ASTM D788-11
(Classification)Standard Classification System for Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Molding and Extrusion Compounds
Standard Classification System for Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Molding and Extrusion Compounds
ABSTRACT
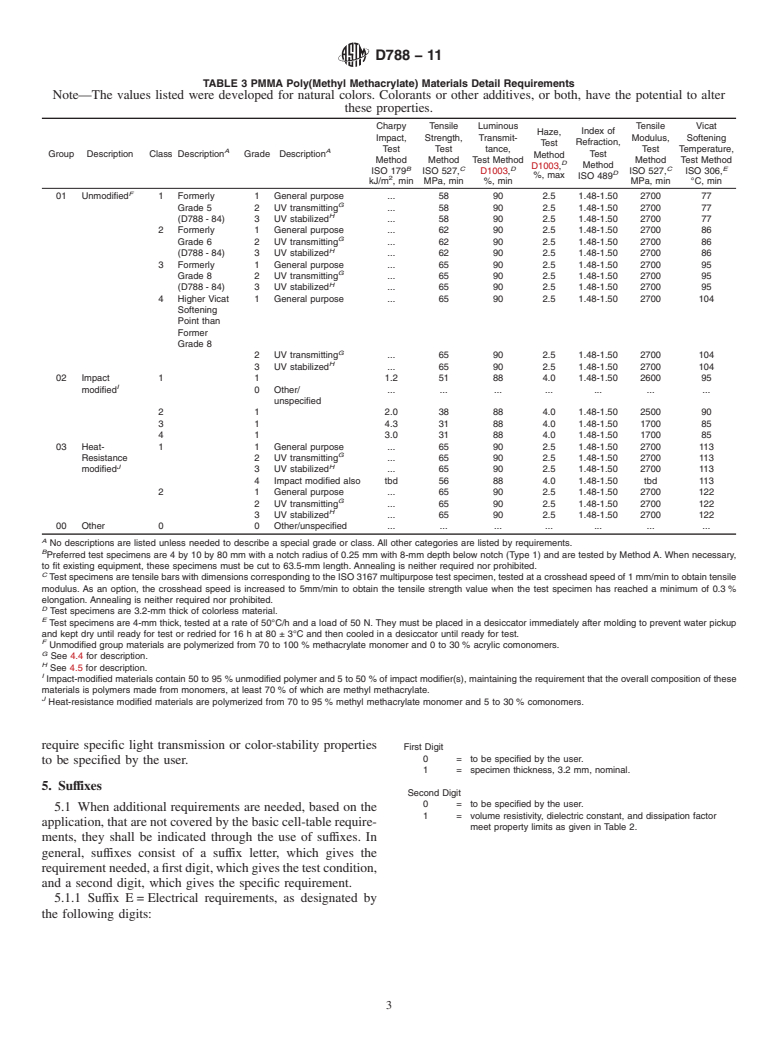
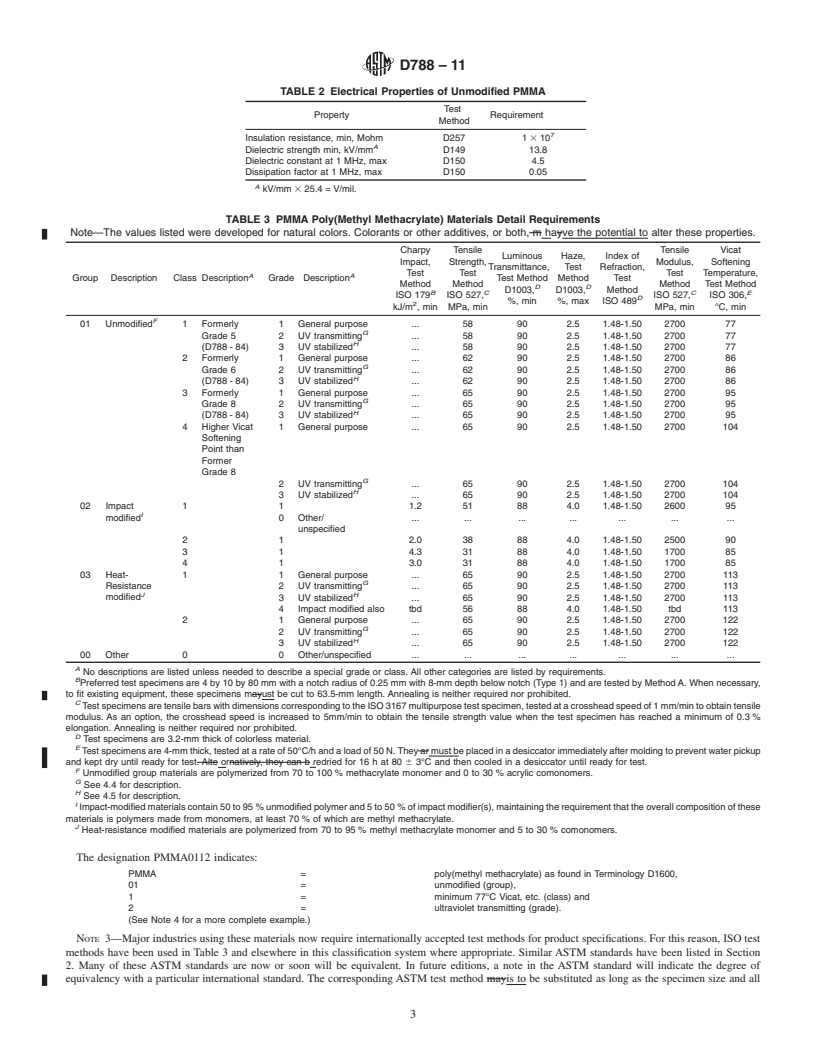
The purpose of this classification system is to provide a method of adequately identifying poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) molding and extrusion compounds. These compounds are polymers based on methyl methacrylate, and at least 70 % of the polymer shall be polymerized from methyl methacrylate. Poly(methyl methacrylate) molding and extrusion compounds are classified into groups in accordance with their composition. These groups are subdivided into classes and grades: class 1, 2, 3, and 4; grade 1 - materials used where special ultraviolet transmission, filtering, or stabilization characteristics are not required, grade 2 - materials used for those specialized applications in which the greatest amount of transmission of UV light is required, and grade 3 - materials (transparent UV stabilized or transparent UV absorbing) used when either special resistance to slight color change over long exposure times or high-intensity UV radiation is required, or when the material is required to filter out ultraviolet light. The plastics composition shall be uniform and shall conform to the requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 The purpose of this classification system is to provide a method of adequately identifying PMMA materials using a system consistent with that of Classification System D4000. It further provides a means for specifying these materials by the use of a simple line callout designation.
1.2 This classification system covers poly(methyl methacrylate) molding and extrusion compounds. These compounds are polymers based on methyl methacrylate, and at least 70 % of the polymer shall be polymerized from methyl methacrylate.
1.3 The properties in this classification system are those required to identify the compositions covered. Other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specific applications shall be described by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.4 Acrylic molding and extrusion compounds are used frequently in applications where extreme clarity and the ability to retain that clarity and color under severe weathering and other environmental exposures are of primary significance. While the test specimen properties of this document extend to the evaluation of nonvirgin materials, the user must take precautions to ensure that parts made from these materials meet the desired end-use requirements. Accordingly, this specification allows for the use of those acrylic plastic materials that can be recycled, reconstituted, and reground provided the following:
1.4.1 The requirements as stated in this specification are met,
1.4.2 The material has not been modified in any way to alter its conformance to food contact regulations or similar requirements, and
1.4.3 The requirements of the particular end-use application are met.
1.5 This classification system and subsequent line callout (specification) are not intended for the selection of materials, but only as a means to call out plastic materials to be used for the manufacture of parts. The selection of these materials is to be made by personnel with expertise in the plastics field in which the environment, inherent properties of the materials, performance of the parts, part design, manufacturing process, and economics are considered.
