ISO 5457:1999
(Main)Technical product documentation — Sizes and layout of drawing sheets
Technical product documentation — Sizes and layout of drawing sheets
This International Standard specifies the size and layout of preprinted sheets for technical drawings in any field of engineering, including those produced by computer. This International Standard is also applicable to other technical documents.
Documentation technique de produits — Formats et présentation des éléments graphiques des feuilles de dessin
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les formats et la présentation des feuilles de dessin préimprimées à utiliser pour tous les dessins techniques dans tous les domaines de la technique, y compris les dessins techniques assistés par ordinateur. La présente Norme internationale est également applicable à d'autres documents techniques.
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 24-Feb-1999
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 10/SC 1 - Basic conventions
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 10/SC 1 - Basic conventions
- Current Stage
- 9093 - International Standard confirmed
- Start Date
- 17-May-2021
- Completion Date
- 14-Feb-2026
Relations
- Consolidates
EN ISO 5457:1999 - Technical product documentation - Sizes and layout of drawing sheets (ISO 5457:1999) - Effective Date
- 12-Feb-2026
- Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
- Effective Date
- 06-Jun-2022
- Effective Date
- 12-May-2008
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 5457:1999, titled Technical product documentation - Sizes and layout of drawing sheets, is an international standard developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). This standard specifies the sizes and layout requirements for preprinted sheets used for technical drawings across all engineering fields. It applies equally to traditional hand-drafted drawings and those produced via computer-aided design (CAD) systems, as well as to other related technical documents.
By standardizing sheet sizes and layouts, ISO 5457 ensures consistency, clarity, and interoperability in the presentation of engineering drawings. It supports efficient communication, reproduction, and filing processes globally, facilitating seamless information exchange among engineers, manufacturers, and stakeholders.
Key Topics
Sheet Sizes and Formats
ISO 5457 adopts sizes from the ISO-A series (A0 to A4) as defined in ISO 216, specifying both trimmed and untrimmed sheet dimensions. The standard encourages using the smallest sheet size that maintains drawing clarity and resolution. It also addresses "elongated sizes," which combine dimensions of different ISO-A sizes where necessary.Drawing Space and Margins
The drawing space is clearly defined on each sheet with specific border widths-20 mm on the left edge for filing purposes and 10 mm on all other edges. A continuous 0.7 mm frame outlines the drawing space, ensuring standardized presentation.Title Blocks
Placement and dimensions of title blocks conform to ISO 7200. For sizes A0 to A3, title blocks are located at the bottom right corner of the horizontally oriented sheets, while A4 sheets are vertical with the title block on the shorter, lower part. The reading direction of the drawing aligns with the title block orientation.Grid Reference System and Centering Marks
To facilitate easy identification of details, revisions, or additions, sheets are divided into grid fields using a reference system combining letters (vertical) and numerals (horizontal). The system varies in complexity per sheet size and excludes letters I and O to avoid confusion. Centering marks support accurate positioning during reproduction or microfilming.Trimming and Reproduction Marks
Trimming marks are provided at the edges for precise sheet cutting, designed as overlapping rectangles sized 10 mm by 5 mm. These make manual or automatic trimming more efficient and reliable.Sheet Designation
This includes a standardized naming format indicating the standard number, sheet size, trimming status, material type (e.g., tracing paper, opaque paper, or polyester-based drafting film), printing side, and title block usage.
Applications
ISO 5457 is essential for professionals and organizations involved in:
Engineering and Manufacturing
Facilitates uniform technical drawings for design, production, quality control, and inspection tasks.Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Ensures CAD outputs are compliant with recognized sheet sizes and drawing layout conventions, simplifying printing and documentation.Archiving and Document Control
Standardized sheet sizes and layout improve filing, reproduction, microfilming, and long-term storage of technical documentation.Educational and Training Materials
Supports consistent teaching aids and technical manuals in engineering disciplines.Cross-Industry Collaboration
By adopting ISO 5457, companies in automotive, aerospace, construction, electronics, and other sectors promote interoperability and reduce miscommunication.
Related Standards
Following are key ISO standards closely linked to ISO 5457 for comprehensive technical documentation:
- ISO 128-20:1996 - General principles of presentation for technical drawings, including basic conventions for lines.
