ASTM E202-12
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Ethylene Glycols and Propylene Glycols
Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Ethylene Glycols and Propylene Glycols
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
These test methods measure certain chemical and physical properties of ethylene glycols and propylene glycols and may be used to determine compliance with specification in which limits are established for these properties. For those tests that use the procedure of another ASTM test method, that test method should be consulted for additional information on the significance and use of that test.
Alternative test methods and technology for several of the methods can be found in the Appendix. Use of these methods is optional and individuals using the alternative methods should assure themselves that the method is sufficient and appropriate for the application. Precision data presented in this standard is only for the original test methods listed.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical and physical analysis of the commonly available grades of ethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and dipropylene glycol. The key sections appear in the following order:
Sections Purity of Reagents 4 Specific Gravity 6-8 Distillation Range 9-11 Acidity12-14 Water15-17 Iron18-20 Color21-23 Gas Chromatographic Analysis24-26 Alternative Test MethodsAppendix X1
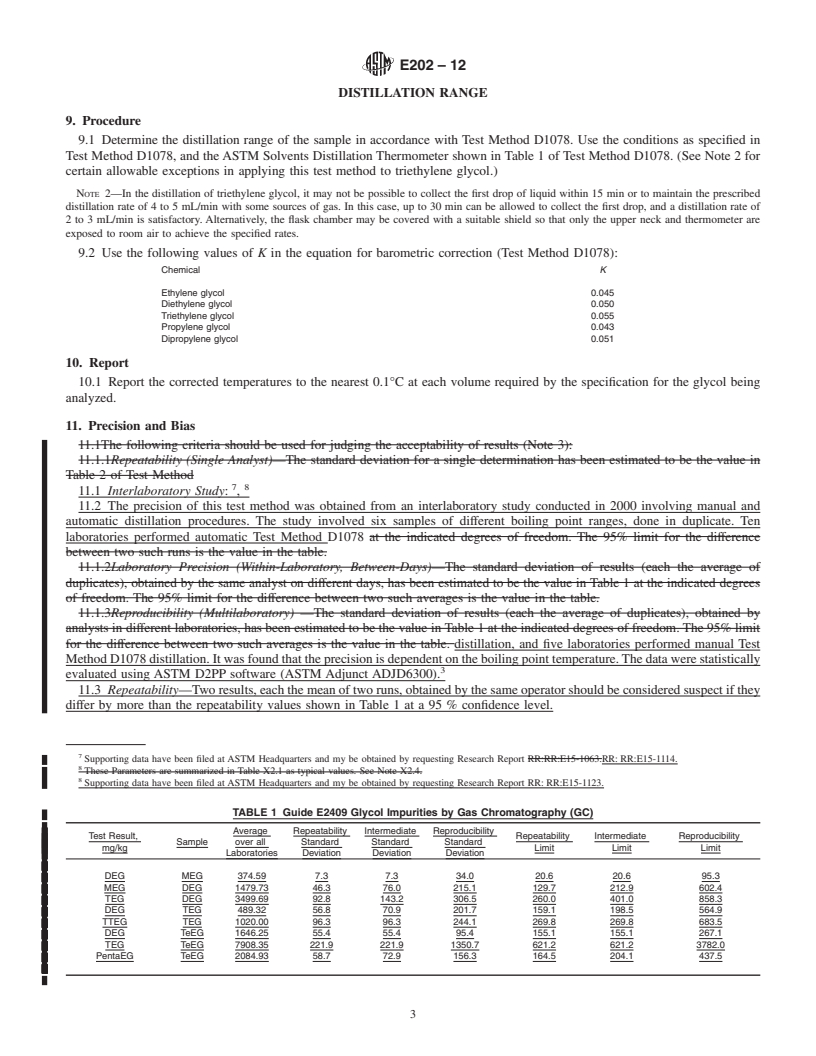
1.2 Review the current appropriate Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid procedures, and safety precautions.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard with the exception of foot-pound for apparatus descriptions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E202 − 12
Standard Test Methods for
1
Analysis of Ethylene Glycols and Propylene Glycols
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E202; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* D1078 Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Or-
ganic Liquids
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical and physical
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
analysis of the commonly available grades of ethylene glycol,
D1209 Test Method for Color of Clear Liquids (Platinum-
diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and
Cobalt Scale)
dipropylene glycol. The key sections appear in the following
D1613 Test Method for Acidity in Volatile Solvents and
order:
Chemical Intermediates Used in Paint, Varnish, Lacquer,
Sections
and Related Products
Purity of Reagents 4 D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API
Specific Gravity 6–8
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
Distillation Range 9–11
D5386 Test Method for Color of Liquids Using Tristimulus
Acidity 12–14
Water 15–17 Colorimetry
Iron 18–20
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
Color 21–23
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
Gas Chromatographic Analysis 24–26
3
Alternative Test Methods Appendix
cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
X1
E203 Test Method for Water Using Volumetric Karl Fischer
1.2 Review the current appropriate Material Safety Data
Titration
Sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity,
E394 Test Method for Iron in Trace Quantities Using the
first aid procedures, and safety precautions.
