ASTM D975-04
(Specification)Standard Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
Standard Specification for Diesel Fuel Oils
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers five grades of diesel fuel oils suitable for various types of diesel engines. These grades are described as follows:
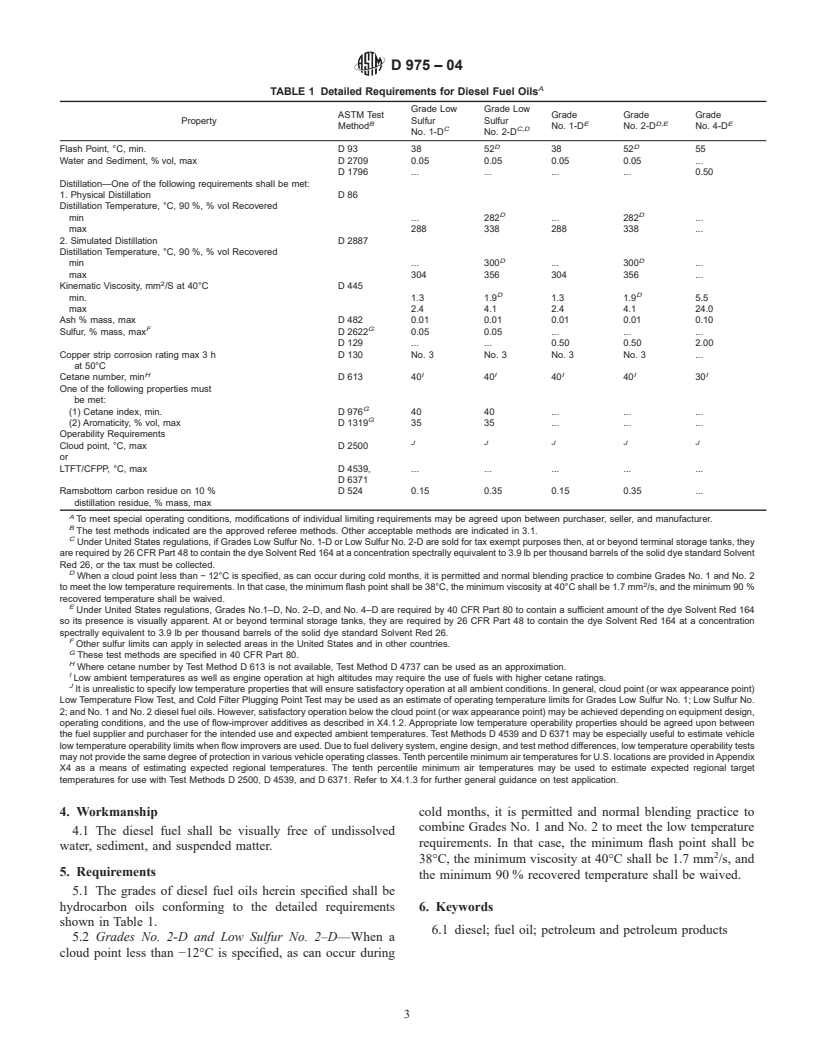
1.1.1 Grade Low Sulfur No. 1-D—A special-purpose, light distillate fuel for automotive diesel engines requiring low sulfur fuel and requiring higher volatility than that provided by Grade Low Sulfur No. 2-D.
1.1.2 Grade Low Sulfur No. 2-D—A general-purpose, middle distillate fuel for automotive diesel engines requiring low sulfur fuel. It is also suitable for use in non-automotive applications, especially in conditions of varying speed and load.
1.1.3 Grade No. 1-D—A special-purpose, light distillate fuel for automotive diesel engines in applications requiring higher volatility than that provided by Grade No. 2-D fuels.
1.1.4 Grade No. 2-D—A general-purpose, middle distillate fuel for automotive diesel engines, which is also suitable for use in non-automotive applications, especially in conditions of frequently varying speed and load.
1.1.5 Grade No. 4-D—A heavy distillate fuel, or a blend of distillate and residual oil, for low- and medium-speed diesel engines in non-automotive applications involving predominantly constant speed and load.
