ISO 1505:1993
(Main)Textile machinery — Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines — Definitions and range of nominal widths
Textile machinery — Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines — Definitions and range of nominal widths
Defines 8 critical widths to enable the specification, without ambiguity, of these essential dimensions, particularly in orders, and specifies the range of nominal width, i.e. the width of the machine elements, which house the textile fabric during a treatment process.
Matériel pour l'industrie textile — Largeurs relatives aux matériels de teinture et de finissage — Définitions et gamme de largeurs nominales
General Information
- Status
- Published
- Publication Date
- 10-Feb-1993
- Current Stage
- 9060 - Close of review
- Completion Date
- 03-Jun-2028
Relations
- Effective Date
- 15-Apr-2008
Overview
ISO 1505:1993 - "Textile machinery - Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines - Definitions and range of nominal widths" standardizes the principal machine widths used in dyeing and finishing equipment. It defines eight critical widths and prescribes a range of nominal widths so that dimensions can be specified without ambiguity in orders, technical drawings and procurement documents.
This standard is essential for manufacturers, specifiers and plant engineers who require clear, repeatable dimensions for machine elements that contact or house textile fabric during treatment.
Key Topics
- Defined widths: The standard defines the principal widths such as maximum working width (a1), minimum working width (a2), nominal width (b) and others related to frames and beam elements.
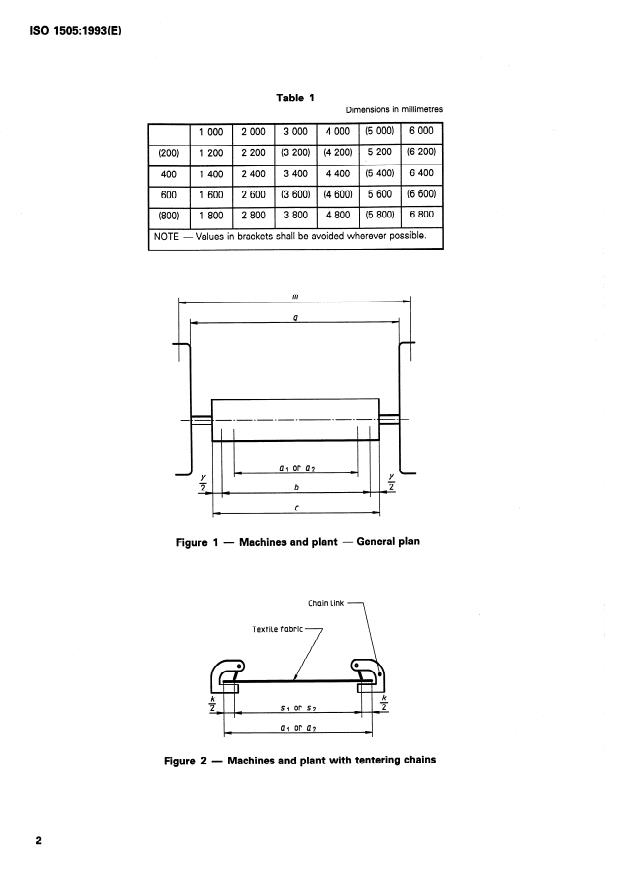
- Range of nominal widths: A tabulated range of nominal widths is provided in millimetres (Table 1). Example values include 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000 ... up to 6800 mm; values shown in parentheses should be avoided where possible.
- Machine element dimensions: Definitions cover widths of machine elements in contact with the fabric, internal frame widths and the effective widths of beams or rakes on machines fitted with tension chains.
- Dimensional relationships: The standard includes algebraic relationships linking widths and adjustment dimensions so manufacturers and integrators can calculate interfaces and clearances consistently.
- Informative annex: Annex A is informative and the bibliography references related classification standards (e.g., ISO 1506:1982).
Applications
- Procurement and orders: Use the standard to specify machine widths unambiguously in purchase orders and contracts, reducing misinterpretation between buyers and suppliers.
- Machine interfacing: Apply nominal-width definitions when engineering connections between dyeing and finishing line modules to ensure proper alignment and fabric handling.
- Plant layout and installation: Use the tabulated nominal widths for planning factory layout, access clearances and integration of modular equipment.
