ASTM F2930-15
(Guide)Standard Guide for Compliance with Light Sport Aircraft Standards
Standard Guide for Compliance with Light Sport Aircraft Standards
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
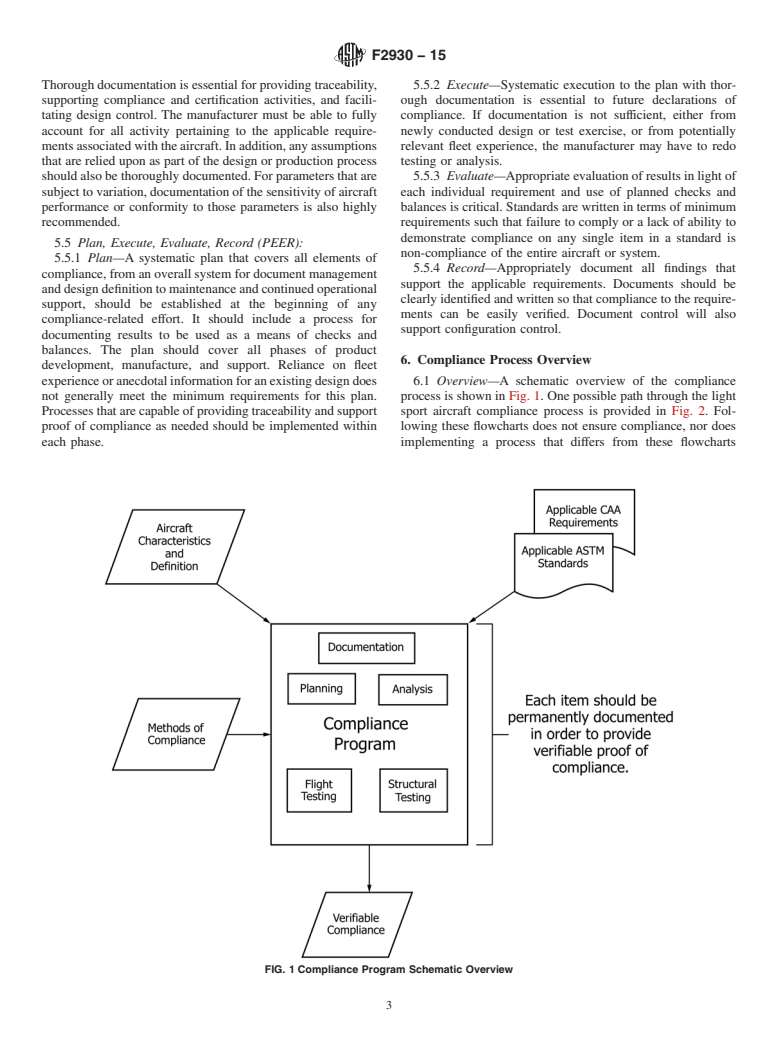
4.1 This guide provides some major themes and examples for consideration related to compliance which are not necessarily captured in any single standard pertinent to light sport aircraft. The outline of this document is intended to loosely reflect the process that an organization would go through in order to reach and maintain production of a light sport aircraft that is demonstrably compliant with the applicable ASTM standards.
4.2 These considerations are applicable to manufacturers which are responsible for conformity to processes and procedures required in ASTM standards for light sport aircraft. Manufacturers are encouraged to think through the contents of this guide, reference the ASTM light sport aircraft standards, establish, document and follow their own procedures.
4.3 Manufacturers are responsible for determining which standards and revisions thereof are part of the regulatory package of any given CAA, along with any other requirements applicable within the agency’s jurisdiction.
4.4 Following this guide does not ensure compliance of a particular light sport aircraft; however, following the explanations provided herein should assist manufacturers in avoiding common pitfalls of declaring compliance prematurely, determining shortcomings in current declarations of compliance, and maintaining a body of documentation sufficient to support a declaration of compliance.
SCOPE
1.1 This document provides guidance to assist manufacturers in understanding and meeting ASTM standards for light sport aircraft. This guidance material presents philosophies, practices and considerations recommended by industry consensus, but does not present technical or business requirements that must be met.
1.2 It is the intent of this guide to provide processes to be considered by organizations looking to develop or improve objective evidence of compliance for light sport aircraft. It does not attempt to identify all of the standards, regulations or other requirements that may be applicable to a given aircraft, production or testing process.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F2930 − 15
StandardGuide for
1
Compliance with Light Sport Aircraft Standards
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2930; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope F3035 Practice for Production Acceptance in the Manufac-
ture of a Fixed Wing Light Sport Aircraft
1.1 This document provides guidance to assist manufactur-
3
ers in understanding and meeting ASTM standards for light 2.2 FAA Standards:
sport aircraft. This guidance material presents philosophies,
FAA Advisory Circular No. 23.629-1B Means of Compli-
practices and considerations recommended by industry ance with Title 14 CFR, Part 23, Section 23.629, Flutter
consensus, but does not present technical or business require-
FAA JASC (Joint Aircraft System/Component) Codes
ments that must be met.
2.3 Other References:
1.2 It is the intent of this guide to provide processes to be
ATA (Air Transport Association) Spec 100, or the newer
considered by organizations looking to develop or improve
iSpec 2200—Information Standards for Aviation Mainte-
4
objective evidence of compliance for light sport aircraft. It
nance
does not attempt to identify all of the standards, regulations or
MetallicMaterialsPropertiesDevelopmentandStandardiza-
5
other requirements that may be applicable to a given aircraft,
tion (MMPDS, formerly MIL-HDBK-5)
production or testing process.
