ASTM G66-99(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Visual Assessment of Exfoliation Corrosion Susceptibility of 5XXX Series Aluminum Alloys (ASSET Test)
Standard Test Method for Visual Assessment of Exfoliation Corrosion Susceptibility of 5XXX Series Aluminum Alloys (ASSET Test)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for continuous immersion exfoliation corrosion testing of 5XXX series aluminum-magnesium alloys containing 2.0% or more magnesium.
1.2 This test method applies only to wrought products.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:G66–99 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Visual Assessment of Exfoliation Corrosion Susceptibility of
5XXX Series Aluminum Alloys (ASSET Test)
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationG 66;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope ceptibility to exfoliation is determined by visual examination
using performance ratings established by reference to standard
1.1 This test method covers a procedure for continuous
photographs.
immersion exfoliation corrosion testing of 5XXX series
aluminum-magnesium alloys containing 2.0 % or more mag-
5. Significance and Use
nesium.
5.1 This test method provides a reliable prediction of the
1.2 This test method applies only to wrought products.
exfoliation corrosion behavior of Al-Mg alloys in marine
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
,
3 4, 5
environments. The test is useful for alloy development
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
studies and quality control of mill products such as sheet and
only.
plate.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
6. Apparatus
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
6.1 Any suitable glass or plastic container can be used to
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
contain the solution and specimens during the test period.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Depending upon the shape and size of the specimens, rods or
racks of glass, plastic, or other inert substance shall be used to
2. Referenced Documents
support the specimens above the bottom of the container. The
2.1 ASTM Standards:
container should be fitted with a removable cover to reduce
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
evaporation.
G15 Terminology Relating to Corrosion and Corrosion
Testing
7. Reagents
3. Terminology 7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
used in all tests.
3.1 Definitions:
7.2 Purity of Water—Distilled or deionized water conform-
3.1.1 exfoliation—corrosion that proceeds laterally from the
ing to Specification D 1193. Type IV shall be used to prepare
sites of initiation along planes parallel to the surface, generally
the test solution except chloride ion sodium limits can be
at grain boundaries, forming corrosion products that force
disregarded.
metal away from the body of the material, giving rise to a
layered appearance (see TerminologyG15).
8. Test Solution
4. Summary of Test Method 8.1 Preparation of Test Solution:
8.1.1 The test solution shall have the following composi-
4.1 Specimens are immersed for 24 h at 65 6 1°C (150 6
tion:
2°F) in a solution containing ammonium chloride, ammonium
NH Cl (1.0 M)
nitrate, ammonium tartrate, and hydrogen peroxide. The sus-
NH NO (0.25 M)
4 3
(NH ) C H O (0.01 M)
4 2 4 4 6
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G01 on
Corrosion of Metals and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G01.05 on AluminumAssociation Technical Report T1,“ Exfoliation Corrosion Testing of
Laboratory Corrosion Tests. This method was developed by a joint task group with Aluminum Alloys 5086 and 5456”.
The Aluminum Assoc., Inc. Sprowls, D. O., Walsh, J. D. and Shumaker, M. B., “Simplified Exfoliation
Current edition approved May 1, 2005. Published May 2005. Originally TestingofAluminumAlloys”, Localized Corrosion—Cause of Metal Failure, ASTM
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as G 66 – 99. STP 516, ASTM, 1972, pp 38–65.
2 5
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Summerson T. J., Interim Report, Aluminum Association Task Group on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Exfoliation and Stress Corrosion Cracking of Aluminum Alloys for Boat Stock;
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on ProceedingsTri-Service Corrosion Military Equipment Conference, October 29–31,
the ASTM website. 1974; Technical Report AFML-TR-75-42, Vol. II, p. 193–221, February 1, 1975.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
G66–99 (2005)
anhydrous calcium sulfate).
H O (0.09 M)
2 2
12.2 Use fresh solution at the start of each test.
8.1.2 Dissolve 53.5 g ammonium chloride (NH Cl), 20.0 g
12.3 Immerse the specimens vertically with the top edge of
ammonium nitrate (NH NO ), 1.8 g ammonium tartrate
4 3
the specimens at least 25 mm (1 in.) below the surface of the
((NH ) C H O ), and 10 mL of 30 % stock solution hydrogen
4 2 4 4 6
solution and the bottom edge at least 25 mm above the bottom
peroxide (H O ) in a small amount of water. After dissolving,
2 2
of the container.
mix the components together thoroughly and adjust the final
12.4 Immerse the specimens in the test solution continu-
dilution to 1 L.
ously for 24 h.
