ASTM F2147-01(2006)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Guinea Pig: Split Adjuvant and Closed Patch Testing for Contact Allergens
Standard Practice for Guinea Pig: Split Adjuvant and Closed Patch Testing for Contact Allergens
ABSTRACT
This practice is intended to determine the potential for a substance, or material extract, to elicit contact dermal allergenicity. It is intended as an alternative to the Guinea Pig Maximization Test (GPMT), given the limitations on dosage form and tendency for false positives associated with the latter test. The split adjuvant method is used when topical application is considered relevant, and the dosage form is a solid, liquid, extract, paste, or gel. The method includes four induction doses applied over a period of time to the same shaved or depilated site on guinea pigs, followed by occlusive patching. Freund's Complete Adjuvant (FCA) is injected near the dose site on a specific time, (second induction dose). Following a rest period, animals are challenged at a previously unexposed site, and the reaction evaluated at regular intervals. The closed patch method is used when topical application is relevant, but the preferred dosage form does not permit injection under the skin or intradermally, and the discomfort involved with extended occlusive patching and adjuvant use is to be avoided. It involves repeated induction doses over a period of time at the same shaved/depilated site, followed each time by occlusive wrapping. After a rest period, animals are challenged at previously untreated sites, and their reactions evaluated after a period of time.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is intended to determine the potential for a substance, or material extract, to elicit contact dermal allergenicity.
1.2 This practice is intended as an alternative to the Guinea Pig Maximization Test (GPMT), given the limitations on dosage form and tendency for false positives associated with the latter test. See Rationale and References.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
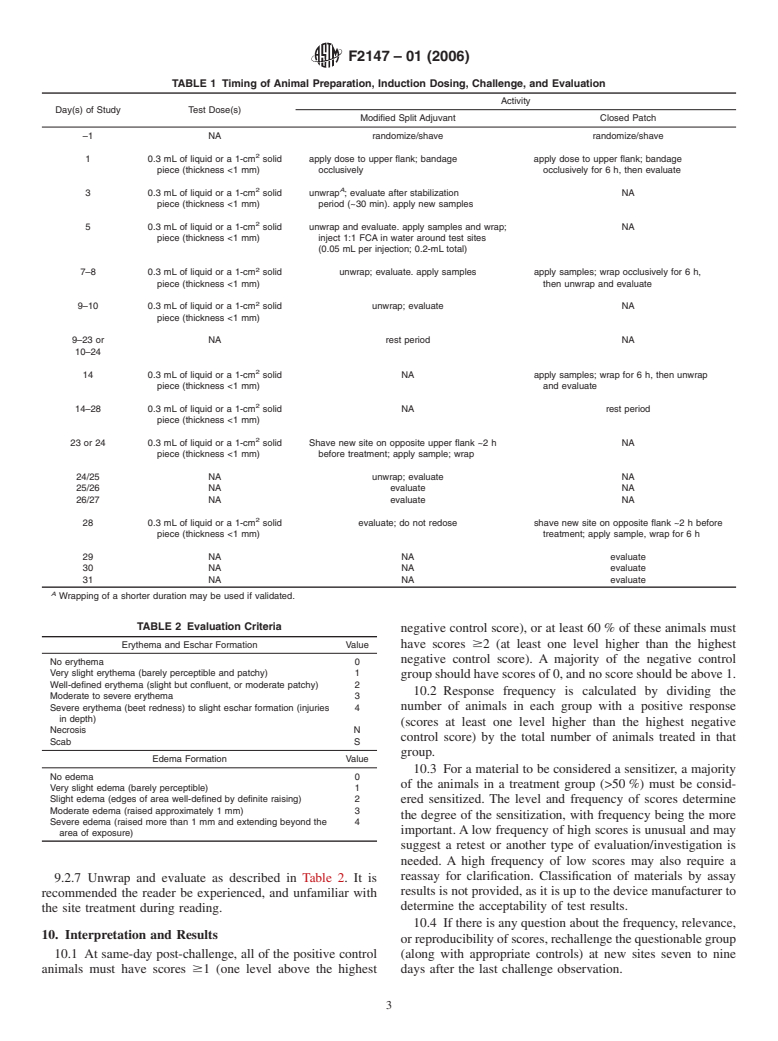
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2147–01 (Reapproved 2006)
Standard Practice for
Guinea Pig: Split Adjuvant and Closed Patch Testing for
Contact Allergens
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2147; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Practice
4.1 The split adjuvant method is used when topical appli-
1.1 This practice is intended to determine the potential for a
substance, or material extract, to elicit contact dermal allerge- cation is considered relevant, and the dosage form is a solid,
nicity. liquid, extract, paste, or gel. The method includes four induc-
1.2 This practice is intended as an alternative to the Guinea tion doses applied over ten days to the same shaved or
Pig Maximization Test (GPMT), given the limitations on depilated site on guinea pigs, followed by occlusive patching.