Note 1—This classification system is similar to ISO 8257-1:1987 in title only. The technical content is significantly different.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D788 −11
StandardClassification System for
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Molding and Extrusion
1
Compounds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D788; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.5 This classification system and subsequent line callout
(specification) are not intended for the selection of materials,
1.1 The purpose of this classification system is to provide a
but only as a means to call out plastic materials to be used for
method of adequately identifying PMMA materials using a
the manufacture of parts. The selection of these materials is to
system consistent with that of Classification System D4000.It
be made by personnel with expertise in the plastics field in
further provides a means for specifying these materials by the
which the environment, inherent properties of the materials,
use of a simple line callout designation.
performance of the parts, part design, manufacturing process,
1.2 Thisclassificationsystemcoverspoly(methylmethacry-
and economics are considered.
late) molding and extrusion compounds.These compounds are
NOTE 1—This classification system is similar to ISO 8257-1:1987 in
polymers based on methyl methacrylate, and at least 70% of
title only. The technical content is significantly different.
the polymer shall be polymerized from methyl methacrylate.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
1.3 The properties in this classification system are those
standard.
required to identify the compositions covered. Other require-
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ments necessary to identify particular characteristics important
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to specific applications shall be described by using the suffixes
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
as given in Section 5.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.4 Acrylic molding and extrusion compounds are used
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
frequentlyinapplicationswhereextremeclarityandtheability
to retain that clarity and color under severe weathering and
2. Referenced Documents
other environmental exposures are of primary significance.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
While the test specimen properties of this document extend to
D149Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
the evaluation of nonvirgin materials, the user must take
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
precautionstoensurethatpartsmadefromthesematerialsmeet
at Commercial Power Frequencies
the desired end-use requirements. Accordingly, this specifica-
D150Test Methods forAC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
tionallowsfortheuseofthoseacrylicplasticmaterialsthatcan
tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
be recycled, reconstituted, and reground provided the follow-
D257Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
ing:
Insulating Materials
1.4.1 The requirements as stated in this specification are
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
met,
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
1.4.2 Thematerialhasnotbeenmodifiedinanywaytoalter
D1003Test Method for Haze and Luminous Transmittance
its conformance to food contact regulations or similar
of Transparent Plastics
requirements, and
D1238Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics
1.4.3 Therequirementsoftheparticularend-useapplication
by Extrusion Plastometer
are met.
D1600TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
tics
1
ThisclassificationsystemisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
2
Materials. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2011. Published January 2012. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 2006 as D788-06. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D0788-11. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D788−11
TABLE 1 Transmission of Grade 2 Materials at Various TABLE 2 Electrical Properties of Unmodified PMMA
A,B
Wavelengths
Test
Property Requirement
Wavelength, nm Transmission, min, % Method
7
400 86
I
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D788–06 Designation: D788 – 11
Standard Classification System for
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Molding and Extrusion
1
Compounds
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D788; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope *
1.1 The purpose of this classification system is to provide a method of adequately identifying PMMAmaterials using a system
consistent with that of Classification System D4000. It further provides a means for specifying these materials by the use of a
simple line callout designation.
1.2 This classification system covers poly(methyl methacrylate) molding and extrusion compounds. These compounds are
polymers based on methyl methacrylate, and at least 70 % of the polymer shall be polymerized from methyl methacrylate.
1.3 The properties in this classification system are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other
Other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specific applications. Theseapplications shall be
described by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.4 Acrylic molding and extrusion compounds are used frequently in applications where extreme clarity and the ability to retain
that clarity and color under severe weathering and other environmental exposures are of primary significance. While the test
specimen properties of this document may be used to evaluateextend to the evaluation of nonvirgin materials, the user shouldmust
take precautions to ensure that parts made from these materials meet the desired end-use requirements. Accordingly, this
specification allows for the use of those acrylic plastic materials that can be recycled, reconstituted, and regroundedreground
provided the following:
1.4.1 The requirements as stated in this specification are met,
1.4.2 Thematerialhasnotbeenmodifiedinanywaytoalteritsconformancetofoodcontactregulationsorsimilarrequirements,
and
1.4.3 The requirements of the particular end-use application are met.
1.5 This classification system and subsequent line callout (specification) are not intended for the selection of materials, but only
as a means to call out plastic materials to be used for the manufacture of parts. The selection of these materials is to be made by
personnel with expertise in the plastics field in which the environment, inherent properties of the materials, performance of the
parts, part design, manufacturing process, and economics are considered.
NOTE 1—This classification system is similar to ISO 8257-1:1987 in title only. The technical content is significantly different.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at
Commercial Power Frequencies
D150 Test Methods for AC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
D257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
1
This classification system is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials.
Current edition approved Sept.Dec. 1, 2006.2011. Published September 2006.January 2012. Originally approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 20052006 as
D788 - 056. DOI: 10.1520/D0788-06.10.1520/D0788-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D788 – 11
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.