ASTM A194/A194M-14a
(Specification)Standard Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or High Temperature Service, or Both
Standard Specification for Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or High Temperature Service, or Both
ABSTRACT
This specification covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and martensitic and austenitic stainless steel nuts. These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high-temperature service, or both. Bars from which the nuts are made shall be hot-wrought. The material may be further processed by centerless grinding or by cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be solution annealed or annealed and strain-hardened. Each alloy shall conform to the chemical composition requirements prescribed. Hardness tests, proof of load tests, and cone proof load tests shall be made to all nuts to meet the requirements specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification2 covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and martensitic stainless steel nuts in the size range 1/4 through 4 in. and metric M6 through M100 nominal. It also covers austenitic stainless steel nuts in the size range 1/4 in. and M6 nominal and above. These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high-temperature service, or both. Grade substitutions without the purchaser's permission are not allowed.
1.2 Bars from which the nuts are made shall be hot-wrought. The material may be further processed by centerless grinding or by cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be solution annealed or annealed and strain-hardened. When annealed and strain hardened austenitic stainless steel is ordered in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S1, the purchaser should take special care to ensure that 8.2.2, Supplementary Requirement S1, and Appendix X1 are thoroughly understood.
1.3 Supplementary requirements of an optional nature are provided. These shall apply only when specified in the inquiry, contract, and order.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable“ M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A194/A194M −14a Endorsedby
Manufacturers Standardization Society
of the Valve and Fittings Industry
Used in USNRC-RDT Standards
Standard Specification for
Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or
High Temperature Service, or Both
This standard is issued under the fixed designationA194/A194M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
1.1 This specification covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and 2.1 ASTM Standards:
martensiticstainlesssteelnutsinthesizerange ⁄4 through4in.
A153/A153M Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on
andmetricM6throughM100nominal.Italsocoversaustenitic Iron and Steel Hardware
stainless steel nuts in the size range ⁄4 in. and M6 nominal and
A276 Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
above. These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high- A320/A320M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless
temperature service, or both. Grade substitutions without the
Steel Bolting for Low-Temperature Service
purchaser’s permission are not allowed.
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
of Steel Products
1.2 Barsfromwhichthenutsaremadeshallbehot-wrought.
A962/A962M Specification for Common Requirements for
The material may be further processed by centerless grinding
Bolting Intended for Use at Any Temperature from Cryo-
or by cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be solution
genic to the Creep Range
annealed or annealed and strain-hardened. When annealed and
B633 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc on
strain hardened austenitic stainless steel is ordered in accor-
Iron and Steel
dance with Supplementary Requirement S1, the purchaser
B695 Specification for Coatings of Zinc Mechanically De-
should take special care to ensure that 8.2.2, Supplementary
posited on Iron and Steel
Requirement S1, and Appendix X1 are thoroughly understood.
B696 Specification for Coatings of Cadmium Mechanically
1.3 Supplementary requirements of an optional nature are
Deposited
provided. These shall apply only when specified in the inquiry,
B766 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Cad-
contract, and order.
mium
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the
E566 PracticeforElectromagnetic(EddyCurrent)Sortingof
applicable“ M” specification designation (SI units), the mate-
Ferrous Metals
rial shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
F606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Proper-
ties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners,
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in Washers, Direct Tension Indicators, and Rivets
F1940 Test Method for Process Control Verification to
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated
Fasteners
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
with the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in F1941 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings on
brackets. Threaded Fasteners (Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN/
UNR))
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee A01 on Steel, F2329 Specification for Zinc Coating, Hot-Dip, Require-
Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
ments for Application to Carbon and Alloy Steel Bolts,
A01.22 on Steel Forgings andWrought Fittings for PipingApplications and Bolting
Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2014. Published November 2014. Originally
approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as A194/A194M–14. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/A0194_A0194M-14A. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specifi- Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
cation SA-194 in Section II of that code. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A194/A194M−14a
Screws, Washers, Nuts, and Special Threaded Fasteners 4.1.3 Dimensions (see Section 9),
2.2 ASME Standards: 4.1.4 Options in accordance with 8.2.2.1, 9.1, 9.2, 10.3, and
12, and
B 1.1 Unified Screw Threads
B 1.2 Gages and Gaging for Unified Inch Screw Threads 4.1.5 Supplementary Requirements, if any.