dosage form and tendency for false positives associated with Freund’s Complete Adjuvant (FCA) is injected near the dose
the latter test. See Rationale and References. siteonthefourthday(secondinductiondose).Followingarest
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the period, animals are challenged at a previously unexposed site,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the and the reaction evaluated at 24, 48, and 72 h.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 4.2 The closed patch method is used when topical applica-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- tion is relevant, but the preferred dosage form does not permit
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. injection under the skin or intradermally, and the discomfort
involved with extended occlusive patching and adjuvant use is
2. Referenced Documents
tobeavoided.Itinvolvesrepeatedinductiondoses(3to6)over
2.1 ASTM Standards: 14 days at the same shaved/depilated site, followed each time
F619 Practice for Extraction of Medical Plastics
by6hof occlusive wrapping. After a rest period, animals are
F720 Practice for Testing Guinea Pigs for Contact Aller- challenged at previously untreated sites, and their reactions
gens: Guinea Pig Maximization Test
evaluated at least 24 and 48 h later.
2.2 ISO Document:
5. Significance and Use
ISO 10993-10, 1995 Tests for Irritation and Sensitization
5.1 In selecting a material for human contact in medical
3. Terminology
applications, it is important to ensure the material will not
3.1 Definitions: stimulate the immune system to produce an allergic reaction
3.1.1 2,4 dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB)—strong sensitizer,
under relevant exposure conditions. Extractable chemicals
used as a positive control. produced by skin contact or during physiological exposures
3.1.2 Freund’s Complete Adjuvant (FCA)—a
may cause allergic reactions. Therefore, this practice provides
commercially-available mixture of oil and Mycobacterium that for evaluations of solid or semisolid dosage forms using
is known to elicit an immune response.
material extracts or direct evaluation of the test article. The
3.1.3 Guinea Pig Maximization Test (GPMT)—procedure rationale for this animal model is based on the fact that the
describedinPracticeF720acceptedasa“worstcase”assayfor
guinea pig has been shown to be an appropriate animal model
allergenic potential. for predicting human contact dermatitis; its tractable nature, its
availability from reputable suppliers, the historical database of
information already acquired using this species, and the corre-
ThispracticeisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF04onMedicaland
lation of such results to data on known human allergens, all
Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
contribute to its widespread use for allergenicity studies (1-5).
F04.16 on Biocompatibility Test Methods.
5.2 The need for sensitization procedures other than the
Current edition approved March 1, 2006. Published April 2006. Originally
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as F2147 – 01. DOI:
maximization test (Practice F720) is based on: (1) the need for
10.1520/F2147-01R06.
a route of exposure more similar to use conditions, (2) concern
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
overtheuseofadjuvantbecauseofitsrecruitmentofcelltypes
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to the list of references at the end of
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036. this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2147–01 (2006)
tothetestsitewhicharenottypicallyinvolvedinimmunologic numbers of these tests and results are consistent. The latter
reactions, and because of the discomfort this causes in the practice reduces animal usage.
animals, (3) absence of a proper FCA-irritant control group in
the traditional maximization design, and (4) the frequency of 8. Trial and Naive Challenge Tests
falsepositivesoftenencounteredwiththeGPMT.Bothofthese
8.1 It is recommended that at least two guinea pigs be used
tests are internationally accepted (1).
to assess the ability of the test article or undiluted extract to
irritate. Each flank of each animal can be used to patch two
6. Materials and Manufacturers
sites (upper and lower) of samples such as test article, 100 %
6.1 Hartley strain guinea pigs, either sex (but all in the test
extract, 75 % extract, and 50 % extract. Animals should be
of the same sex), 300 to 500 g at start of test, should be from
shavedandwrappedasinthecompletetest(seeSection9),and
the same shipment, same supplier, and should be healthy.
the sites evaluated after 24 to 72 h. Scoring should also be
6.2 At least ten animals are used for each test material and
performed as in the complete test.
five for each control group.
