at least 10 mm
at its front edge.
4.6.2 Spacer
A squared sectioned piece of aluminium 40 mm by 40 mm with a minimum length of 200 mm.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
4.7 Test equipment for prevention of fall down steps test
4.7.1 Test platform
A horizontal test platform as shown in Figure B.1 with a flat smooth surface made of beech wood with a
minimum thickness of 18 mm.
The front edge shall be straight cut, without any radius (Figure 7).
Figure 7 — Front edge of the test platform
The grain of the wooden surface shall be orientated in line with the longitudinal axis of the test platform
and there shall be no joints perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the test platform (see Figure 8).
The top shall be pre-finished with wood floor polyurethane varnish with a nominal gloss of (75 ± 5) gloss
units measured with an angle of 60° according to ISO 2813.
The wooden surface shall be fixed to the frame to avoid deformation of the wooden surface during the
tests. If variations in temperature and/or humidity in the laboratory cause the wooden surface to deform,
the fixing shall be adjusted to ensure the wooden surface is flat.
Key
1 direction of the baby walking frame movement
Figure 8 — Orientation of the wooden surface
4.7.2 Steel cable
A galvanised steel cable with a nominal diameter of 2 mm ± 0,1 mm.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
4.7.3 Pulley
A stainless steel ball bearing pulley with the functional diameter of 80 mm with a rounded groove suitable
for the cable. The centre of the pulley is positioned at a minimum distance of 510 mm from the platform
edge (see Figure B.1). The height of the pulley shall be adjustable.
4.7.4 Aluminium angle
A 25 mm by 25 mm rigid aluminium angle with a thickness of (2 ± 0,5) mm and a length of 1,5 m.
4.7.5 Rigid plate
A rigid plate of a dimensions of 50 mm × 50 mm.
4.7.6 Structural characteristics for the test equipment
The different parts of the test equipment shall fulfil the following (see Figure 9):
i. have a maximum vertical displacement of 1 mm when a force of 400 N is applied over a diameter of
100 mm flush on the centre of the front edge of the platform (point a);
ii. have a maximum horizontal displacement of 1 mm when a force of 200 N is applied over a diameter
of 100 mm on the edge parallel to the longitudinal axis of the platform at the following points: (b)
front edge, (c) middle point, (d) rear edge;
iii. have a maximum horizontal displacement of 1 mm when a force of 200 N is applied over a diameter
of 100 mm in the middle of the front or rear edge along the longitudinal axis of the platform (point
e);
iv. have a maximum vertical displacement of 1 mm when a 20 kg mass is hung on the pulley.
Key
a) top view b) side view
a the centre of the front edge of the platform d rear edge
b front edge e the longitudinal axis of the platform
c middle point
Figure 9 — Application of forces on the platform
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
4.8 Foam
A polyurethane foam sheet with a thickness of 60 mm, a bulk density of 35 kg/m ± 10 % or an
indentation hardness index of (170 ± 40) N in accordance with EN ISO 2439:2008, A.40.
5 General requirements and test conditions
5.1 Product conditioning
Before testing, any fabrics used shall be cleaned or washed and dried twice in accordance with the
manufacturer's instructions.
5.2 Test conditions
The tests shall be carried out in ambient conditions of (20 ± 5) °C.
The tests are designed to be applied to baby walking frames that are fully assembled and ready for use in
accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. If the baby walking frame can be assembled or adjusted
in different ways in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, the most onerous combinations
shall be used for each test, unless otherwise specified in the test method.
5.3 Application of forces
The forces in the static load tests shall be applied sufficiently slowly to ensure that negligible dynamic
force is applied.
5.4 Tolerances
Unless otherwise stated, the accuracy of the test equipment shall be:
— Forces: ± 5 % of the nominal force;
— Masses: ± 0,5 % of the nominal mass;
— Dimensions: ± 0,5 mm of the nominal dimension;
— Angles: ± 0,5° of the nominal angle;
— Duration: ± 1 s of the nominal duration.
The tests are described in terms of the application of forces. Masses can however be used. The
relationship 10 N = 1 kg may be used for this purpose.
