ASTM D6042-23
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Phenolic Antioxidants and Erucamide Slip Additives in Polypropylene Homopolymer Formulations Using Liquid Chromatography (LC)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Phenolic Antioxidants and Erucamide Slip Additives in Polypropylene Homopolymer Formulations Using Liquid Chromatography (LC)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Separation and identification of stabilizers used in the manufacture of polypropylene is necessary in order to correlate performance properties with polymer composition. This test method provides a means to determine erucamide slip, Vitamin E, Irgafos 168, Irganox 3114, Irganox 1010, and Irganox 1076 levels in polypropylene samples. This test method is also applicable for the determination of other antioxidants, such as Ultranox 626, Ethanox 330, Santanox R, and BHT, but the applicability of this test method has not been investigated for these antioxidants.
5.2 The additive-extraction procedure is made effective by the insolubility of the polymer sample in solvents generally used for liquid chromatographic analysis.
5.3 Under optimum conditions, the lowest level of detection for a phenolic antioxidant is approximately 2 ppm.
Note 2: Other methods that have been used successfully to remove additives from the plastics matrix include thin film, microwave, ultrasonic, and supercritical fluid extractions. Other methods have been used successfully to separate additives including SFC and capillary GC.
5.4 Irgafos 168 is a phosphite antioxidant. Phosphites are known to undergo both oxidation and hydrolysis reactions. Less Irgafos 168 will be determined in the polymer when oxidation occurs during processing. The HPLC separation is capable of separating the phosphite, phosphate (oxidation product), and hydrolysis product and quantify them if standards are obtained. No significant breakdown of the phosphite antioxidant has been seen due to either extraction technique or the separation presented in this standard.
SCOPE
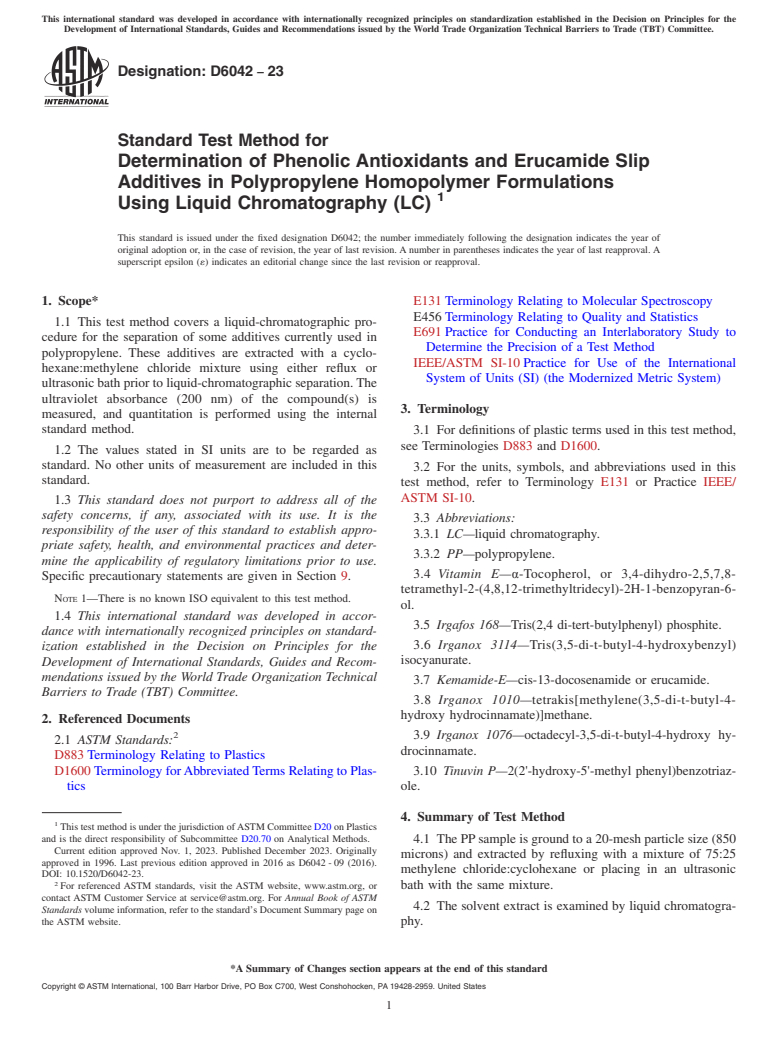
1.1 This test method covers a liquid-chromatographic procedure for the separation of some additives currently used in polypropylene. These additives are extracted with a cyclohexane:methylene chloride mixture using either reflux or ultrasonic bath prior to liquid-chromatographic separation. The ultraviolet absorbance (200 nm) of the compound(s) is measured, and quantitation is performed using the internal standard method.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 9.