CMH-17 (formerly MIL-HDBK-17) for composite material
5
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the properties
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
CICTT (Commercial Aviation Safety Team/International
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Civil Aviation Organization Common Taxonomy
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Team) International Standard for Aircraft Make, Model,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
and Series Groupings – Business Rules, October 2012
6
(1.3)
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: 3. Terminology
F2245 Specification for Design and Performance of a Light
3.1 The following are a selection of relevant terms. See
Sport Airplane
Terminology F2626 for more definitions and abbreviations.
F2295 Practice for Continued Operational Safety Monitor-
3.2 Definitions:
ing of a Light Sport Aircraft
F2483 Practice for Maintenance and the Development of
3.2.1 compliance package—a set of documents which pro-
Maintenance Manuals for Light Sport Aircraft vides objective, verifiable evidence for compliance to appli-
F2626 Terminology for Light Sport Aircraft
cable ASTM standards.
F2746 Specification for Pilot’s Operating Handbook (POH)
3.2.2 compliance program—a set of activities planned for,
for Light Sport Airplane
executed, and for which results are reviewed against ASTM
F2839 Practice for Compliance Audits to ASTM Standards
standards for the purpose of declaring compliance to a particu-
on Light Sport Aircraft
lar standard.
F2972 Specification for Light SportAircraft Manufacturer’s
3.2.2.1 Discussion—The program may be short and simple
Quality Assurance System
or extensive and comprehensive, depending on the standard or
purpose of the program (for example, initial design versus
modification).
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F37 on Light Sport
Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F37.70 on Cross Cutting.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2015. Published September 2015. Originally
approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as F2930 – 14a. DOI:
3
10.1520/F2930-15. Available from Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), 800 Independence
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20591, http://www.faa.gov.
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from http://www.airlines.org.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from http://www.everyspec.com.
6
the ASTM website. Available from http://intlaviationstandards.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2930 − 15
3.2.3 continued compliance activity—work that is con- 3.3.16 QA—Quality Assurance
ducted as part of the ongoing support and production of an
3.3.17 QAM—Quality Assurance Manual
aircraft following the initial design definition and statement of
3.3.18 QAP—Quality Assurance Program
compliance.
3.3.19 QAR—Quality Assurance Record
3.2.4 control drawing—discloses
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F2930 − 14a F2930 − 15
Standard Guide for
1
Compliance with Light Sport Aircraft Standards
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2930; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This document provides guidance to assist manufacturers in understanding and meeting ASTM standards for light sport
aircraft. This guidance material presents philosophies, practices and considerations recommended by industry consensus, but does
not present technical or business requirements that must be met.
1.2 It is the intent of this guide to provide processes to be considered by organizations looking to develop or improve objective
evidence of compliance for light sport aircraft. It does not attempt to identify all of the standards, regulations or other requirements
that may be applicable to a given aircraft, production or testing process.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F2245 Specification for Design and Performance of a Light Sport Airplane
F2295 Practice for Continued Operational Safety Monitoring of a Light Sport Aircraft
F2483 Practice for Maintenance and the Development of Maintenance Manuals for Light Sport Aircraft
F2626 Terminology for Light Sport Aircraft
F2746 Specification for Pilot’s Operating Handbook (POH) for Light Sport Airplane
F2839 Practice for Compliance Audits to ASTM Standards on Light Sport Aircraft
F2972 Specification for Light Sport Aircraft Manufacturer’s Quality Assurance System
F3035 Practice for Production Acceptance in the Manufacture of a Fixed Wing Light Sport Aircraft
3
2.2 FAA Standards:
FAA Advisory Circular No. 23.629-1B Means of Compliance with Title 14 CFR, Part 23, Section 23.629, Flutter
FAA JASC (Joint Aircraft System/Component) Codes
2.3 Other References:
4
ATA (Air Transport Association) Spec 100, or the newer iSpec 2200—Information Standards for Aviation Maintenance
5
Metallic Materials Properties Development and Standardization (MMPDS, formerly MIL-HDBK-5)
5
CMH-17 (formerly MIL-HDBK-17) for composite material properties
CICTT (Commercial Aviation Safety Team/International Civil Aviation Organization Common Taxonomy Team) International
6
Standard for Aircraft Make, Model, and Series Groupings – Business Rules, October 2012 (1.3)
3. Terminology
3.1 The following are a selection of relevant terms. See Terminology F2626 for more definitions and abbreviations.
3.2 Definitions:
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F37 on Light Sport Aircraft and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F37.70 on Cross Cutting.
Current edition approved June 1, 2014Aug. 1, 2015. Published July 2014September 2015. Originally approved in 2012. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as
F2930 – 14.F2930 – 14a. DOI: 10.1520/F2930-14A.10.1520/F2930-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), 800 Independence Ave., SW, Washington, DC 20591, http://www.faa.gov.
4
Available from http://www.airlines.org.
5
Available from http://www.everyspec.com.
6
Available from http://intlaviationstandards.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2930 − 15
3.2.1 compliance package—a set of documents which provides objective, verifiable evidence for compliance to applicable
ASTM standards.
3.2.2 compliance program—a set of activities planned for, executed, and for which results are reviewed against ASTM standards
for the purpose of declaring compliance to a particular standard.
3.2.2.1 Discussion—
The program may be short and simple or extensive and comprehensive, depending on the standard or purpose of the program (for
example, initial design versus modification).
3.2.3 continued compliance activit
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.