B 1.13M Metric Screw Threads
4.2 Coatings—Coatings are prohibited unless specified by
B 18.2.2 Square and Hex Nuts
the purchaser (see Supplementary Requirements S7 and S8).
B 18.2.4.6M Metric Heavy Hex Nuts
When coated nuts are ordered, the purchaser should take
2.3 ISO Standards:
special care to ensure that Appendix X2 is thoroughly under-
4033 Hexagon High Nuts (Style 2) – Product A and B
stood.
3. Terminology 4.3 See Supplementary Requirement S3 for nuts to be used
in low temperature applications (Specification A320/A320M).
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 Austenitic Grades—All grades with a prefix of “8” or 4.4 Proof Load Testing—See Supplementary Requirement
S9 for proof load testing of nuts manufactured to dimensions
“9.”
and configurations other than those covered in Tables 3 and 4.
3.1.2 Ferritic Grades—Grades 1, 2, 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 6, 6F, 7,
7M, and 16.
5. Common Requirements
3.1.3 Lot—Unless otherwise specified (see Discussion
5.1 Materialandfastenerssuppliedtothisspecificationshall
below),alotisthequantityofnutsofasinglenominalsizeand
conform to the requirements of Specification A962/A962M.
grade produced by the same manufacturing process.
These requirements include test methods, finish, thread
3.1.3.1 Discussion—When Supplementary Requirement S5
dimensions, marking, certification, optional supplementary
is invoked on the purchase order, the following definitions of a
requirements, and others. Failure to comply with the require-
lot shall apply:
ments of Specification A962/A962M constitutes nonconfor-
3.1.3.2 For Grade 8 Nuts—The quantity of all the nuts of a
mance with this specification. In case of conflict between the
single nominal diameter and grade made from the same heat of
requirements of this specification and Specification A962/
steel and made by the same manufacturing process.
A962M, this specification shall prevail.
3.1.3.3 For All Other Grade Nuts—(see 8.2 and
8.1.2.1)—All the nuts of a single nominal diameter and grade 6. Manufacture (Process)
made from the same heat number and heat treated in the same
6.1 Stainless steels for all types of Grade 6 and 8 nuts shall
batch if batch-type heat treating equipment is used or heat
be made by one of the following processes:
treated in the same continuous run of not more than 8 h under
6.1.1 Electric-furnace (with separate degassing and refining
the same conditions if continuous-type heat treating equipment
optional),
is used.
6.1.2 Vacuum induction furnace, or
3.1.4 Type:
6.1.3 Either of the above followed by electroslag remelting,
3.1.4.1 For Grade 8 Nuts—Variations within the grade
or consumable-arc remelting.
designated by a letter and differentiated by chemistry and by
6.2 The steel producer shall exercise adequate control to
manufacturing process.
eliminate excessive unhomogeneity, nonmetallics, pipe,
3.1.4.2 For Grade 6 Nuts—Variations within the grade
porosity, and other defects.
designated by the letter F as differentiated by chemical addi-
6.3 Grades 1 and 2 nuts shall be hot or cold forged, or shall
tions made for machineability.
be machined from hot-forged, hot-rolled, or cold-drawn bars.
3.1.5 Series—The dimensional relationship and geometry of
6.3.1 All Grade 1 and 2 nuts shall be stress-relief annealed
the nuts as described inASME B 18.2.2 for inch nuts and ISO
at a temperature of at least 1000 °F [538 °C] after forming or
4033 for metric nuts sizes M6 through M10 and ASME B
machining from bar with the following exceptions:
18.2.4.6M for nuts sizes M12 through M100.
