ASTM C417-21
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Unfired Monolithic Refractories
Standard Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Unfired Monolithic Refractories
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories is a property required for selecting their thermal transmission characteristics. Users select monolithic refractories to provide specified conditions of heat loss and cold face temperature, without exceeding the temperature limitation of the monolithic refractory. This test method establishes placement of thermocouples and positioning of test specimens in the calorimeter.
3.2 This procedure must be used with Test Method C201 and requires a large thermal gradient and steady-state conditions. The results are based upon a mean temperature.
3.3 The data from this test method are suitable for specification acceptance, estimating heat loss and surface temperature, and the design of multi-layer refractory construction.
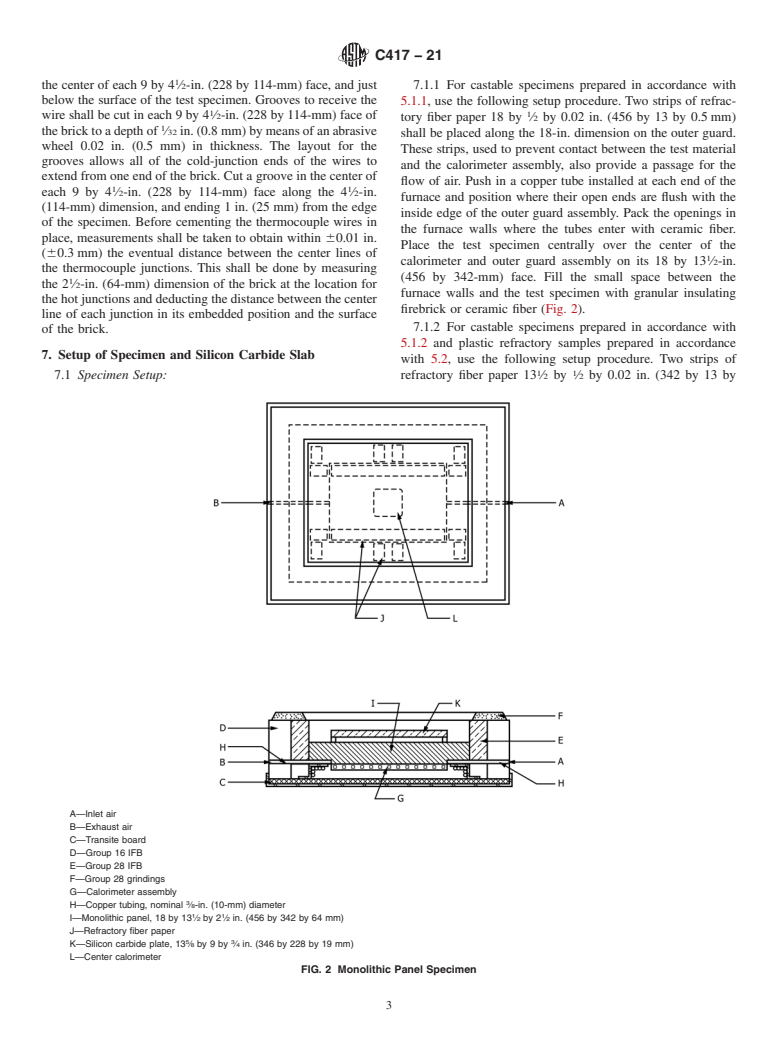
3.4 The use of these data requires consideration of the actual application environment and conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method supplements Test Method C201, and shall be used in conjunction with that test method for determining the thermal conductivity of unfired monolithic refractories.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:C417 −21
Standard Test Method for
1
Thermal Conductivity of Unfired Monolithic Refractories
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C417; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Significance and Use
3.1 The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories is a
1.1 This test method supplements Test Method C201, and
shall be used in conjunction with that test method for deter- property required for selecting their thermal transmission
characteristics. Users select monolithic refractories to provide
mining the thermal conductivity of unfired monolithic refrac-
tories. specified conditions of heat loss and cold face temperature,
without exceeding the temperature limitation of the monolithic
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
refractory. This test method establishes placement of thermo-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
couples and positioning of test specimens in the calorimeter.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.2 This procedure must be used with Test Method C201
and are not considered standard.
and requires a large thermal gradient and steady-state condi-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
tions. The results are based upon a mean temperature.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.3 The data from this test method are suitable for specifi-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- cation acceptance, estimating heat loss and surface
temperature, and the design of multi-layer refractory construc-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tion.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.4 Theuseofthesedatarequiresconsiderationoftheactual
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
application environment and conditions.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4. Apparatus
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4.1 The apparatus shall consist of that described in Test
Method C201, modified as in 4.2 of this test method, with the
2. Referenced Documents
addition of thermocouples and refractory fiber paper, as de-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
scribed in Sections 6 and 7.