- ISO 216:1975 - Defines standard paper sizes in the A and B series, fundamental to ISO 5457’s sheet dimensions.
- ISO 3098-1:1974 - Specifies lettering styles for technical drawings.
- ISO 7200:1984 - Details content and layout of title blocks.
- ISO 9958-1:1992 - Defines drafting films with polyester base requirements and marking methods.
- ISO 9961:1992 - Covers specifications for natural tracing paper used in technical drawings.
By adhering to ISO 5457, organizations ensure that their technical drawings are presented in a clear, consistent, and standardized manner, improving communication quality and operational efficiency across engineering documentation workflows.
Buy Documents
ISO 5457:1999 - Technical product documentation -- Sizes and layout of drawing sheets
ISO 5457:1999 - Documentation technique de produits -- Formats et présentation des éléments graphiques des feuilles de dessin
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 5457:1999 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Technical product documentation — Sizes and layout of drawing sheets". This standard covers: This International Standard specifies the size and layout of preprinted sheets for technical drawings in any field of engineering, including those produced by computer. This International Standard is also applicable to other technical documents.
This International Standard specifies the size and layout of preprinted sheets for technical drawings in any field of engineering, including those produced by computer. This International Standard is also applicable to other technical documents.
ISO 5457:1999 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 01.100.01 - Technical drawings in general. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 5457:1999 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to EN ISO 5457:1999, ISO/IEC 10032:1995, ISO 5457:1999/Amd 1:2010, SIST ISO 5457:1995, ISO 5457:1980; is excused to ISO 5457:1999/Amd 1:2010. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 5457:1999 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL ISO
STANDARD 5457
Second edition
1999-02-01
Technical product documentation — Sizes
and layout of drawing sheets
Documentation technique de produits — Formats et présentation des
éléments graphiques des feuilles de dessin
A
Reference number
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of
preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which
a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented
on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-
governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 5457 was prepared by Technical Committee
ISO/TC 10, Technical drawings, product definition and related
documentation, Subcommittee SC 1, Basic conventions.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (ISO 5457:1980),
which has been technically revised.
Annex A of this International Standard is for information only.
© ISO 1999
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced
or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and
microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Genève 20 • Switzerland
Internet iso@iso.ch
Printed in Switzerland
ii
©
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO ISO 5457:1999(E)
Technical product documentation — Sizes and layout of drawing
sheets
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies the size and layout of preprinted sheets for technical drawings in any field of
engineering, including those produced by computer. This International Standard is also applicable to other technical
documents.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this
International Standard. At the time of publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards are subject to
revision, and parties to agreements based on this International Standard are encouraged to investigate the
possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards indicated below. Members of IEC and ISO maintain
registers of currently valid International Standards.
ISO 128-20:1996, Technical drawings — General principles of presentation — Part 20: Basic conventions for lines.
ISO 216:1975, Writing paper and certain classes of printed matter — Trimmed sizes — A and B series.
ISO 3098-1:1974, Technical drawings — Lettering — Part 1: Currently used characters.
ISO 7200:1984, Technical drawings — Title blocks.
ISO 9958-1:1992, Draughting media for technical drawings — Draughting film with polyester base — Part 1:
Requirements and marking
ISO 9961:1992, Draughting media for technical drawings — Natural tracing paper.
3 Sizes
3.1 Size of series ISO-A
The original drawing should be made on the smallest sheet permitting the necessary clarity and resolution.
The preferred sizes of the trimmed and untrimmed sheets as well as the drawing space of the main ISO-A series
(see ISO 216) are given in table 1.