6.3.1.1 Nuts made by hot forging.
6.3.1.2 Nuts machined from hot-forged or hot-rolled bar.
4. Ordering Information
6.3.1.3 Nuts machined from hot-forged/hot-rolled and cold-
4.1 The inquiry and order for material under this specifica-
finished (max 10 % reduction in area) bar.
tion shall include the following as required to describe the
6.3.1.4 Nuts machined from cold-drawn and annealed (min
material adequately:
1000 °F [538 °C]) bar.
4.1.1 Specification designation, year date, and grade, issue
6.3.2 Grade 1 and 2 nuts made by hot forging or by
date and revision letter,
machiningfromhot-forgedorhot-rolledbarsneednotbegiven
4.1.2 Quantity, number of pieces,
any stress relief annealing treatment.
6.4 Grades 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 6, 6F, 7, 7M, and 16 nuts shall
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
be hot- or cold-forged or shall be machined from hot-forged,
International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
hot-rolled, or cold-drawn bars and shall be heat treated to meet
www.asme.org.
the required mechanical properties. These grades shall be
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org. uniformly reheated to the proper austenitizing temperature (a
A194/A194M−14a
A,B,C,D
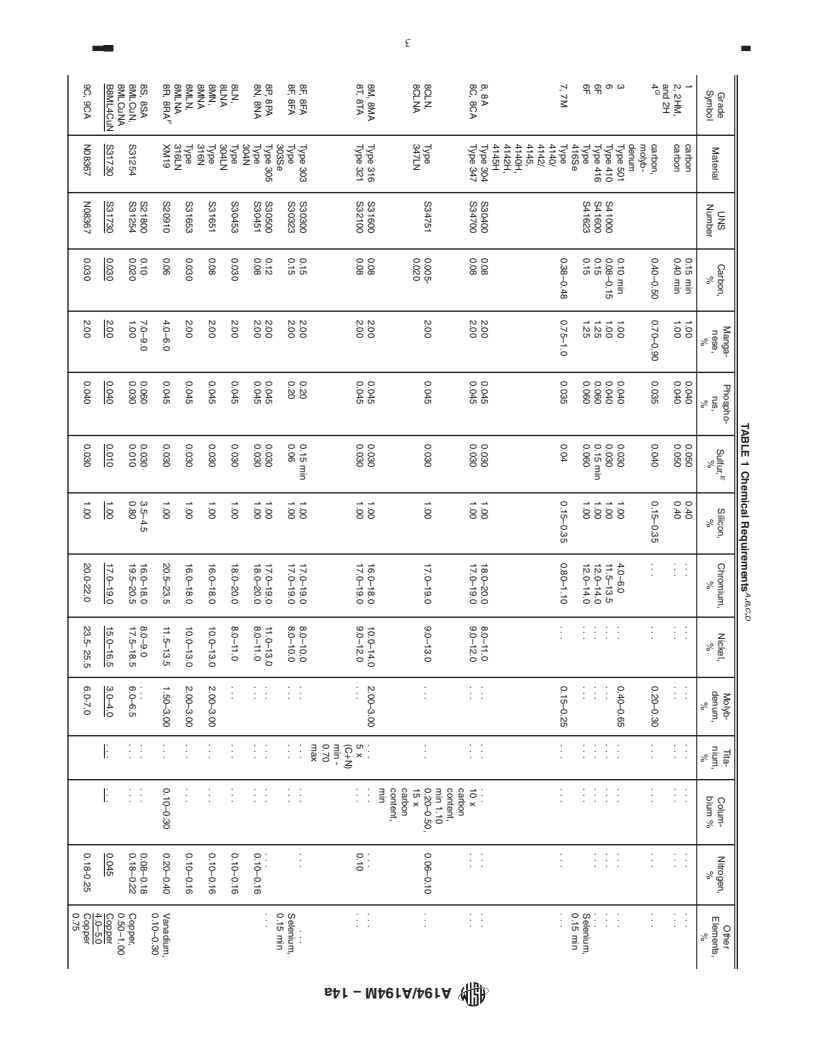
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Manga- Phospho- Molyb- Tita- Other
E
Grade UNS Carbon, Silicon, Chromium, Nickel, Colum- Nitrogen,
Sulfur,
Material nese, rus, denum, nium, Elements,
%
Symbol Number % % % % bium % %
% % % % %
1 carbon 0.15 min 1.00 0.040 0.050 0.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2, 2HM, and carbon 0.40 min 1.00 0.040 0.050 0.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2H
G
4 carbon, 0.40–0.50 0.70–0.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . . . . 0.20–0.30 . . . . . . . . . . . .