C182 Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Insulating
4.2 The furnace shall be modified by drilling a nominal
Firebrick
3
⁄8-in. (10-mm) diameter hole (Fig. 1) through the insulating
C201 Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Refractories
firebrick in the furnace wall at each end of the center line of the
C862 Practice for Preparing Refractory Concrete Specimens
18-in. (456-mm) dimension of the furnace cavity. These holes
by Casting
shall be positioned so that the length of the hole will be parallel
C1054 Practice for Pressing and Drying Refractory Plastic
to the calorimeter surface and the bottom of the hole will
and Ramming Mix Specimens
coincide with the surface of the calorimeter. Copper tubing
E220 Test Method for Calibration of Thermocouples By
shallbeplacedwithineachholesothatacompressedairsource
Comparison Techniques
can be attached to one side and flexible leads to a flowmeter
can be attached to the other.
4.3 A compressed air supply and flowmeter for air.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C08 on
Refractoriesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C08.02 on Thermal
Properties.
5. Test Specimens
Current edition approved April 1, 2021. Published April 2021. Originally
5.1 Castable Refractories—The test specimens may consist
approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as C417 – 05 (2015).
1 1
DOI: 10.1520/C0417-21.
of either a panel 18 by 13 ⁄2 by 2 ⁄2 in. (456 by 342 by 64 mm),
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1 1
or an assembly of three straights 9 by 4 ⁄2 by 2 ⁄2 in. (228 by
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1 1
114 by 64 mm) and six soaps 9 by 2 ⁄4 by 2 ⁄2 in. (228 by 57
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. by 64 mm). These specimens shall be prepared as in one of the
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959.
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C417 − 05 (Reapproved 2015) C417 − 21
Standard Test Method for
1
Thermal Conductivity of Unfired Monolithic Refractories
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C417; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method supplements Test Method C201, and shall be used in conjunction with that test method for determining the
thermal conductivity of unfired monolithic refractories.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C182 Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Insulating Firebrick
C201 Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Refractories
C862 Practice for Preparing Refractory Concrete Specimens by Casting
C1054 Practice for Pressing and Drying Refractory Plastic and Ramming Mix Specimens
E220 Test Method for Calibration of Thermocouples By Comparison Techniques
3. Significance and Use
3.1 The thermal conductivity of monolithic refractories is a property required for selecting their thermal transmission
characteristics. Users select monolithic refractories to provide specified conditions of heat loss and cold face temperature, without
exceeding the temperature limitation of the monolithic refractory. This test method establishes placement of thermocouples and
positioning of test specimens in the calorimeter.
3.2 This procedure must be used with Test Method C201 and requires a large thermal gradient and steady state steady-state
conditions. The results are based upon a mean temperature.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C08 on Refractoriesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C08.02 on Thermal Properties.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2015April 1, 2021. Published October 2015April 2021. Originally approved in 1958. Last previous edition approved in 20102015 as
ϵ1
C417 – 05 (2015).(2010) . DOI: 10.1520/C0417-05R15.10.1520/C0417-21.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C417 − 21
3.3 The data from this test method are suitable for specification acceptance, estimating heat loss and surface temperature, and the
design of multi-layer refractory construction.
3.4 The use of these data requires consideration of the actual application environment and conditions.
4. Apparatus
4.1 The apparatus shall be in accordance with consist of that described in Test Method C201, modified as in 4.2 of this test method,
with the addition of thermocouples and refractory fiber paper, as described in Sections 6 and 7.
3
4.2 The furnace shall be modified by drilling a nominal ⁄8-in. (10-mm) diameter hole (Fig. 1) through the insulating firebrick in
the furnace wall at each end of the center line of the 18-in. (456-mm) dimension of the furnace cavity. These holes shall be
positioned so that the length of the hole will be parallel to the calorimeter surface and the bottom of the hole will coincide with
the surface of the calorimeter. Copper tubing shall be placed within each hole so that a compressed-air compressed air source can
be attached to one side and flexible leads to a flowmeter can be attached to the other.
4.3 A compressed-air compressed ai
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.