NOTE 1—If a stock solution of the above chemicals is to be stored, the
12.5 Rinse the specimens gently in running tap water
hydrogen peroxide should not be added until the solution is heated for the
immediately after removal from the solution, then soak in
test.
concentrated nitric acid at room temperature until they appear
clean, again rinse in water, and air dry.
8.2 The solution will have a typical pH of 5.2 to 5.4.
12.5.1 Air-blast drying is to be avoided in order to prevent
8.3 The solution shall be used in sufficient quantity to
mechanical removal of exfoliated metal.
provide a volume-to-exposed specimen surface area ratio of at
2 2
least 100 L/m (65 mL/in. ).
13. Rating of Specimens
8.4 The temperature of the solution shall be maintained at
13.1 The following codes and classifications shall be used
65 6 1°C (150 6 2°F).
for reporting the visual appearance of corroded specimens.
Code Classification
9. Sampling
N No appreciable attack
P Pitting
9.1 The procedure for sampling mill products is covered in
E Exfoliation
product specifications, or otherwise, and is considered outside
13.2 Descriptions of the various classifications, which are
the scope of this standard.
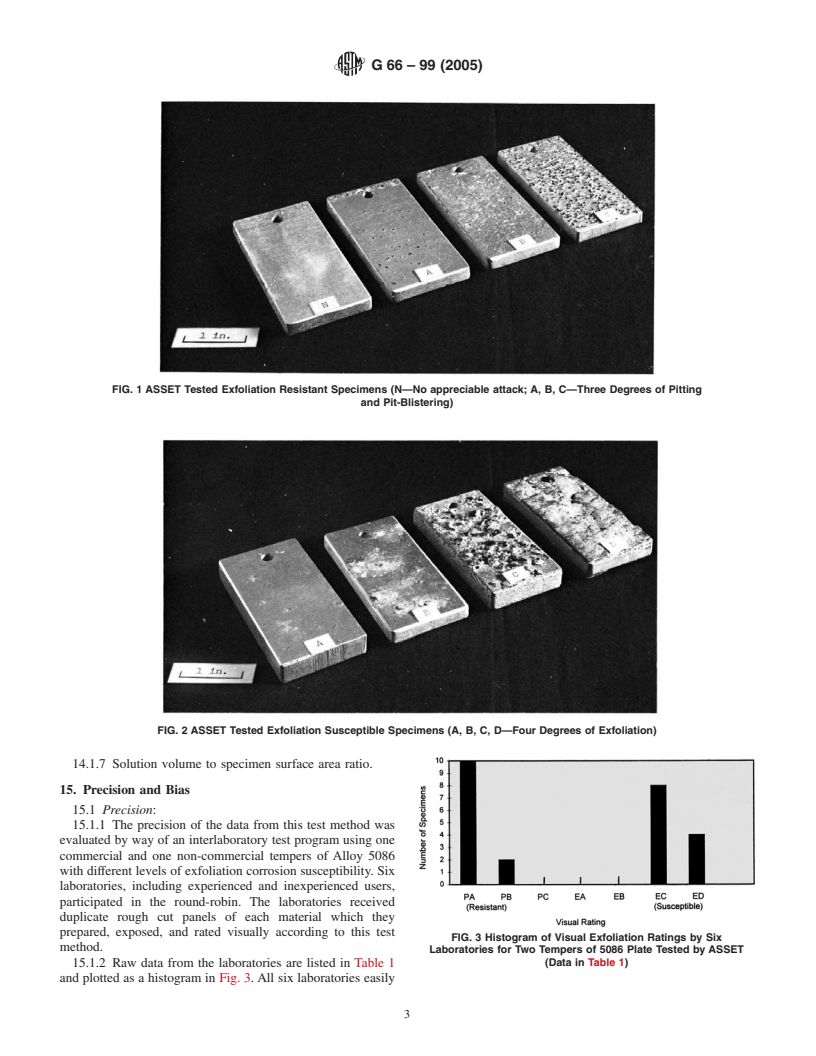
illustrated in Figs. 1 and 2, are as follows:
13.2.1 N (no appreciable attack)—Surfacemaybeetchedor
10. Test Specimen
discolored.
10.1 While this test method can be used with any form of
13.2.2 P (Pitting)—Includes discrete pitting or pit-
specimen or part that can be immersed in the test solution, it is
blistering. In the latter case, attack results in a slight undercut-
preferred that specimens be at least 40 by 100 mm (1.5 by 4.0
ting of the surface. Pi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.