ASTM D5801-95(2006)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
Standard Test Method for Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is useful in confirming that an asphalt cement has been modified with a material that provides a significant elastomeric component. Elastomer modified asphalts can be characterized by their ability to be stretched to a large elongation while at the same time resisting further stretching. Toughness and tenacity are two parameters for measuring this ability.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for measuring the toughness and tenacity of bituminous materials. Typically, the test method has been used to characterize elastomer modified asphalts, although values for toughness and tenacity may be obtained for any type of polymer-modified or non-modified asphalt.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.2 The values given in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in inch-pound units in parentheses are for informational purposes only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D5801 − 95(Reapproved 2006)
Standard Test Method for
Toughness and Tenacity of Bituminous Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5801; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—Added Note 3 editorially in December 2006.
1. Scope sample. The test is run at room temperature (25 6 3°C [77 6
5°F]), after the sample has been subjected to a specified
1.1 This test method describes the procedure for measuring
temperature history.
the toughness and tenacity of bituminous materials. Typically,
the test method has been used to characterize elastomer 3.2 Toughness is defined in this procedure as the total work
modified asphalts, although values for toughness and tenacity required to completely separate the tension head from the
may be obtained for any type of polymer-modified or non- sample under the specified test conditions. Tenacity is a
modified asphalt. measure of the increasing force as the sample is stretched past
the initial peak, and may indicate the type and amount of
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
polymer used to modify the asphalt. It is defined as the work
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
required to stretch the material after the initial resistance is
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
overcome.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4. Significance and Use
1.3 The values given in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in inch-pound units in parentheses 4.1 This test method is useful in confirming that an asphalt
are for informational purposes only. cement has been modified with a material that provides a
significant elastomeric component. Elastomer modified as-
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
phalts can be characterized by their ability to be stretched to a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
large elongation while at the same time resisting further
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
stretching. Toughness and tenacity are two parameters for
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
measuring this ability.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Apparatus
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 Sample Container—A metal, cylindrical, flat bottom
2.1 ASTM Standards:
container with a nominal inside diameter of 55 mm (2 ⁄8 in.)
D5 Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials
andadepthof35mm(1 ⁄8in.)shallbeusedtoholdthesample.
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
Containers known as tin boxes or seamless ointment boxes
with a 3-oz capacity meet these requirements.
3. Summary of Test Method
5.2 Tension Head—The tension head shall consist of a
3.1 Atensionheadofspecifiedsizeandshapeispulledfrom
polished metal, hemispherical head with an 11 mm ( ⁄16 in.)
an asphalt sample at a rate of 50 cm/min (20 in./min). A
radius, which is integrally connected to a 6.4 mm ( ⁄4 in.)
continuous record of the force versus elongation curve is made
diameter stem approximately 33 mm (1 ⁄16 in.) long. The stem
and used to calculate the toughness and the tenacity of the
shall be threaded and fitted with a knurled lowering screw to
allow for accurate adjustment of the tension head height in the
sample container. The stem of the tension head shall be fitted
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road
with a small pin to prevent twisting of the head while adjusting
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.44 on
Rheological Tests.
the height. Dimensions of the tension head are shown in Fig. 1.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2006. Published December 2006. Originally
approved as Proposal P 243 in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as NOTE 1—Brass and stainless steel are acceptable metals for construct-
D5801 – 95 (2001). DOI: 10.1520/D5801-95R06E01.