- Quality assurance and documentation: Include defined width terms in drawings, test plans and validation records to maintain consistency across suppliers and production sites.
Related Standards
- ISO 1506:1982 - referenced in the bibliography for general classification and nomenclature of dyeing and finishing equipment.
ISO 1505:1993 improves interoperability and reduces ambiguity by standardizing how widths are defined and selected for textile machinery. For engineers and procurement teams, adopting these definitions supports clearer orders, consistent machine interfacing and more efficient plant layouts.
Buy Documents
ISO 1505:1993 - Textile machinery -- Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines -- Definitions and range of nominal widths
ISO 1505:1993 - Matériel pour l'industrie textile -- Largeurs relatives aux matériels de teinture et de finissage -- Définitions et gamme de largeurs nominales
ISO 1505:1993 - Matériel pour l'industrie textile -- Largeurs relatives aux matériels de teinture et de finissage -- Définitions et gamme de largeurs nominales
Get Certified
Connect with accredited certification bodies for this standard

Control Union Certifications
Global certification for agriculture and sustainability.

Bureau Veritas Bangladesh
Bureau Veritas certification services in Bangladesh.

ECOCERT France
Leader in organic and sustainability certification worldwide.
Sponsored listings
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 1505:1993 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Textile machinery — Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines — Definitions and range of nominal widths". This standard covers: Defines 8 critical widths to enable the specification, without ambiguity, of these essential dimensions, particularly in orders, and specifies the range of nominal width, i.e. the width of the machine elements, which house the textile fabric during a treatment process.
Defines 8 critical widths to enable the specification, without ambiguity, of these essential dimensions, particularly in orders, and specifies the range of nominal width, i.e. the width of the machine elements, which house the textile fabric during a treatment process.
ISO 1505:1993 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 59.120.50 - Dying and finishing equipment. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 1505:1993 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 1505:1982. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 1505:1993 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL ISO
STANDARD 1505
Second edition
1993-02-15
- Widths relating to
Textile machinery
dyeing and finishing machines -
Definitions and range of nominal widths
Ma Wie1 pour I’indus trie textile - Largeurs relatives aux ma tkriels de
teinture et de finissage - Dbfinitions et gamme de largeurs nominales
Reference number
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national Standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work
of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Esch member body interested in a subject for
which a technical committee has been established has the right to be
represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental
and non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(1 EC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 1505 was prepared by Technical Committee
ISO/TC 72, Textile machinery and allied machinery and accessories, Sub-
Committee SC 4, Dyeing, finishing and allied machinery and accessories.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition
(ISO 1505:1982), of which it constitutes a technical revision.
Annex A of this International Standard is for information only.
0 ISO 1993
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized in any form or
by any means, electronie or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm, without per-
mission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case Postale 56 l CH-1 211 Geneve 20 l Switzerland
Printed in Switzerland
ii
t. ’
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
ISO i505:1993(E)
Textile machinery - Widths relatbg to dyei.ng and
finishing machiries - DefinitionS and range of nominal
widths
two selvedge overhangs k/2 at the edges of the textile
1 Scope
fabric (see figure 2).
This International Standard defines the critical widths
2.5 minimum stentering width, s2 (only for ma-
relating to dyeing and finishing machines to enable
chines with tentering chains): Minimum permissible
the specification, without ambiguity, of these essen-
width, in millimetres, between stentering elements,
tial dimensions, particularly in order
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxième édition
1993-02-15
Matériel pour l’industrie textile - Largeurs
relatives aux matériels de teinture et de
finissage - Définitions et gamme de
largeurs nominales
Textile machinery - Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines -
Definitions and range of nominal widths
f hméro de référence
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique crée à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 1505 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 72, Matériel pour l’industrie textile et matériel connexe, sous-
comité SC 4, Matériel de teinture, de finissage et maténel connexe.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 1505:1982), dont elle constitue une révision technique.
L’annexe A de la présente Norme internationale est donnée uniquement
à titre d’information.