Unless otherwise specified, the test forces may be applied by any suitable device which does not adversely
affect the results.
5.5 Order of tests
Unless otherwise stated in the test methods, the tests shall be carried out on the same baby walking frame
in the order listed in this standard.
6 Chemical hazards (see A.2)
6.1 General
If testing is required, a separate unconditioned sample shall be used for the tests in Clause 6.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
6.2 Migration of certain elements (see A.2)
The migration of elements from materials on exterior surfaces shall not exceed the limits listed in Table 1.
Table 1 — Limits for heavy metals migration
Element mg/kg Element mg/kg
Aluminium 70 000 Lead 23
Antimony 560 Manganese 15 000
Arsenic 47 Mercury 94
Barium 18 750 Nickel 930
Boron 15 000 Selenium 460
Cadmium 17 Strontium 56 000
Chromium (III) 460 Tin 180 000
Chromium (VI) 0,2 Organic tin 12
Cobalt 130 Zinc 46 000
Copper 7 700
When testing is performed, the method described in EN 71-3 shall be used.
Components under the base (e.g. castors or wheels, braking pads, …) are excluded from these
requirements.
6.3 Formaldehyde (see A.2)
Accessible textile components shall not contain free and hydrolysed formaldehyde in excess of 30 mg/kg.
When testing is performed, the method described in EN ISO 14184-1 shall be used.
Resin-bonded wood components shall not release formaldehyde in excess of 0,124 mg/m (class E1
according to EN 622-1).
When testing is performed, the method described in EN 717-1 shall be used.
6.4 Colorants (see A.2)
When tested in accordance with EN 71-10:2005, Annex A, if the colour fastness to sweat of accessible
textile components is lower than 3-4 on the grey scale as defined in EN 20105-A03, the part shall be tested
for colorants with the methods described in EN 71-10 and EN 71-11 and the limits in Table 2 shall be
fulfilled.
Table 2 — Colourants limits
CoIour Index Generic Colour Index CAS Number Limit
Name (CIGN) Constitution
Number (CICN)
Disperse Blue 1 64500 2475–45–8 Action limit
Disperse Blue 3 61505 2475–46–9 Action limit
Disperse Blue 106 111935 12223–01–7 Action limit
Disperse Blue 124 111938 61951–51–7 Action limit
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
CoIour Index Generic Colour Index CAS Number Limit
Name (CIGN) Constitution
Number (CICN)
Disperse Yellow 3 11855 2832–40–8 Action limit
Disperse Orange 3 11855 730–40–5 Action limit
Disperse Orange 11132 12223–33–5 Action limit
37/76/59
13301–61–6
Disperse Red 1 11110 2872–52–8 Action limit
Solvent Yellow 1 11000 60–09–3 Action limit
Solvent Yellow 2 11020 60–11–7 Action limit
Solvent Yellow 3 11160 97–56–3 Action limit
Basic Red 9 42500 569–61–9 Action limit
Basic Violet 1 42535 8004–87–3 Action limit
Basic Violet 3 42555 548–62–9 Action limit
Acid Red 26 16150 3761–53–3 Action limit
Acid Violet 49 42640 1694–09–3 Action limit
6.5 Aniline (see A.2)
Aniline shall not exceed the limit of 30 mg/kg after reductive cleavage from accessible textile
components.
When testing is performed the method of EN ISO 14362-1 and EN ISO 17234-1, adapted as appropriate
to measure aniline, shall be used.
7 Thermal hazards (see A.3)
7.1 Requirement
When tested in accordance with 7.2, there shall be no surface flash and the rate of spread of flame shall
not exceed 50 mm/s.
A separate sample, conditioned according to 5.1, may be used for these tests.
7.2 Test method
To verify the surface flash effect apply the test flame defined in EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014, 5.5 for (3 ± 0,5) s
to the baby walking frame in different places likely to cause surface flash.
