ASTM C690-86(1997)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Alumina or Quartz by Electric Sensing Zone Technique
Standard Test Method for Particle Size Distribution of Alumina or Quartz by Electric Sensing Zone Technique
SCOPE
1.1 This test method, one of several found valuable for the measurement of particle size, covers the determination of the particle size distribution of alumina or quartz powders (0.6 to 56.0 [mu]m) using electric sensing zone particle size analyzers. These instruments use an electric current path of small dimensions which is modulated by individual particle passage through an aperture, and produces individual pulses of amplitude proportional to the particle volume.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
e1
Designation: C 690 – 86 (Reapproved 1997)
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Particle Size Distribution of Alumina or Quartz by Electric
Sensing Zone Technique
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 690; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e NOTE—Section 9 was added editorially in October 1997.
1. Scope 4. Apparatus
1.1 This test method, one of several found valuable for the 4.1 Electric Sensing Zone Particle Counter, Coulter
measurement of particle size, covers the determination of the Counter Industrial Models B, ZB, ZM, T, TA, TA II. Particle
particle size distribution of alumina or quartz powders (0.6 to Data Elzone Models EZ 211, 80XY, 111, 112, 180, 180t,
56.0 μm) using electric sensing zone particle size analyzers. 180XY. Equivalent instruments may be used.
These instruments use an electric current path of small dimen- 4.2 Aperture Tubes, diameter ranging from approximately
sions which is modulated by individual particle passage 30 to 140 μm. The diameter required is dependent upon the
through an aperture, and produces individual pulses of ampli- particle size distribution of the sample. Generally any given
tude proportional to the particle volume. tube will cover a particle size range from 2 to 40 % of its
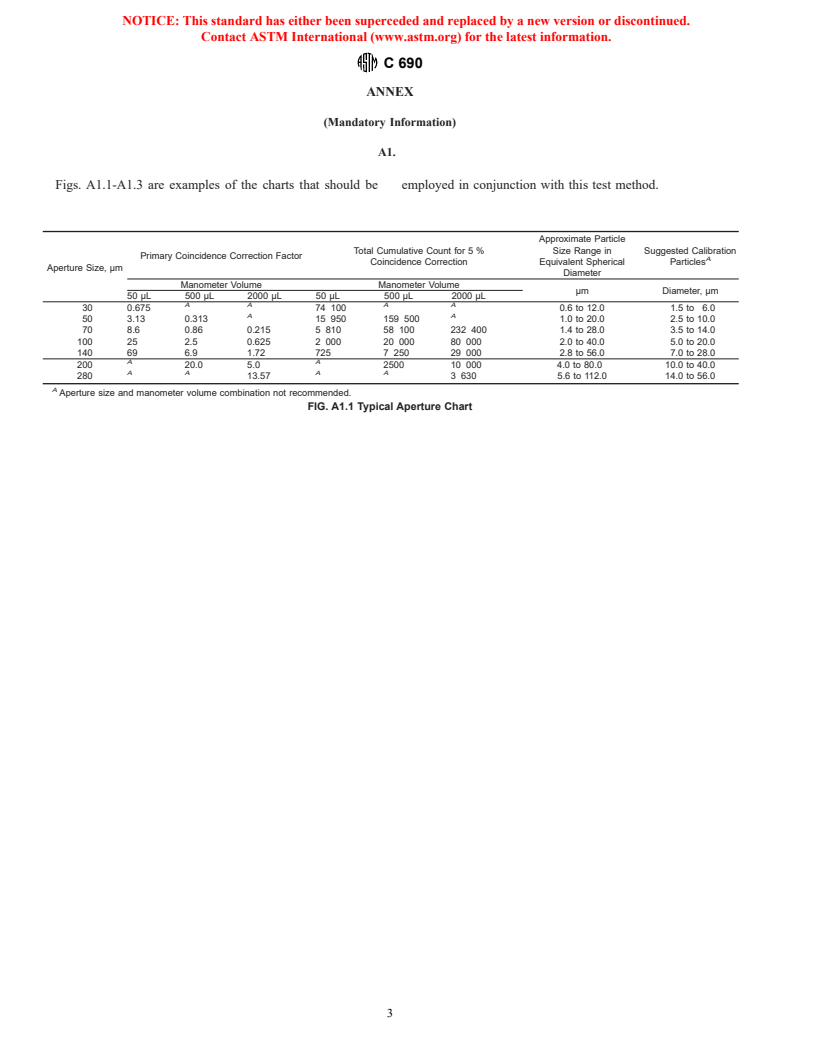
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the aperture diameter (see Fig. A1.1).