molyb-
denum
3 Type 501 0.10 min 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 4.0–6.0 . . . 0.40–0.65 . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Type 410 S41000 0.08–0.15 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 11.5–13.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6F Type 416 S41600 0.15 1.25 0.060 0.15 min 1.00 12.0–14.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6F Type S41623 0.15 1.25 0.060 0.060 1.00 12.0–14.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . Selenium,
416Se 0.15 min
7, 7M Type 0.38–0.48 0.75–1.0 0.035 0.04 0.15–0.35 0.80–1.10 . . . 0.15–0.25 . . . . . . . . . . . .
4140/
4142/
4145,
4140H,
4142H,
4145H
8, 8A Type 304 S30400 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8C, 8CA Type 347 S34700 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 . . . . . . 10 x . .
carbon
content,
min 1.10
8CLN, Type S34751 0.005- 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–13.0 . . . . . . 0.20–0.50, 0.06–0.10 . . .
8CLNA 347LN 0.020 15 x
carbon
content,
min
8M, 8MA Type 316 S31600 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 2.00–3.00 . . . . . . . . . . . .
8T, 8TA Type 321 S32100 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 . . . 5 x . 0.10 .
(C+N)
min -
0.70
max
8F, 8FA Type 303 S30300 0.15 2.00 0.20 0.15 min 1.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8F, 8FA Type S30323 0.15 2.00 0.20 0.06 1.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0 . . . . . . . . . Selenium,
303Se 0.15 min
8P, 8PA Type 305 S30500 0.12 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 11.0–13.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8N, 8NA Type S30451 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
304N
8LN, 8LNA Type S30453 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
304LN
8MN, 8MNA Type S31651 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–13.0 2.00–3.00 . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
316N
8MLN, Type S31653 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–13.0 2.00–3.00 . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
8MLNA 316LN
F
8R, 8RA XM19 S20910 0.06 4.0–6.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 20.5–23.5 11.5–13.5 1.50–3.00 . . . 0.10–0.30 0.20–0.40 Vanadium,
0.10–0.30
8S, 8SA S21800 0.10 7.0–9.0 0.060 0.030 3.5–4.5 16.0–18.0 8.0–9.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.08–0.18
8MLCuN, S31254 S31254 0.020 1.00 0.030 0.010 0.80 19.5–20.5 17.5–18.5 6.0–6.5 . . . . . . 0.18–0.22 Copper,
8MLCuNA 0.50–1.00
B8ML4CuN S31730 S31730 0.030 2.00 0.040 0.010 1.00 17.0–19.0 15.0–16.5 3.0–4.0 . . . . . . 0.045 Copper
4.0–5.0
9C, 9CA N08367 N08367 0.030 2.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 20.0-22.0 23.5- 25.5 6.0-7.0 0.18-0.25 Copper
0.75
A194/A194M−14a
TABLE1 Continued
Manga- Phospho- Molyb- Tita- Other
E
Grade UNS Carbon, Silicon, Chromium, Nickel, Colum- Nitrogen,
Sulfur,
Material nese, rus, denum, nium, Elements,
%
Symbol Number % % % % bium % %
% % % % %
16 Chromium 0.36–0.47 0.45–0.70 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 0.80–1.15 . . . 0.50–0.65 . . . . . . . . . Vanadium,
Molyb- 0.25–0.35
B
denum Aluminum
0.015
Vanadium
A
The intentional addition of Bi, Se, Te, and Pb is not permitted except for Grades 6F, 8F, and 8FA, in which Se is specified and required.