Note 1—A more detailed description of the grades of diesel fuel oils is given in X1.2.
1.2 This specification, unless otherwise provided by agreement between the purchaser and the supplier, prescribes the required properties of diesel fuels at the time and place of delivery.
1.2.1 Nothing in this specification shall preclude observance of federal, state, or local regulations which may be more restrictive.
Note 2—The generation and dissipation of static electricity can create problems in the handling of distillate diesel fuel oils. For more information on the subject, see Guide D 4865.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation: D 975 – 04
Standard Specification for
1
Diesel Fuel Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 975; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
problems in the handling of distillate diesel fuel oils. For more informa-
1. Scope
tion on the subject, see Guide D 4865.
1.1 This specification covers five grades of diesel fuel oils
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
suitable for various types of diesel engines. These grades are
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
described as follows:
only.
1.1.1 Grade Low Sulfur No. 1-D—A special-purpose, light
distillate fuel for automotive diesel engines requiring low
2. Referenced Documents
sulfur fuel and requiring higher volatility than that provided by
3
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Grade Low Sulfur No. 2-D.
D 56 Test Method for Flash Point by Tag Closed Tester
1.1.2 Grade Low Sulfur No. 2-D—A general-purpose,
D 86 Test Method for Distillation of Petroleum Products at
middle distillate fuel for automotive diesel engines requiring
Atmospheric Pressure
low sulfur fuel. It is also suitable for use in non-automotive
D 93 Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens
applications, especially in conditions of varying speed and
2
Closed Cup Tester
load.
D 97 Test Method for Pour Point of Petroleum Products
1.1.3 Grade No. 1-D—A special-purpose, light distillate
D 129 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products (Gen-
fuel for automotive diesel engines in applications requiring
eral Bomb Method)
higher volatility than that provided by Grade No. 2-D fuels.
D 130 Test Method for Detection of Copper Corrosion from
1.1.4 Grade No. 2-D—A general-purpose, middle distillate
Petroleum Products by the Copper Strip Tarnish Test
fuel for automotive diesel engines, which is also suitable for
D 445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
use in non-automotive applications, especially in conditions of
and Opaque Liquids (and the Calculation of Dynamic
frequently varying speed and load.
Viscosity)
1.1.5 Grade No. 4-D—A heavy distillate fuel, or a blend of
D 482 Test Method for Ash from Petroleum Products
distillate and residual oil, for low- and medium-speed diesel
D 524 Test Method for Ramsbottom Carbon Residue of
engines in non-automotive applications involving predomi-
Petroleum Products
nantly constant speed and load.
D 613 Test Method for Cetane Number of Diesel Fuel Oil
NOTE 1—A more detailed description of the grades of diesel fuel oils is
D 976 Test Methods for Calculated Cetane Index of Distil-
given in X1.2.
late Fuels
1.2 This specification, unless otherwise provided by agree-
D 1266 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products
ment between the purchaser and the supplier, prescribes the
(Lamp Method)
required properties of diesel fuels at the time and place of
D 1319 Test Method for Hydrocarbon Types in Liquid
delivery.
Petroleum Products by Fluorescent Indicator Adsorption
1.2.1 Nothing in this specification shall preclude observance
D 1500 Test Method for ASTM Color of Petroleum Prod-
of federal, state, or local regulations which may be more
ucts (ASTM Color Scale)
restrictive.
D 1552 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products
(High-Temperature Method)
NOTE 2—The generation and dissipation of static electricity can create
D 1796 Test Method for Water and Sediment in Fuel Oils by
the Centrifuge Method (Laboratory Procedure)
1
D 2274 Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Distillate
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.E0 on Burner, Diesel, Non–Aviation Gas Turbine, and Marine Fuels.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2004. Published March 2004. Originally
3
approved in 1948. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D 975–03. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
2
This fuel complies with 40 CFR Part 80—Regulation of Fuels and Fuel contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Additives: Fuel Quality Regulations for Highway Diesel Fuel Sold in 1993 and Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Later Calendar Years. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D975–04
Fuel Oil (Accelerated Method) IP 309 Diesel and Domes
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.