1,10-Phenanthroline Method
E611 Test Methods for Low Concentrations of Diethlyene
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Glycol in Ethylene Glycol by Gas Chromatography
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
E1064 Test Method for Water in Organic Liquids by Coulo-
standard with the exception of foot-pound for apparatus
metric Karl Fischer Titration
descriptions.
E1615 Test Method for Iron in Trace Quantities Using the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
FerroZine Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
E2409 TestMethodforGlycolImpuritiesinMono-,Di-,Tri-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
and Tetraethylene Glycol and in Mono- and Dipropylene
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Glycol(Gas Chromatographic Method)
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
E2679 Test Method for Acidity in Mono-, Di-, Tri- and
Tetraethylene Glycol byNon-Aqueous Potentiometric
2. Referenced Documents
Titration
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
D891 TestMethodsforSpecificGravity,Apparent,ofLiquid
AdjunctADJD6300 Determination of Precision and Bias for
Industrial Chemicals
Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubri-
4
cants
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and are the direct responsibility of 3. Significance and Use
Subcommittee D16.15 on Industrial and Specialty General Standards.
3.1 These test methods measure certain chemical and physi-
Current edition approved April 1, 2012. Published May 2012. Originally
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as E202–10. DOI: cal properties of ethylene glycols and propylene glycols and
10.1520/E0202-12.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
3
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on www.astm.org.
4
the ASTM website. Available from ASTM International Headquarters.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E202 − 12
may be used to determine compliance with specification in 8.1.1 Repeatability (Single Analyst)—The standard devia-
whichlimitsareestablishedfortheseproperties.Forthosetests tion for a single determination has been estimated to be
that use the procedure of another ASTM test method, that test 0.0000651 unit at 96 dF. The 95 % limit for the difference
method should be consulted for additional information on the between two such runs is 0.0002 unit.
significance and use of that test. 8.1.2
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:E202–10 Designation:E202–12
Standard Test Methods for
1
Analysis of Ethylene Glycols and Propylene Glycols
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E202; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 These test methods cover the chemical and physical analysis of the commonly available grades of ethylene glycol,
diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and dipropylene glycol. The key sections appear in the following order:
Sections
Purity of Reagents 4
Specific Gravity 6-8
Distillation Range 9-11
Acidity 12-14
Water 15-17
Iron 18-20
Color 21-23
Gas Chromatographic Analysis 24-26
Alternative Test Methods Appendix
X1
1.2 Review the current appropriate Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for detailed information concerning toxicity, first aid
procedures, and safety precautions.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard
with the exception of foot-pound for apparatus descriptions.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D891 Test Methods for Specific Gravity, Apparent, of Liquid Industrial Chemicals
D1078 Test Method for Distillation Range of Volatile Organic Liquids
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1209 Test Method for Color of Clear Liquids (Platinum-Cobalt Scale)
D1613 Test Method forAcidity in Volatile Solvents and Chemical Intermediates Used in Paint, Varnish, Lacquer, and Related
Products
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D5386 Test Method for Color of Liquids Using Tristimulus Colorimetry
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision ofASTM Methods forAnalysis andTesting of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
E203 Test Method for Water Using Volumetric Karl Fischer Titration
E394 Test Method for Iron in Trace Quantities Using the 1,10-Phenanthroline Method
E611 Test Methods for Low Concentrations of Diethlyene Glycol in Ethylene Glycol by Gas Chromatography
E1064 Test Method for Water in Organic Liquids by Coulometric Karl Fischer Titration
E1615 Test Method for Iron in Trace Quantities Using the FerroZine Method
E2409 Test Method for Glycol Impurities in Mono-, Di-, Tri- and Tetraethylene Glycol (Gas Chromatographic Method)
E2679 Test Method for Acidity in Mono-, Di-, Tri- and Tetraethylene Glycol byNon-Aqueous Potentiometric Titration
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee E15 on Industrial and Specialty Chemicals and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E15.01
on General Standards.
Current edition approved Aug.April 1, 2010.2012. Published September 2010.May 2012. Originally approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 20092010 as
E202–09.E202–10. DOI: 10.1520/E0202-102.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E202–12
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
3
Adjunct ADJD6300 Determination of Precision and Bias for Use in Test Methods for Petroleum Products and Lubricants
3. Significance and Use
3.1 These test methods measure certain chemical and physical properties of ethylene glycols and propylene glycols and may
be used to determine compliance with specification in which limits are established for these properties. For those tests that use the
procedure of another ASTM test method, that test method should be consulted for additional information on the significance and
use of that test.
3.2 Alternative test methods and technology for several of the methods can be found in the Appendix. Use of these
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.