B
Total aluminum, soluble and insoluble.
C
Maximum, unless minimum or range is indicated.
D
Where ellipses ({) appear in this table there is no requirement and the element need not be determined or reported.
E
Because of the degree to which sulfur segregates, product analysis for sulfur over 0.060 % max is not technologically appropriate.
F
As described in Specification A276.
G
Grade 4 is expected to be withdrawn within approximately 2 years. Grade 7 is an acceptable substitute for Grade 4. See 7.2.
A194/A194M−14a
A
TABLE 2 Hardness Requirements
Completed Nuts Sample Nut after Treatment as in 8.1.5
Brinell Rockwell Hardness Brinell Rockwell
Grade and Type
Hardness Hardness, Hardness B
C Scale B Scale
min Scale, min
1 121 min . 70 min 121 70
2 159 to 352 . 84 min 159 84
2H to 1 ⁄2 in. or M36, incl 248 to 327 24 to 35 . 179 89
2H over 1 ⁄2 in. or M36 212 to 327 35 max 95 min 147 79
2HM and 7M 159 to 235 . 84 to 99 159 84
3, 4, 7, and 16 248 to 327 24 to 35 . 201 94
6 and 6F 228 to 271 20 to 28 . . .
8, 8C, 8CLN, 8M, 8T, 8F, 8P, 126 to 300 32 max 60 min . .
8N,
8MN, 8LN, 8MLN,
8MLCuN, 8ML4CuN,
and 9C
8A, 8CA, 8CLNA, 8MA, 8TA, 126 to 192 . 60 to 90 . .
8FA, 8PA, 8NA, 8MNA,
8LNA, 8MLNA,
8MLCuNA,
8ML4CuNA,
and 9CA
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A194/A194M − 14 A194/A194M − 14a Endorsed by
Manufacturers Standardization Society
of the Valve and Fittings Industry
Used in USNRC-RDT Standards
Standard Specification for
Carbon and Alloy Steel Nuts for Bolts for High Pressure or
High Temperature Service, or Both
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A194/A194M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers a variety of carbon, alloy, and martensitic stainless steel nuts in the size range ⁄4 through 4 in.
and metric M6 through M100 nominal. It also covers austenitic stainless steel nuts in the size range ⁄4 in. and M6 nominal and
above. These nuts are intended for high-pressure or high-temperature service, or both. Grade substitutions without the purchaser’s
permission are not allowed.
1.2 Bars from which the nuts are made shall be hot-wrought. The material may be further processed by centerless grinding or
by cold drawing. Austenitic stainless steel may be solution annealed or annealed and strain-hardened. When annealed and strain
hardened austenitic stainless steel is ordered in accordance with Supplementary Requirement S1, the purchaser should take special
care to ensure that 8.2.2, Supplementary Requirement S1, and Appendix X1 are thoroughly understood.
1.3 Supplementary requirements of an optional nature are provided. These shall apply only when specified in the inquiry,
contract, and order.
1.4 This specification is expressed in both inch-pound units and in SI units. However, unless the order specifies the applicable“
M” specification designation (SI units), the material shall be furnished to inch-pound units.
1.5 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A153/A153M Specification for Zinc Coating (Hot-Dip) on Iron and Steel Hardware
A276 Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes
A320/A320M Specification for Alloy-Steel and Stainless Steel Bolting for Low-Temperature Service
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A962/A962M Specification for Common Requirements for Bolting Intended for Use at Any Temperature from Cryogenic to the
Creep Range
B633 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc on Iron and Steel
B695 Specification for Coatings of Zinc Mechanically Deposited on Iron and Steel
B696 Specification for Coatings of Cadmium Mechanically Deposited
B766 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings of Cadmium
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
E566 Practice for Electromagnetic (Eddy Current) Sorting of Ferrous Metals
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloysand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.22
on Steel Forgings and Wrought Fittings for Piping Applications and Bolting Materials for Piping and Special Purpose Applications.