0 ISO 1993
Droits de reproduction réservés. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mecanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-121 1 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 1505:1993(F)
Matériel pour l’industrie textile - Largeurs relatives
Définitions
aux matériels de teinture et de finissage -
et gamme de largeurs nominales
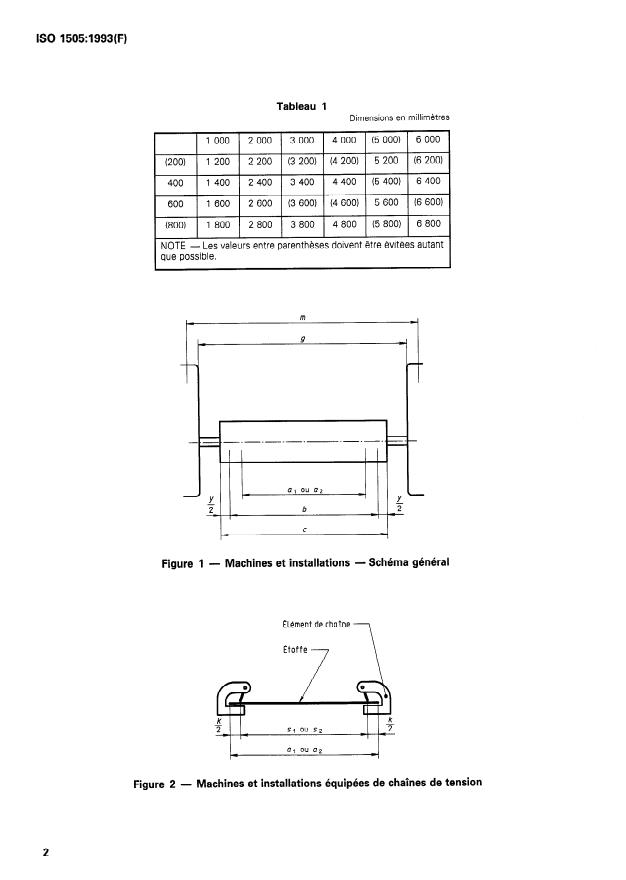
geurs de lisière k/2 à chaque extrémité de l’étoffe (voir
1 Domaine d’application
figure 2).
La présente Norme internationale définit les largeurs
les plus importantes relatives aux matériels de tein- 2.5 largeur minimale effective, s2 (seulement pour
ture et de finissage afin de permettre l’indication sans les machines équipées de chaînes de tension): Lar-
ambiguïté de ces dimensions essentielles quand cela geur minimale permise (possible), en millimètres, en-
est nécessaire, et particulièrement pour les comman- tre les éléments (de préhension) des rames fournies
de
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE
Deuxième édition
1993-02-15
Matériel pour l’industrie textile - Largeurs
relatives aux matériels de teinture et de
finissage - Définitions et gamme de
largeurs nominales
Textile machinery - Widths relating to dyeing and finishing machines -
Definitions and range of nominal widths
f hméro de référence
Avant-propos
L’ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d’organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
I’ISO). L’élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de I’ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique crée à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernemen-
tales, en liaison avec I’ISO participent également aux travaux. L’ISO colla-
bore étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI)
en ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l’approbation de 75 % au moins des co-
mités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 1505 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 72, Matériel pour l’industrie textile et matériel connexe, sous-
comité SC 4, Matériel de teinture, de finissage et maténel connexe.
Cette deuxième édition annule et remplace la première édition
(ISO 1505:1982), dont elle constitue une révision technique.
L’annexe A de la présente Norme internationale est donnée uniquement
à titre d’information.
0 ISO 1993
Droits de reproduction réservés. Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut être reproduite
ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, électronique ou mecanique,
y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l’accord écrit de l’éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case Postale 56 l CH-121 1 Genève 20 l Suisse
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO 1505:1993(F)
Matériel pour l’industrie textile - Largeurs relatives
Définitions
aux matériels de teinture et de finissage -
et gamme de largeurs nominales
geurs de lisière k/2 à chaque extrémité de l’étoffe (voir
1 Domaine d’application
figure 2).
La présente Norme internationale définit les largeurs
les plus importantes relatives aux matériels de tein- 2.5 largeur minimale effective, s2 (seulement pour
ture et de finissage afin de permettre l’indication sans les machines équipées de chaînes de tension): Lar-
ambiguïté de ces dimensions essentielles quand cela geur minimale permise (possible), en millimètres, en-
est nécessaire, et particulièrement pour les comman- tre les éléments (de préhension) des rames fournies
de
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...