ASTM F1005-91(2013)
(Practice)Standard Practice for HVAC Duct Shapes; Identification and Description of Design Configuration
Standard Practice for HVAC Duct Shapes; Identification and Description of Design Configuration
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 Standard nomenclature shall be used to facilitate communication between designers, suppliers, and users of HVAC ventilation ductwork components.
3.2 Standard design parameters shall be used to define ventilation ductwork shapes.
3.3 Standard variables for design parameters (see 2.2) are useful in writing CAD/CAM software for automatic fabrication of ventilation ductwork shapes.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the identification of design configurations and descriptive nomenclature for sheetmetal HVAC ductwork shapes frequently used in shipbuilding. This practice also covers parametric dimensions of these shapes. (See Table 1.)TABLE 1 HVAC Standard Nomenclature and Numbering System
1. Straight:
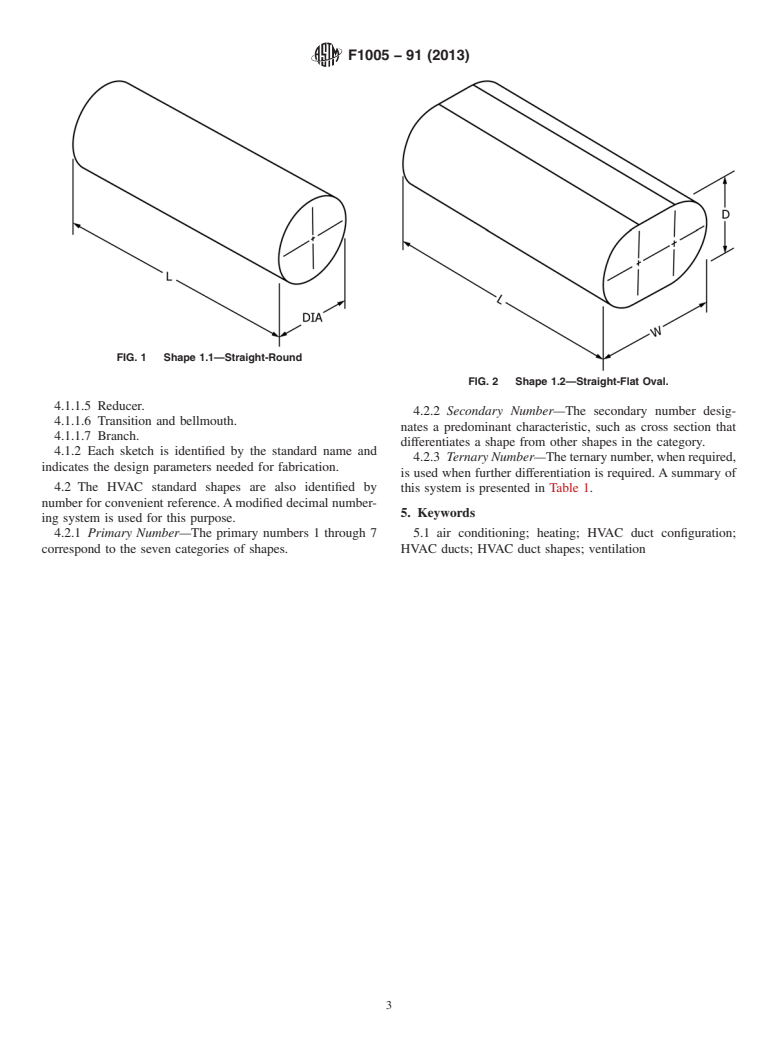
1.1 Straight-round
1.2 Straight-flat oval
1.3 Straight-rectangular
2. Offset:
2.1 Offset-round
2.2.1 Offset-flat oval-long axis
2.2.2 Offset-flat oval-short axis
2.3.1 Offset-rectangular-without splitters
2.3.2 Offset-rectangular-with splitters
2.4.1 Offset-ogee-without splitters
2.4.2 Offset-ogee-with splitters
2.5.1 Offset-rectangular reducing-without
splitters
2.5.2 Offset-rectangular reducing-with splitters
3. Elbow:
3.1 Elbow-round
3.2.1 Elbow-flat oval-long axis
3.2.2 Elbow-flat oval-short axis
3.3.1 Elbow-rectangular-without splitters
3.3.2 Elbow-rectangular-with splitters
3.4.1 Elbow-rectangular reducing-without
splitters
3.4.2 Elbow-rectangular reducing-with splitters
3.5.1 Elbow-rectangular transition-without
splitters
3.5.2 Elbow-rectangular transition-with splitters
4. Vaned Turn:
4.1 Vaned turn
5. Reducer:
5.1 Reducer-round
5.2 Reducer-flat oval
5.3 Reducer-rectangular
6. Transition and Bellmouth:
6.1 Transition-flat oval to round
6.2 Transition-rectangular to round
6.3 Transition-rectangular to flat oval
6.4 Transition-rectangular to radius corner
6.5 Transition-radius corner to flat oval
6.6.1 Bellmouth-round
6.6.2 Bellmouth-rectangular
7. Branch:
7.1.1 Branch-round-on equal diameter round
7.1.2 Branch-round-on larger diameter round
7.1.3 Branch-round-on round reducer
7.1.4 Branch-round-on rectangular straight
7.1.5 Branch-round-on rectangular reducer
7.1.6 Branch-round “Y”
7.1.7 Branch-rectangular to round-“Y”
7.2.1 Branch-rectangular-on rectangular straight
7.2.2 Branch-rectangular-on rectangular reducer
1.2 This practice does not cover the location of seams or joints within a shape or the method of joining shapes together.
1.3 Since this practice is not measurement sensitive, it is applicable whether inch-pound or SI metric dimensions are used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F1005 −91 (Reapproved 2013) An American National Standard
Standard Practice for
HVAC Duct Shapes; Identification and Description of Design