Current edition approved May 1, 2014Nov. 1, 2014. Published June 2014November 2014. Originally approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as
A194/A194M–13.–14. DOI: 10.1520/A0194_A0194M-14.10.1520/A0194_A0194M-14A.
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Specification SA-194 in Section II of that code.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A194/A194M − 14a
F606 Test Methods for Determining the Mechanical Properties of Externally and Internally Threaded Fasteners, Washers, Direct
Tension Indicators, and Rivets
F1940 Test Method for Process Control Verification to Prevent Hydrogen Embrittlement in Plated or Coated Fasteners
F1941 Specification for Electrodeposited Coatings on Threaded Fasteners (Unified Inch Screw Threads (UN/UNR))
F2329 Specification for Zinc Coating, Hot-Dip, Requirements for Application to Carbon and Alloy Steel Bolts, Screws, Washers,
Nuts, and Special Threaded Fasteners
2.2 ASME Standards:
B 1.1 Unified Screw Threads
B 1.2 Gages and Gaging for Unified Inch Screw Threads
B 1.13M Metric Screw Threads
B 18.2.2 Square and Hex Nuts
B 18.2.4.6M Metric Heavy Hex Nuts
2.3 ISO Standards:
4033 Hexagon High Nuts (Style 2) – Product A and B
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 Austenitic Grades—All grades with a prefix of “8” or “9.”
3.1.2 Ferritic Grades—Grades 1, 2, 2H, 2HM, 3, 4, 6, 6F, 7, 7M, and 16.
3.1.3 Lot—Unless otherwise specified (see Discussion below), a lot is the quantity of nuts of a single nominal size and grade
produced by the same manufacturing process.
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, Two Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
www.asme.org.
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—
When Supplementary Requirement S5 is invoked on the purchase order, the following definitions of a lot shall apply:
3.1.3.2 For Grade 8 Nuts—The quantity of all the nuts of a single nominal diameter and grade made from the same heat of steel
and made by the same manufacturing process.
3.1.3.3 For All Other Grade Nuts—(see 8.2 and 8.1.2.1)—All the nuts of a single nominal diameter and grade made from the
same heat number and heat treated in the same batch if batch-type heat treating equipment is used or heat treated in the same
continuous run of not more than 8 h under the same conditions if continuous-type heat treating equipment is used.
3.1.4 Type:
3.1.4.1 For Grade 8 Nuts—Variations within the grade designated by a letter and differentiated by chemistry and by
manufacturing process.
3.1.4.2 For Grade 6 Nuts—Variations within the grade designated by the letter F as differentiated by chemical additions made
for machineability.
3.1.5 Series—The dimensional relationship and geometry of the nuts as described in ASME B 18.2.2 or B 18.2.4.6M.for inch
nuts and ISO 4033 for metric nuts sizes M6 through M10 and ASME B 18.2.4.6M for nuts sizes M12 through M100.
4. Ordering Information
4.1 The inquiry and order for material under this specification shall include the following as required to describe the material
adequately:
4.1.1 Specification designation, year date, and grade, issue date and revision letter,
4.1.2 Quantity, number of pieces,
4.1.3 Dimensions (see Section 9),
4.1.4 Options in accordance with 8.2.2.1, 9.1, 9.2, 10.3, and 12, and
4.1.5 Supplementary Requirements, if any.
4.2 Coatings—Coatings are prohibited unless specified by the purchaser (see Supplementary Requirements S7 and S8). When
coated nuts are ordered, the purchaser should take special care to ensure that Appendix X2 is thoroughly understood.
4.3 See Supplementary Requirement S3 for nuts to be used in low temperature applications (Specification A320/A320M).
4.4 Proof Load Testing—See Supplementary Requirement S9 for proof load testing of nuts manufactured to dimensions and
configurations other than those covered in Tables 3 and 4.