8.2 It is also advisable to determine the difference between
6.3 Freund’s Complete Adjuvant (FCA) (split adjuvant test
irritation and sensitization under full test conditions for the
only).
positive control by including in at least one test per laboratory
6.4 Cotton gauze and occlusive bandage (examples, Elasto-
a“naivechallenge”groupwhichisexposedtocontrolsonlyfor
pore from 3M) or Hilltop chambers (Hilltop, Cincinnati, OH)
the challenge period. DNCB, for example, can be an irritant,
(optional for solid samples) and Vet wrap.
and it is important that erythema and edema reactions seen
6.5 Positive control substance (0.1 to 1 % 2,4 DNCB is a
after challenge be true sensitization responses.
strong sensitizer; to test method sensitivity, it may be advisable
to use cinnamaldehyde (10 % induction, 1 % challenge) as a
9. Procedure
positive control (2)).
NOTE 3—This procedure is applicable to both methods except as noted.
7. Preparation of Test Samples
9.1 Table 1 shows the timing of animal preparation, induc-
tion dosing, challenge, and evaluation.
NOTE 1—All steps are applicable to both methods.
9.2 Animal Preparation:
7.1 Solid Samples—Cut flat sheet-like samples into 1- by
9.2.1 Weigh and shave or depilate animals within 24 h of
1-cm squares. These can be used for direct contact testing as
test start. Depilatories should be used carefully and tested
long as the sample thickness does not exceed 1.0 mm.
beforehand to understand proper use regimen so as not to
NOTE 2—Pressureexertedbybandagingthicksamplescausesmechani-
produce background irritation. Shave or depilate a site on the
cal irritation. The cotton pad may be removed from the Hilltop chamber
left flank or shoulder area (use one or the other consistently)
(or the chamber need not be used) to reduce pressure on thick solid test
approximately a 2-in. square to expose bare skin, avoiding any
articles. Further cutting should be considered if test articles are still
abrasions or other abnormalities. Check animal health daily
causing pressure without the chamber or chamber pad.
throughout the test.
7.2 Gels, Pastes, Ointments—Semisolid test articles can be
9.2.2 Apply 0.3 mL of extract or semisolid (or less, if the
used directly, applied at 0.2 mL/site.
amount has been validated, or 1 cm of a solid sample (less
7.3 Extracts—Prepare extracts in accordance with Practice
than 1.0 mm thick) to the cotton pad of a Hilltop chamber. (A
F619, at the highest temperature tolerated by the material
padless chamber can be used to dose gels or thicker samples).
without physical melting or decomposition. Both aqueous and
Stick the chamber to the skin and wrap with an appropriate
nonaqueous extracts are recommended. Extracts should be
elastic bandage. If a Hilltop chamber is not used, apply the test
decanted upon cooling, stored at room temperature (22 to
sample to gauze and cover with occlusive wrap. Follow the
30°C), and used within 24 h. Extracts should be prepared fresh
unwrap/evaluate schedule for the particular procedure as in
for each treatment, preferably using a solvent which does not
Table 1.
give background reactions (ethanol is sometimes a problem in
9.2.3 After unwrapping, wait about 30 min before evalua-
this regard), and is known to produce measurable extractables
tion. The test article may be removed by gentle wiping with
(determined by a technique such as a nonvolatile residue test)
gauze soaked with purified water or isopropyl alcohol (IPA)
without dissolving the test article.
that has been diluted such that it will not dry the skin. Evaluate
7.4 Negative Controls—Prepare solvent sham controls
the site using the criteria in Table 2. Rewrap if required (split
(“blanks”) under the same conditions as test article extracts.
adjuvant.)
Saline controls may be eliminated if there are sufficient data
9.2.4 Repeat doses as outlined in Table 1. At the second
available to
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.