To verify rate of spread of flame apply the test flame defined in EN 71-2:2011+A1:2014, 5.4.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
8 Mechanical hazards (see A.4)
8.1 Entrapment hazards (see A.4.1)
8.1.1 Requirements
When tested in accordance with 8.1.2, there shall be no completely bounded openings between 7 mm and
12 mm unless the depth is less than 10 mm or unless the shape assessment probe (see 4.6) enters when
tested in accordance with 8.1.2.
When tested in accordance with 8.1.2, there shall be no openings in mesh that allow the test probe for
mesh (see 4.6) to penetrate to the 7 mm diameter section.
The test shall be carried out with the product in any intended position of use.
This requirement does not apply to the castors, wheels, the whole base of the baby walking frame, and to
any other part of the underside of the tray more than 100 mm from the vertical projection of the outer
edge (see Figure 10).
Key
100 mm distance from the edge
Figure 10 — Underside of the tray
8.1.2 Test methods
Check whether the 7 mm probe (see 4.6), with an applied force of up to 30 N, enters 10 mm or more into
any accessible completely bounded opening in any possible orientation.
If the 7 mm probe enters 10 mm or more, then the 12 mm probe (see 4.6) shall also enter 10 mm or more
with an applied force of up to 5 N.
If the 7 mm probe enters with an applied force of up to 30 N but the 12 mm probe does not enter 10 mm
or more with an applied force of up to 5 N, check whether the 12 mm shape assessment probe (see 4.6)
enters 10 mm or more with an applied force of up to 5 N.
Check whether the test probe for mesh (see 4.6), with an applied force of up to 30 N, penetrates accessible
openings in mesh up to the 7 mm diameter section.
8.2 Hazards due to moving parts (see A.4.2)
8.2.1 General
Shear and compression points which are created only when setting up or folding are acceptable as the
carer can be assumed to be in control of these actions.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
The castors, wheels, whole base of the baby walking frame and the underside of the tray, more than
100 mm from the vertical projection of the outer edge of the tray, are excluded from the requirements of
8.2.
8.2.2 Requirements for compression points
After the baby walking frame is set up for normal use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions
there shall be no compression points which can close to less than 12 mm unless they are always less than
5 mm, through the whole range of movement.
Movement due elasticity of materials shall not be considered as a compression hazard.
8.2.3 Requirements for shear points
After the baby walking frame is set up for normal use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions
there shall be no shear points which can close to less than 12 mm.
Movement due to play and/or elasticity of materials shall not be considered as a shearing hazard.
8.3 Protective function of the seat
8.3.1 General
There shall be no harness-based restraint system.
8.3.2 Crotch strap
The baby walking frame shall be fitted with a crotch strap.
Where a crotch strap is made of flexible material, the width shall be at least 50 mm.
Where a crotch strap is made of rigid material, the width shall be at least 20 mm.
8.3.3 Removable seats
If the seat is removable, the fixing mechanism(s) to attach the seat shall be designed so as to prevent the
seat from inadvertently becoming detached.
This requirement is met if one of the following is fulfilled:
a) the removal of the seat requires at least two independent fixing mechanisms which shall be operated
simultaneously; or
b) a single fixing mechanism is designed to be operated only with the use of a tool; or
c) a single fixing mechanism requires a force of at least 50 N to release it; or
d) two consecutive actions are required to release the fixing mechanism, the operation of the second
action being dependent on the first action being carried out and maintained; or
e) 3 or more independent actions (e.g. undoing a clip) are required to remove the seat.
8.3.4 Seat height
8.3.4.1 Requirement
The height of the seat in the lowest position shall be at least 180 mm above the ground, when measured
in accordance with 8.3.4.2.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
8.3.4.2 Test methods
Place the baby walking frame on a smooth level horizontal surface.
Place the test mass A (4.4.1) centrally in a vertical position on the seat of the baby walking frame
(Figure 3) and leave it for 10 min before measuring.
Measure the seat height from the lower surface of the test mass to the horizontal surface (see Figure 11).
Key
h height of the seat in the lowest position
Figure 11 — Measurement of the minimum height of adjustable seat
8.4 Hazards due to height adjustment and folding of the product
8.4.1 Requirements
8.4.1.1 General
Baby walking frames which may be folded or adjusted shall be fitted with locking mechanism(s) for the
folding and height adjustment system.