A194/A194M − 14a
A,B,C,D
TABLE 1 Chemical Requirements
Manga- Phospho- Molyb- Tita- Other
E
Grade UNS Carbon, Silicon, Chromium, Nickel, Colum- Nitrogen,
Sulfur,
Material nese, rus, denum, nium, Elements,
Symbol Number % % % % % bium % %
% % % % %
1 carbon 0.15 min 1.00 0.040 0.050 0.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2, 2HM, carbon 0.40 min 1.00 0.040 0.050 0.40 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
and 2H
G
4 carbon, 0.40–0.50 0.70–0.90 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 . . . . . . 0.20–0.30 . . . . . . . . . . . .
molyb-
denum
3 Type 501 0.10 min 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 4.0–6.0 . . . 0.40–0.65 . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Type 410 S41000 0.08–0.15 1.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 11.5–13.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6F Type 416 S41600 0.15 1.25 0.060 0.15 min 1.00 12.0–14.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6F Type S41623 0.15 1.25 0.060 0.060 1.00 12.0–14.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . Selenium,
416Se 0.15 min
7, 7M Type 0.38–0.48 0.75–1.0 0.035 0.04 0.15–0.35 0.80–1.10 . . . 0.15–0.25 . . . . . . . . . . . .
4140/
4142/
4145,
4140H,
4142H,
4145H
8, 8A Type 304 S30400 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8C, 8CA Type 347 S34700 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 . . . . . . 10 x . . . . . .
carbon
content,
min 1.10
8CLN, Type S34751 0.005- 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–13.0 . . . . . . 0.20–0.50, 0.06–0.10 . . .
8CLNA 347LN 0.020 15 x
carbon
content,
min
8M, 8MA Type 316 S31600 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–14.0 2.00–3.00 . . . . . . . . . . . .
8T, 8TA Type 321 S32100 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 9.0–12.0 . . . 5 x . . . 0.10 . . .
(C+N)
min -
0.70
max
8F, 8FA Type 303 S30300 0.15 2.00 0.20 0.15 min 1.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8F, 8FA Type S30323 0.15 2.00 0.20 0.06 1.00 17.0–19.0 8.0–10.0 . . . . . . . . . Selenium,
303Se 0.15 min
8P, 8PA Type 305 S30500 0.12 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 17.0–19.0 11.0–13.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8N, 8NA Type S30451 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
304N
8LN, Type S30453 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 18.0–20.0 8.0–11.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
8LNA 304LN
8MN, Type S31651 0.08 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–13.0 2.00–3.00 . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
8MNA 316N
8MLN, Type S31653 0.030 2.00 0.045 0.030 1.00 16.0–18.0 10.0–13.0 2.00–3.00 . . . . . . 0.10–0.16
8MLNA 316LN
F
8R, 8RA XM19 S20910 0.06 4.0–6.0 0.045 0.030 1.00 20.5–23.5 11.5–13.5 1.50–3.00 . . . 0.10–0.30 0.20–0.40 Vanadium,
0.10–0.30
8S, 8SA S21800 0.10 7.0–9.0 0.060 0.030 3.5–4.5 16.0–18.0 8.0–9.0 . . . . . . . . . 0.08–0.18
8MLCuN, S31254 S31254 0.020 1.00 0.030 0.010 0.80 19.5–20.5 17.5–18.5 6.0–6.5 . . . . . . 0.18–0.22 Copper,
8MLCuNA 0.50–1.00
B8ML4CuN S31730 S31730 0.030 2.00 0.040 0.010 1.00 17.0–19.0 15.0–16.5 3.0–4.0 . . . . . . 0.045 Copper
4.0–5.0
9C, 9CA N08367 N08367 0.030 2.00 0.040 0.030 1.00 20.0-22.0 23.5- 25.5 6.0-7.0 0.18-0.25 Copper
0.75
A194/A194M − 14a
TABLE 1 Continued
Manga- Phospho- Molyb- Tita- Other
E
Grade UNS Carbon, Silicon, Chromium, Nickel, Colum- Nitrogen,
Sulfur,
Material nese, rus, denum, nium, Elements,
%
Symbol Number % % % % bium % %
% % % % %
16 Chromium 0.36–0.47 0.45–0.70 0.035 0.040 0.15–0.35 0.80–1.15 . . . 0.50–0.65 . . . . . . . . . Vanadium,
Molyb- 0.25–0.35
B
denum Aluminum
0.015
Vanadium
A
The intentional addition of Bi, Se, Te, and Pb is not permitted except for Grades 6F, 8F, and 8FA, in which Se is specified and required.