©
ISO
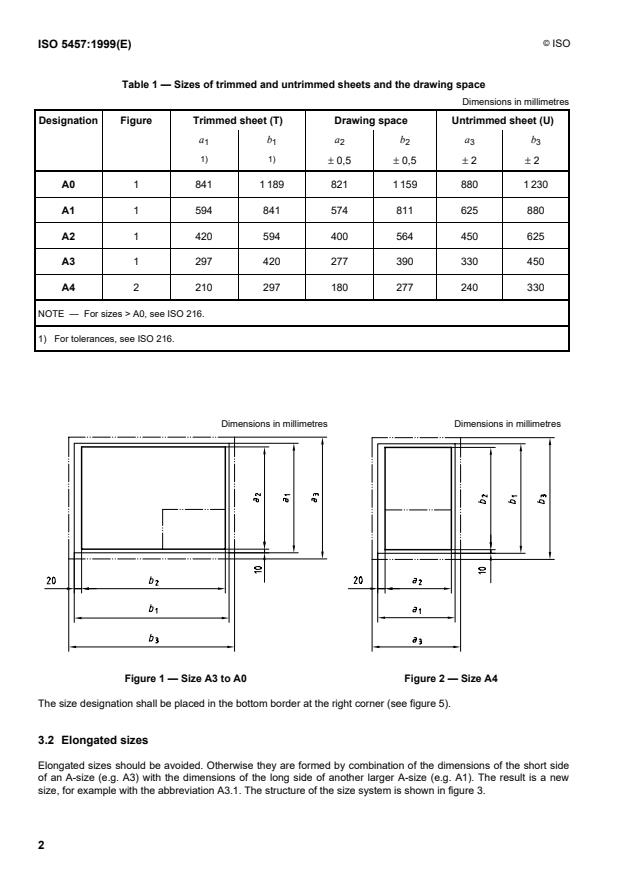
Table 1 — Sizes of trimmed and untrimmed sheets and the drawing space
Dimensions in millimetres
Designation Figure Trimmed sheet (T) Drawing space Untrimmed sheet (U)
a b a b a b
1 1 2 2 3 3
1) 1)
± 0,5 ± 0,5 ± 2 ± 2
A0 1 841 1 189 821 1 159 880 1 230
A1 1 594 841 574 811 625 880
1 420 594 400 564 450 625
A2
A3 1 297 420 277 390 330 450
A4 2 210 297 180 277 240 330
NOTE — For sizes > A0, see ISO 216.
1) For tolerances, see ISO 216.
Dimensions in millimetres Dimensions in millimetres
Figure 1 — Size A3 to A0 Figure 2 — Size A4
The size designation shall be placed in the bottom border at the right corner (see figure 5).
3.2 Elongated sizes
Elongated sizes should be avoided. Otherwise they are formed by combination of the dimensions of the short side
of an A-size (e.g. A3) with the dimensions of the long side of another larger A-size (e.g. A1). The result is a new
size, for example with the abbreviation A3.1. The structure of the size system is sh
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE 5457
Deuxième édition
1999-02-01
Documentation technique de produits —
Formats et présentation des éléments
graphiques des feuilles de dessin
Technical product documentation — Sizes and layout of drawing sheets
A
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L'ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
l'ISO). L'élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de l'ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernementales,
en liaison avec l'ISO participent également aux travaux. L'ISO collabore
étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en
ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l'approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 5457 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 10, Dessins techniques, définition de produits et documentation y
relative, sous-comité SC 1, Conventions générales.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 5457:1980), dont elle constitue une révision technique.
L’annexe A de la présente Norme internationale est donnée uniquement à
titre d’information.
© ISO 1999
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l'accord
écrit de l'éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Genève 20 • Suisse
Internet iso@iso.ch
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
©
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO ISO 5457:1999(F)
Documentation technique de produits — Formats et présentation
des éléments graphiques des feuilles de dessin
1 Domaine d’application
La présente Norme internationale spécifie les formats et la présentation des feuilles de dessin préimprimées à
utiliser pour tous les dessins techniques dans tous les domaines de la technique, y compris les dessins techniques
assistés par ordinateur. La présente Norme internationale est également applicable à d’autres documents
techniques.
2 Références normatives
Les normes suivantes contiennent des dispositions qui, par suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent des
dispositions valables pour la présente Norme internationale. Au moment de la publication, les éditions indiquées
étaient en vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties prenantes des accords fondés sur la présente
Norme internationale sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d’appliquer les éditions les plus récentes des normes
indiquées ci-après. Les membres de la CEI et de l’ISO possèdent le registre des Normes internationales en vigueur
à un moment donné.