8.4.1.2 Incomplete deployment
To avoid the hazard due to incomplete deployment, at least one locking mechanism shall engage
automatically when the product is deployed for use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions
for use.
8.4.1.3 Unintentional release of locking mechanism(s)
To avoid the hazards due to unintentional release, when tested in accordance with 8.4.2, the baby walking
frame shall not collapse, shall remain locked in the position for use and one of the following conditions
shall be fulfilled:
a) there are at least two independent locking devices that shall be operated simultaneously; or
b) it is designed to be operated only with the use of a tool; or
c) two consecutive actions are required to release the folding mechanism, the operation of the second
action being dependent on the first action being carried out and maintained.
8.4.2 Test methods for height adjustment and folding mechanisms
8.4.2.1 Durability test
Release any height adjustment and/or folding mechanisms.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
Completely fold the baby walking frame and erect in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Repeat the test for a total of 100 cycles.
8.4.2.2 Strength test
Set up the baby walking frame for normal use in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Apply a force of 200 N in the direction of the folding action of the baby walking frame and maintain the
force for 2 min.
Apply the force 5 times in total.
8.5 Hazards from entanglement in cords, ribbons and similar parts (see A.4.3)
8.5.1 Requirements
Cords, ribbons and similar parts shall have a free length not exceeding 220 mm when tested in accordance
with 8.6.2.
Where cords, ribbons and similar parts are attached to the baby walking frame together or within 80 mm
of each other, any single cord shall have a free length not exceeding 220 mm and the combined length
from one loose end to the end of another loose end shall not exceed 360 mm (see Figure 12), when tested
in accordance with 8.6.2.
Loops shall have a peripheral dimension not exceeding 360 mm, when tested in accordance with 8.6.2.
Monofilament threads shall not be used.
Dimensions in millimetres
Key
L length
D distance
Figure 12 — Examples of measuring cords, ribbons or similar parts
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
8.5.2 Test method
The length of a cord, ribbon or similar part is measured from the fixing point on the baby walking frame
to the free end of the cord, ribbon or similar part while a 25 N tensile force is applied.
The peripheral dimension of a loop shall be measured while a 25 N tensile force is applied.
8.6 Choking and ingestion hazard (see A.4.4)
8.6.1 Requirements
When tested in accordance with 8.6.2 any component or part of a component that is removed, whether
intended to be removed without the use of a tool or not, shall not fit entirely within the small parts
cylinder specified in 4.2.
8.6.2 Test methods
8.6.2.1 Assessment of child’s ability to grip components
A component is considered to be able to be gripped by a child if it can grip the component between its
thumb and forefinger or between its teeth.
Where it is difficult to assess whether a child can grip a component, establish whether it can be gripped
by inserting once the feeler gauge specified in 4.3 between the component and the underlying layer at an
angle between 0° and 10° from the surface of the underlying layer using a force of (10 ± 1) N. If the gauge
can be inserted more than 2 mm, the component is considered to be able to be gripped by the child.
8.6.2.2 Torque test
Apply a torque gradually to the component within a period of 5 s in a clockwise direction until either:
a) a rotation of 180° from the original position has been attained; or
b) a torque of 0,34 Nm is reached.
The maximum rotation or required torque shall be applied for (10 ± 1) s.
The component shall then be allowed to return to a relaxed condition and the procedure repeated in an
anticlockwise direction.
Where projections, components or assemblies are rigidly mounted on an accessible rod or shaft, designed
to rotate together with the projections, components or assemblies, during the test the rod or shaft shall
be clamped to prevent rotation.
If a component attached by a screw thread becomes loosened during application of the required torque,
the torque shall continue to be applied until the required torque is exceeded or the component
disassembles or it becomes apparent that the component will not disassemble.
When using clamps and test equipment, care shall be taken not to damage the attachment mechanism or
body of the component.
Check whether any component or part of a component that is removed during the test fits wholly in any
orientation, without compressing or manipulating it, within the small parts cylinder specified in 4.2.