Configuration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1005; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.1.6 ogee—a smoothly curved type of offset. The inside
curve of each end is tangent to the outside curve of the other
1.1 This practice covers the identification of design configu-
end.
rations and descriptive nomenclature for sheetmetal HVAC
2.1.7 radius corner—cross section that is generally
ductwork shapes frequently used in shipbuilding. This practice
rectangular, but with the corners softened to a radius.
also covers parametric dimensions of these shapes. (See Table
1.)
2.1.8 rectangular—rectangular or square cross section.
1.2 This practice does not cover the location of seams or
2.1.9 reducer—a fitting that changes the size but not the
joints within a shape or the method of joining shapes together.
cross-section type of duct.
1.3 Since this practice is not measurement sensitive, it is 2.1.10 round—circular cross section.
applicable whether inch-pound or SI metric dimensions are
2.1.11 shortaxisofflatoval—curved so that the flat sides of
used.
the flat oval correspond to the curve.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.1.12 splitter—internal part of some elbows and offsets;
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
sometimes required in diverging transitions. Used to provide
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
more uniform velocity and distribution of air flow.The number
priate safety, health and environmental practices and deter-
and location of splitters is determined by calculation or from a
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
nomograph.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
2.1.13 straight—duct that remains constant in cross section
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
and size throughout its length.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
2.1.14 throat—wrapper around the inside of a fitting.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
2.1.15 transition—fitting that changes the cross-section type
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. of the duct.
2.1.16 vane—internal part of vaned turns. Used to provide
2. Terminology
more uniform velocity of air flow. Configuration, number, and
2.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
location of vanes is determined from drawing, NAVSHIPS No.
2.1.1 branch—portion of a duct system connection to a
S3801-385260. The direction of airflow must be marked on
main duct.
vaned turns.
2.1.2 elbow—a fitting used to change direction of air flow.
2.1.17 vaned turn—a fitting containing vanes that is used to
change the direction of air flow.
2.1.3 flat oval—cross section that has flat sides and semicir-
cular ends.
2.2 Variables Specific to This Standard:
A—Angle. Included angle of an elbow, branch, vaned turn,
2.1.4 longaxis of flat oval curved so that the flat sides of the
or slant-top fitting.
flat oval remain in a plane.
AI—Air In indicates the length of the straight portion of a
2.1.5 offset—fitting that changes the location of the duct
vaned turn in the “air in-flow” side.
with the line of the duct remaining parallel.