Note 1: There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D6042 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Phenolic Antioxidants and Erucamide Slip
Additives in Polypropylene Homopolymer Formulations
1
Using Liquid Chromatography (LC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6042; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* E131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
1.1 This test method covers a liquid-chromatographic pro-
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
cedure for the separation of some additives currently used in
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
polypropylene. These additives are extracted with a cyclo-
IEEE/ASTM SI-10 Practice for Use of the International
hexane:methylene chloride mixture using either reflux or
System of Units (SI) (the Modernized Metric System)
ultrasonic bath prior to liquid-chromatographic separation. The
ultraviolet absorbance (200 nm) of the compound(s) is
3. Terminology
measured, and quantitation is performed using the internal
standard method.
3.1 For definitions of plastic terms used in this test method,
see Terminologies D883 and D1600.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.2 For the units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this
standard.
test method, refer to Terminology E131 or Practice IEEE/
ASTM SI-10.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.3 Abbreviations:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.3.1 LC—liquid chromatography.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.3.2 PP—polypropylene.
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.4 Vitamin E—α-Tocopherol, or 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-
Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 9.
tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
ol.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
3.5 Irgafos 168—Tris(2,4 di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphite.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.6 Irganox 3114—Tris(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
isocyanurate.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.7 Kemamide-E—cis-13-docosenamide or erucamide.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
3.8 Irganox 1010—tetrakis[methylene(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-
hydroxy hydrocinnamate)]methane.
2. Referenced Documents
2
3.9 Irganox 1076—octadecyl-3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxy hy-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
drocinnamate.
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plas- 3.10 Tinuvin P—2(2'-hydroxy-5'-methyl phenyl)benzotriaz-
tics ole.
4. Summary of Test Method
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods.
4.1 The PP sample is ground to a 20-mesh particle size (850
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2023. Published December 2023. Originally
microns) and extracted by refluxing with a mixture of 75:25
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D6042 - 09 (2016).
methylene chloride:cyclohexane or placing in an ultrasonic
DOI: 10.1520/D6042-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or bath with the same mixture.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.2 The solvent extract is examined by liquid chromatogra-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. phy.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6042 − 23
4.3 Additive concentrations are determined relative to an
internal standard (contained in the solvent) using reverse-phase
chromatography (C-18 column) with ultraviolet (UV) detection
at 200 nm.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 Separation and identification of stabilizers used in the
manufacture of polypropylene is necessary in order to correlate
performance properties with polymer composition. This te
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6042 − 09 (Reapproved 2016) D6042 − 23
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Phenolic Antioxidants and Erucamide Slip
Additives in Polypropylene Homopolymer Formulations
1
Using Liquid Chromatography (LC)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6042; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers a liquid-chromatographic procedure for the separation of some additives currently used in
polypropylene. These additives are extracted with a cyclohexane:methylene chloride mixture using either reflux or ultrasonic bath
prior to liquid-chromatographic separation. The ultraviolet absorbance (200 nm) of the compound(s) is measured, and quantitation
is performed using the internal standard method.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and healthsafety, health, and environmental practices and determine
the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 9.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this test method.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
E131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
IEEE/ASTM SI-10 Practice for Use of the International System of Units (SI) (the Modernized Metric System)
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of plastic terms used in this test method, see Terminologies D883 and D1600.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.70 on Analytical Methods
(D20.70.02).
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2016Nov. 1, 2023. Published September 2016December 2023. Originally approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 20092016
as D6042 - 09.D6042 - 09 (2016). DOI: 10.1520/D6042-09R16.10.1520/D6042-23.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6042 − 23
3.2 For the units, symbols, and abbreviations used in this test method, refer to Terminology E131 or Practice IEEE/ASTM SI-10.
3.3 Abbreviations:
3.3.1 LC—liquid chromatography.
3.3.2 PP—polypropylene.
3.4 Trade Names:
3.4 Vitamin E—α-Tocopherol, or 3,4-dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6- ol.
3.5 Irgafos 168—Tris(2,4 di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphite.
3.6 Irganox 3114—Tris(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl) isocyanurate.
3.7 Kemamide-E—cis-13-docosenamide or erucamide.
3.8 Irganox 1010—tetrakis[methylene(3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxy hydrocinnamate)]methane.
3.9 Irganox 1076—octadecyl-3,5-di-t-butyl-4-hydroxy hydrocinnamate.
3.10 Tinuvin P—2(2'-hydroxy-5'-methyl phenyl)benzotriazole.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The PP sample is ground to a 20-mesh particle size (850 microns) and extracted by refluxing with a mixture of 75:25
methylene chloride:cyclohexane or placing in an ultrasonic bath with the same mixture.
4.2 The solvent extract is examined by liquid chromatography.
4.3 Additive concentrations are determined relative to an internal standard (contained in the solvent) using reverse-phase
chromatography (C-18 column) with
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.