8.6.2.3 Tensile test
The tensile test shall be carried out on the same components as the torque test.
Attach a suitable clamp to the component, taking care not to damage the attachment mechanism or body
of the component.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
Fasten the component in a tensile testing machine and apply a tensile force of 90 N to the component to
be tested. Apply the force gradually within a period of 5 s and maintain for (10 ± 1) s.
Check whether any component or part of a component that is removed during the test fits wholly in any
orientation, without compressing or manipulating it, within the small parts cylinder specified in 4.2.
8.7 Suffocation hazards from plastic packaging (see A.4.5)
8.7.1 Plastic packaging
Any plastic covering used for packaging with an area greater than 100 mm × 100 mm shall conform to at
least one of the following requirements:
a) have an average sheet thickness of 0,038 mm or more; or
b) be perforated with defined holes so that a minimum of 1 % of the area has been removed over any
area of 30 mm × 30 mm.
Any plastic covering used for packaging with an opening perimeter greater than 360 mm shall not have
a drawstring or cord as a means of closing and shall be marked in the official language(s) of the country
of sale with the word “WARNING” followed by the statement “Keep plastic covering away from children
to avoid suffocation”.
The statement may be expressed in different words providing they clearly convey the same warning.
The text shall be accompanied by the symbol of the warning triangle ( ). The symbol, with a minimum
height of 1 cm, can be put on the top of the list of warnings when different languages are used.
Shrunk-on films that are destroyed when the packaging is opened by the user are excluded from these
requirements.
8.7.2 Plastic decals
8.7.2.1 Requirement
Plastic decals or parts of plastic decals shall not become detached when tested in accordance with 8.7.2.2.
8.7.2.2 Test method
Completely submerge the area to be tested in a container of demineralized water at a temperature of
(20 ± 5)°C for 4 min ± 10 s. Remove the product, shake off excess water and keep the product in ambient
temperature for 10 min ± 10 s.
Repeat the test for additional 3 times.
8.8 Hazards from edges, corners and protruding parts (see A.4.6)
All edges, corners and protruding parts of the baby walking frame shall be rounded and free from burrs.
All surfaces shall be free from burrs and sharp edges.
8.9 Hazards from inadequate structural integrity (see A.4.7)
8.9.1 Static strength
8.9.1.1 Requirement
When tested in accordance with 8.9.1.2.1 or 8.9.1.2.2 the baby walking frame shall not collapse or change
from one height adjustment position to another.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
8.9.1.2 Test method
8.9.1.2.1 Baby walking frames not fitted with a tray
Adjustable seats shall be adjusted to their highest position.
Place a mass of 30 kg evenly distributed on the seat.
Maintain the mass for 24 h.
Remove the mass and allow the baby walking frame to recover for 1 h before proceeding to the next
clause.
8.9.1.2.2 Baby walking frames fitted with a tray
Adjustable seats shall be adjusted to their highest position.
Place a mass of 30 kg evenly distributed on the seat and a mass of 10 kg evenly distributed over a
diameter of 120 mm on the centre of the tray.
Maintain the masses for 24 h.
Remove the masses and allow the baby walking frame to recover for 1 h before proceeding to the next
clause.
8.9.2 Dynamic strength
8.9.2.1 Requirement
When tested in accordance with 8.9.2.2 the seat and crotch strap shall not tear and the baby walking
frame shall not collapse or change from one height adjustment position to another.
8.9.2.2 Test method
Adjustable seats shall be adjusted to their highest position.
Place the foam (see 4.8) on the seat.
Hold the test mass A (4.1.1) in a vertical position 70 mm above the centre of the seat and allow it to drop
freely on to the seat.
Carry out the test for a total of 100 drops.
8.10 Hazards from inadequate stability (see A.4.8)
8.10.1 Static stability
8.10.1.1 Requirements
When tested in accordance with 8.10.1.2, the baby walking frame shall not overturn.
8.10.1.2 Test method
Adjustable seats shall be adjusted to their highest position.
Position the test mass A (4.1.1) vertically in the centre of the seat.