B
Total aluminum, soluble and insoluble.
C
Maximum, unless minimum or range is indicated.
D
Where ellipses ({) appear in this table there is no requirement.requirement and the element need not be determined or reported.
E
Because of the degree to which sulfur segregates, product analysis for sulfur over 0.060 % max is not technologically appropriate.
F
As described in Specification A276.
G
Grade 4 is expected to be withdrawn within approximately 2 years. Grade 7 is an acceptable substitute for Grade 4. See 7.2.
A194/A194M − 14a
A
TABLE 2 Hardness Requirements
Completed Nuts Sample Nut after Treatment as in 8.1.5
Brinell Rockwell Hardness Brinell Rockwell
Grade and Type
Hardness Hardness, Hardness B
C Scale B Scale
min Scale, min
1 121 min . 70 min 121 70
2 159 to 352 . 84 min 159 84
2H to 1 ⁄2 in. or M36, incl 248 to 327 24 to 35 . 179 89
2H over 1 ⁄2 in. or M36 212 to 327 35 max 95 min 147 79
2HM and 7M 159 to 235 . 84 to 99 159 84
3, 4, 7, and 16 248 to 327 24 to 35 . 201 94
6 and 6F 228 to 271 20 to 28 . . .
8, 8C, 8CLN, 8M, 8T, 8F, 8P, 126 to 300 32 max 60 min . .
8N,
8MN, 8LN, 8MLN,
8MLCuN, and
9C
8, 8C, 8CLN, 8M, 8T, 8F, 8P, 126 to 300 32 max 60 min . .
8N,
8MN, 8LN, 8MLN,
8MLCuN, 8ML4CuN,
and 9C
8A, 8CA, 8CLNA, 8MA, 8TA, 126 to 192 . 60 to 90 . .
8FA, 8PA, 8NA, 8MNA,
8LNA, 8MLNA,
8MLCuNA,
and 9CA
8A, 8CA, 8CLNA, 8MA, 8TA, 126 to 192 . 60 to 90 . .
8FA, 8PA, 8NA, 8MNA,
8LNA, 8MLNA,
8MLCuNA,
8ML4CuNA,
and 9CA
8R, 8RA, 8S, and 8SA 183 to 271 25 max 88 min . .
A
Where ellipses ({) appear in this table there is no requirement.
5. Common Requirements
5.1 Material and fasteners supplied to this specification shall conform to the requirements of Specification A962/A962M. These
requirements include test methods, finish, thread dimensions, marking, certification, optional supplementary requirements, and
others. Failure to comply with the requirements of Specification A962/A962M constitutes nonconformance with this specification.
In case of conflict between the requirements of this specification and Specification A962/A962M, this specification shall prevail.
6. Manufacture (Process)
6.1 Stainless steels for all types of Grade 6 and 8 nuts shall be made by one of the following processes:
6.1.1 Electric-furnace (with separate degassing and refining optional),
6.1.2 Vacuum induction furnace, or
6.1.3 Either of the above followed by electroslag remelting, or consumable-arc remelting.
6.2 The steel producer shall exercise adequate control to eliminate excessive unhomogeneity, nonmetallics, pipe, porosity, and
other defects.
6.3 Grades 1 and 2 nuts shall be hot or cold forged, or shall be machined from hot-forged, hot-rolled, or cold-drawn bars.
6.3.1 All Grade 1 and 2 nuts shall be stress-relief annealed at a temperature of at least 1000 °F [538 °C] after forming or
machining from bar wi
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.