ing tension heads. Aluminum scratches easily and steel rusts, so these
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
metals should not be used.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
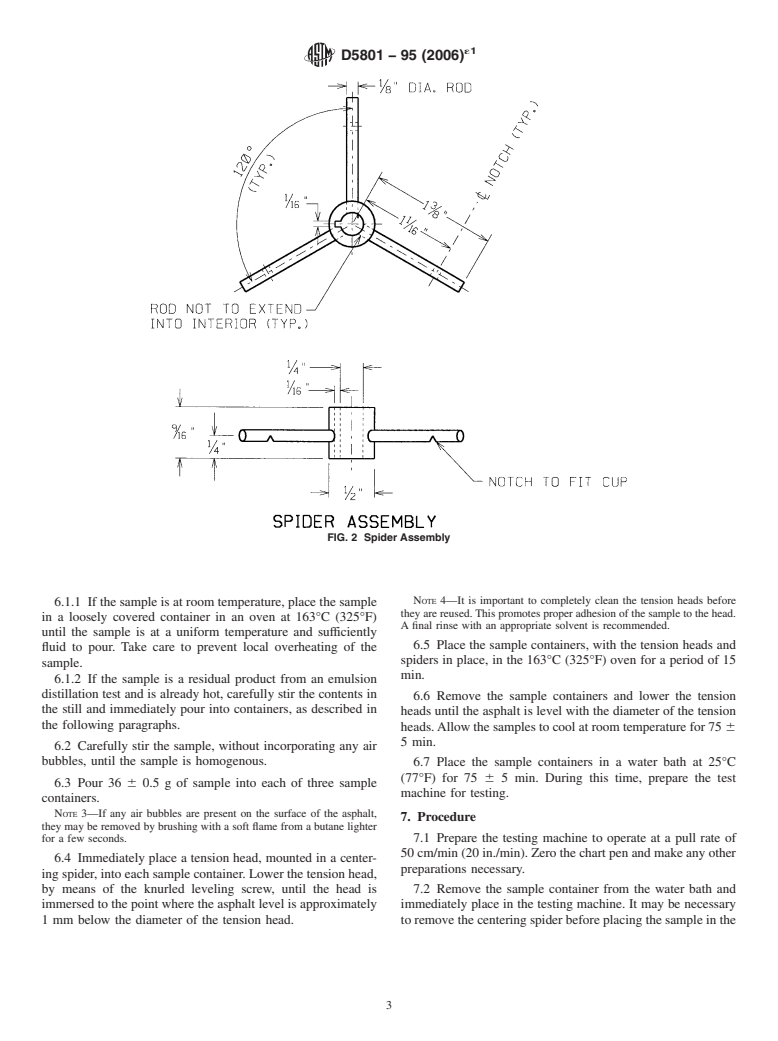
5.3 Spider—Thesupportforthetensionheadshallconsistof
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. a cylindrical center section through which the stem of the
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
D5801 − 95 (2006)
FIG. 1 Tension Head and Lowering Screw
tension head may freely move parallel to the axis of the 5.5 Water Bath—A bath capable of maintaining a tempera-
cylinder. The inner wall of the cylinder shall be grooved to ture of 25 6 0.1°C (77 6 0.18°F) is required. The bath shall
receive the pin mounted on the stem of the tension head. The have a perforated shelf supported in a position not less than 50
spider cylinder shall be fitted with three arms, equally spaced mm (2 in.) from the bottom and not less than 100 mm (4 in.)
at 120 degrees, extending from the center and notched to below the liquid level.
receive the lip of the sample container, thereby centering the
5.6 Oven—A gravity convection oven capable of maintain-
spider and tension head in the sample container. Details of the
ing a temperature of 163 6 5.5°C (325 6 10°F) shall be used
spider construction are shown in Fig. 2.
to heat the samples.
5.4 Testing Machine—Any tensile tester capable of pulling
5.7 Thermometer—Acalibratedthermometerhavingarange
the tension head at a uniform rate of 50 cm/min (20 in./min),
as shown as follows and conforming to the requirements
and recording the force versus elongation curve, may be used.
prescribed in Specification E1.
The accuracy of the pull rate shall be 62 % or better. The
Temperature Range ASTM Thermometer Number
maximum load capacity shall be at least 45 kg (100 lb). If
−8 to 32°C 63C
polymer modified asphalts are to be tested after aging in the
18 to 89°F 63F
thin film oven or the rolling thin film oven, higher load
NOTE 2—In those cases where the samples are conditioned in the
capacities are needed.Amaximum load capacity of 90 kg (200
standard penetration bath, the thermometer as prescribed for Test Method
lb) is suggested.
D5 may be substituted in place of the above.
5.4.1 The tensile tester must be equipped to hold the sample
container firmly in place while the tension head is pulled away.
6. Sample Preparation
The details of this sample holder will vary with the type of
tester used. The tester must have a minimum effective pull 6.1 Bring the sample to a temperature where it is sufficiently
length of 61 cm (24 in.) after installing the sample holder. fluid to pour, as described in the following paragraphs.
´1
D5801 − 95 (2006)
FIG. 2 Spider Assembly
NOTE 4—It is
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.