The movement of the test mass during the test shall be minimized as far as possible by any appropriate
means of negligible mass.
Place the baby walking frame on the slope against the stop.
Adjust the castors or wheels to their most onerous position.
Carry out the test in forward, sideward and rearward direction.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
8.10.2 Dynamic stability
8.10.2.1 Requirements
When tested in accordance with 8.10.2.2, the baby walking frame shall not overturn, there shall be no
fracture and shall still function as intended. Where the baby walking frame is supplied with toy
accessories which are intended to be fitted to or removed from the baby walking frame by the carer, the
baby walking frame shall be tested with the toy accessories. If removable toys become detached from the
frame during the test, this shall not be considered as a failure.
8.10.2.2 Test method
8.10.2.2.1 General
Adjustable seats shall be adjusted to their highest position.
Unlock parking devices and any devices used to slow down the product (if any).
Establish a vertical plane A that passes through the centre of the seating area and is parallel to the
direction the child faces. Establish a vertical plane B that is perpendicular to plane A and passes through
the centre of the seating area.
The dynamic stability test shall be carried out in the forward (8.10.2.2.2) and rearward (8.10.2.2.3)
direction.
In case the forward and rearward directions are not evident, the baby walking frame shall be tested in
the most onerous forward direction allowed in the instructions for use and in its opposite rearward
direction.
8.10.2.2.2 Forward facing dynamic stability test
Position the baby walking frame on the test platform facing forward, so that plane A is perpendicular to
the front edge of the platform and passes through the centre of the pulley (4.7.3).
Position the test mass B (4.1.2) vertically in the centre of the seat.
The movement of the test mass during the test shall be minimized as far as possible by any appropriate
means of negligible mass.
Place a spacer (4.6.2) on the platform next to the stop. Move the baby walking frame towards the stop so
that the most protruding part(s) of the baby walking frame base touch(es) the squared aluminium
piece(s) thus keeping the most protruding part(s) of the baby walking frame base at a distance of 40 mm
from the stop. If one spacer is not high enough, add one more spacer on top of the previous one.
Attach test mass D (4.1.4) to the front of the baby walking frame base at plane A by means of a steel cable
(4.7.2) and a pulley (4.7.3) and adjust the pulley so that the force is applied horizontally.
The mass shall drop into a bucket containing sand. The surface of the bag shall be levelled to ensure that
the whole base area of the mass hits the surface of the bag filled with sand simultaneously.
Adjust the length of the steel cable so that the bottom surface of the test mass D just touches the surface
of the sand.
To fine tune the length of the steel cable, move the baby walking frame 10 mm to 20 mm from the
spacer(s) and release it in order to verify that, at this position, the tension of the steel cable is sufficient
to propel the baby walking frame forward. Remove the spacer(s) to verify that when the baby walking
frame is 40 mm from the stop the tension of the steel cable is not sufficient to propel the baby walking
frame forward.
NOTE The fine-tuning may have to be done in an iterative way.
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2019 (E)
Re-position the baby walking frame so that the distance d from the most protruding part(s) of the baby
walking frame base to the stop is 580 mm. Ensure that castors face in the direction of the intended travel
by moving the baby walking frame away from the front edge and back again to the start position.
Release the baby walking frame.
Repeat the test by using test mass C (4.1.3) and a distance d of 720 mm.
8.10.2.2.3 Rearward facing dynamic stability test
Carry out the test as described in 8.10.2.2.2 but with the baby walking frame rearward facing.
8.11 Hazards due to falling down stairs (see A.4.9)
8.11.1 Requirements
When tested in accordance with 8.11.2 the baby walking frame shall maintain contact with and be
supported only by the test platform in each of the tests.
8.11.2 Test method
8.11.2.1 General
Clean the test platform and the underside of the base (e.g. wheels, stoppers) of the baby walking frame
with a cloth dampened with demineralized water. Let it dry before performing the tests.
Detachable toys shall be removed.
Position test mass B (4.1.2) vertically in the centre of the seat. The movement of the test mass inside the
seat shall not be restricted.