ISO 128-20:1996, Dessins techniques — Principes généraux de représentation — Partie 20: Conventions de base
pour les traits.
ISO 216:1975, Papiers d'écriture et certaines catégories d'imprimés — Formats finis — Séries A et B.
ISO 3098-1:1974, Dessins techniques — Écriture — Partie 1: Caractères courants.
ISO 7200:1984, Dessins techniques — Cartouches d'inscriptions.
ISO 9958-1:1992, Supports de traçage pour dessins techniques — Films à dessin à base de polyester —
Partie 1: Caractéristiques et marquage.
ISO 9961:1992, Supports de traçage pour dessins techniques — Papier calque naturel.
3 Formats
3.1 Formats de série A, ISO
Il convient que le dessin original soit exécuté sur un support du plus petit format permettant la clarté et la netteté
voulues.
Les formats préférentiels des feuilles finies et non finies, ainsi que la zone d’exécution du dessin, de la série
principale A, ISO (voir l’ISO 216) sont donnés dans le tableau 1.
©
ISO
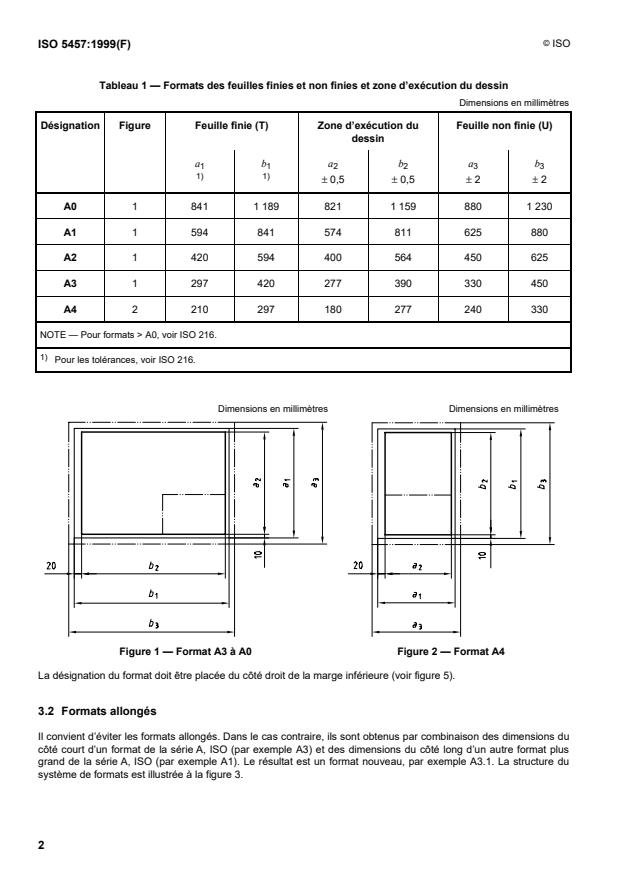
Tableau 1 — Formats des feuilles finies et non finies et zone d’exécution du dessin
Dimensions en millimètres
Désignation Figure Feuille finie (T) Zone d’exécution du Feuille non finie (U)
dessin
a b a b a b
1 1 2 2 3 3
1) 1)
– 0,5 – 0,5 – 2 – 2
A0 1 841 1 189 821 1 159 880 1 230
A1 1 594 841 574 811 625 880
A2 1 420 594 400 564 450 625
A3 1 297 420 277 390 330 450
A4 2 210 297 180 277 240 330
NOTE — Pour formats > A0, voir ISO 216.
1)
Pour les tolérances, voir ISO 216.
Dimensions en millimètres Dimensions en millimètres
Figure 1 — Format A3 à A0 Figure 2 — Format A4
La désignation du format doit être placée du côté droit de la marge inférieure (voir figure 5).
3.2 Formats allongés
Il convient d’éviter les formats allongés. Dans le cas contraire, ils sont obtenus par combinaison des dimensions du
côté court d’un format de la série A, ISO (par exemple A3) et des dimensions du côté long d’un autre format plus
grand de la série A, ISO (par exemple A1). Le résultat est un format nouveau, par exemple A3.1. La structure du
système de formats est illustrée à la
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...