AO—Air Out indicates the length of the straight portion of
a vaned turn on the “air out-flow” side.
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F25 on Ships and
Marine Technology and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F25.11 on
Machinery and Piping Systems. Drawing: Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA) NAVSHIPS S3801-
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013. Published October 2013. Originally 385260 Vanes Channels Ventilation Vane, available from Commander, Portsmouth
approved in 1986. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as F1005 – 91 (2007). Naval Shipyard, Naval Engineering Drawing Support Activity, Code 202.2,
DOI: 10.1520/F1005-91R13. Portsmouth, NH 03804-5000.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1005−91 (2013)
TABLE 1 HVAC Standard Nomenclature and Numbering System
1.2—Minor length of a Y branch.
1. Straight: O—Offset in one direction.
1.1 Straight-round
R—Radius of a bellmouth.
1.2 Straight-flat oval
RC—Radius corner.
1.3 Straight-rectangular
2. Offset: RV1—Radius of first splitter at V extension.
2.1 Offset-round
RV2—Radius of second splitter at V extension.
2.2.1 Offset-flat oval-long axis
RV3—Radius of third splitter at V extension.
2.2.2 Offset-flat oval-short axis
2.3.1 Offset-rectangular-without splitters
RZ1—Radius of first splitter at Z extension.
2.3.2 Offset-rectangular-with splitters
RZ2—Radius of second splitter at Z extension.
2.4.1 Offset-ogee-without splitters
RZ3—Radius of third splitter at Z extension.
2.4.2 Offset-ogee-with splitters
2.5.1 Offset-rectangular reducing-without R1—Radius of first splitter.
splitters
R2—Radius of second splitter.
2.5.2 Offset-rectangular reducing-with splitters
R3—Radius of third splitter.
3. Elbow:
3.1 Elbow-round
S1—Distance of first splitter from the outside curve of an
3.2.1 Elbow-flat oval-long axis
ogee offset.
3.2.2 Elbow-flat oval-short axis
S2—Distance of second splitter from the outside curve of
3.3.1 Elbow-rectangular-without splitters
3.3.2 Elbow-rectangular-with splitters
an ogee offset.
3.4.1 Elbow-rectangular reducing-without
S3—Distance of third splitter from the outside curve of an
splitters
ogee offset.
3.4.2 Elbow-rectangular reducing-with splitters
3.5.1 Elbow-rectangular transition-without
TR—Throat radius is the radius of the inside surface of an
splitters
elbow or offset. Normally TR is equal to the width (of a
3.5.2 Elbow-rectangular transition-with splitters
rectangular elbow).
4. Vaned Turn:
4.1 Vaned turn
TR1—Major throat radius of a reducing offset.
5. Reducer:
TR2—Minor throat radius of a reducing offset.
5.1 Reducer-round
V—Extension on one end of a part, opposite from Z.
5.2 Reducer-flat oval
5.3 Reducer-rectangular
W—Width of a part.
6. Transition and Bellmouth:
WB—Width of a branch.
6.1 Transition-flat oval to round
W1—Major width of a part.
6.2 Transition-rectangular to round
6.3 Transition-rectangular to flat oval
W2—Minor width of a part.
6.4 Transition-rectangular to radius corner
X+—Offsetofatransitionorreducertowardtherightalong
6.5 Transition-radius corner to flat oval
the X axis, looking down from above.
6.6.1 Bellmouth-round
6.6.2 Bellmouth-rectangular
X−—Offset of a transition or reducer toward the left along
7. Branch:
the X axis, looking down from above.
7.1.1 Branch-round-on equal diameter round
Y+—Offset of a transition or reducer toward the top of the
7.1.2 Branch-round-on larger diameter round
7.1.3 Branch-round-on round reducer
Y axis, looking down from above.
7.1.4 Branch-round-on rectangular straight
Y−—Offset of a transition or reducer toward the bottom of
7.1.5 Branch-round-on rectangular reducer
the Y axis, looking down from above.
7.1.6 Branch-round “Y”
7.1.7 Branch-rectangular to round-“Y”
Z—Extension on one end of a part, opposite from V.
7.2.1 Branch-rectangular-on rectangular straight
7.2.2 Branch-rectangul
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.