Establish a vertical plane A that passes through the centre of the test mass and is parallel to the direction
the child faces. Establish a vertical plane B that is perpendicular to plane A and passes through the centre
of the test mass.
Drill hole(s) in the base at a height of 60 mm from the test platform aligned with plane A at the front and
at the rear and plane B on both sides (see Figure 13). The hole(s) shall not affect the performance of the
product during the tests.
If the design of the product does not allow to drill the hole(s) as defined above, drill the hole(s) in the
base aligned with plane A and plane B as described above at a height as close as possible to 60 mm by
increments of ± 5 mm but not higher than 100 mm (see Figure 13). This only applies to the front, back or
side where it is not possible to drill the hole at 60 mm. If this applies only to the back of the product, for
example, then the holes on the front and the sides shall be at 60 mm.
If the design of the product does not allow to drill the hole(s) as defined above, attach a piece of steel
cable (see 4.7.2) wherever possible along the walking frame base at the same height defined above (see
Figure 14). This steel cable shall be fitted with an attachment device aligned with plane A or plane B as
relevant.
Additional holes may be required on the tray to fix the bar required for the tip over test (see 8.11.3).
oSIST prEN 1273:2019
prEN 1273:2018 Rev (E)
Key
h Fixed height of 60 mm (if this fixed height is not feasible, increments of ± 5 mm, but not higher than 100 mm,
from h are allowed)
Figure 13 — Position of holes on the base
Key
1 base
2 steel wire
3 wheels
4 test platform
Figure 14 — Preparation of product (holes for cables) for products with open base
Parking devices and speed controls shall be unlocked or adjusted to allow the maximum speed; in case of
systems that cannot be unlocked or adjusted (e.g. automatic weight based brakes on wheels), the test
shall be done by forcing these systems not to slow down the product. This can be achieved by any means
not affecting the weight of the product.
8.11.2.2 Forward facing step test
Place the baby walking frame on the test platform.
Adjustable seats shall be adjusted to their highest position.
Position test mass B (4.1.2) vertically in the centre of the seat.
Attach the steel cable to the front of the base through the hole aligned with plane A or to the attachment
device on the steel cable attached along
...







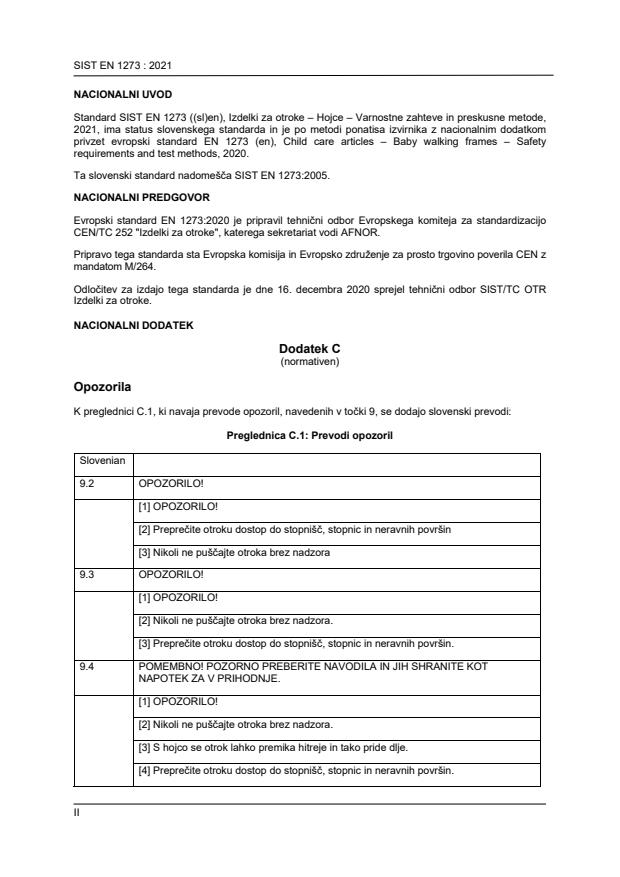






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...