standard.
NOTE 1—In certain cases, apertures up to 280 μm are usable.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.3 Sample Beaker, capable of maintaining all particles
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
uniformly in suspension (for example, round-bottom).
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.4 Blender, capacity 1-L glass container. Speed control
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
with a variable transformer is required.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.5 Beakers, 100, 500, and 1000-mL.
2. Summary of Test Method 4.6 Pipet.
4.7 Wash Bottles.
2.1 A carefully dispersed, dilute suspension of the powder
4.8 Membrane Filtering Device, rated at 0.45-μm filters or
in a beaker filled with an electrolyte is placed in the counting
finer.
position on the instrument sample stand. The suspension is
forced through a restricting aperture. Each particle passing is
5. Reagents
recorded on an electronic counter according to selected particle
5.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
size levels.
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
2.2 The instrument response is essentially particle volume
all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
(liquid displacement), therefore equivalent spherical diameter
tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
is commonly used to express the particle size. (Comparisons
where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
with other techniques have been found to be good for spherical
used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
particles: for non-spherical particles results may differ.)
sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
3. Significance and Use
accuracy of the determination.
5.2 Dispersing Media—Ten percent solution of purified or
3.1 This test method is useful to both sellers and purchasers
of alumina and quartz for determining particle size distribu-
tions for materials specifications, manufacturing control, and
The Waring Blender model PB-5A, or equivalent has been found suitable for
development and research.
this test method.
The Variac transformer has been found suitable for this test method.
The membrane filters may be the Millipore, Gelman, General Electric, Selas
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-21 on Flotronics metal type, or their equivalent.
Ceramic Whitewares and Related Products and is the direct responsibility of Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Subcommittee C21.07 on Nonplastics. Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
Current edition approved Dec. 26, 1986. Published February 1987. Originally listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
published as C 690 – 71 T. Last previous edition C 690 – 80. Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
Available from the Coulter Electronics Inc., Hialeah, FL 33010 or from Particle and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
Data Inc., Box 265, Elmhurst, IL 60126. MD.
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
C 690
reagent grade sodium hexametaphosphate in distilled water 6.8 Take the particle count readings progressively at the
twice filtered through the membrane filtering device. prescheduled dial settings (see Fig. A1.3 for a typical single
channel instrument schedule). Repeat the scheduled settings
NOTE 2—Deionized water may be substituted for distilled water.
three times, beginning and ending at the smallest particle size
NOTE 3—This liquid should not be retained longer than 1 month and
level. Make additional count readings where values are below
should not be pH modified or heated.
100. Average the count readings for each size level. Multi-
5.3 Electrolyte—Dissolve 10.0 g of reagent grade sodium
channel instruments record all the size levels simultaneously.
chloride (NaCl) in 1000 mL of distilled water and filter twice
Computer-connected instruments record, average, manipulate,
through the membrane filtering device.
and output the data automatically.
5.4 Wash Water—Distilled water twice filtered through the
6.8.1 Recommended Number of Count Readings:
membrane filtering device.
6 for below 10 particles per reading
5.5 Calibration Particles—Monosized systems listed in
4 for below 100 particles per reading
Fig. A1.1.
2 for above 100 particles per reading
6.9 Precautions:
6. Procedure
6.9.1 Before each analysis, using wash bottle and filtered
6.1 Summary—Disperse the test powder in the electrolyte
wash water, wash all surfaces co
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.