ASTM G155-21
(Practice)Standard Practice for Operating Xenon Arc Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Materials
Standard Practice for Operating Xenon Arc Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The apparatus exposes specimens to light, heat, and optionally moisture, often to attempt to replicate specimen property changes observed in outdoor and indoor end-use environments. Exposures are not intended to simulate the deterioration caused by localized weather phenomena, such as atmospheric pollution, biological attack, and saltwater exposure.
5.2 This practice allows a wide range of exposure conditions that may produce significantly different results. Therefore, no reference shall be made to results from its use unless accompanied by a report in conformance with Section 10 detailing the specific operating conditions.
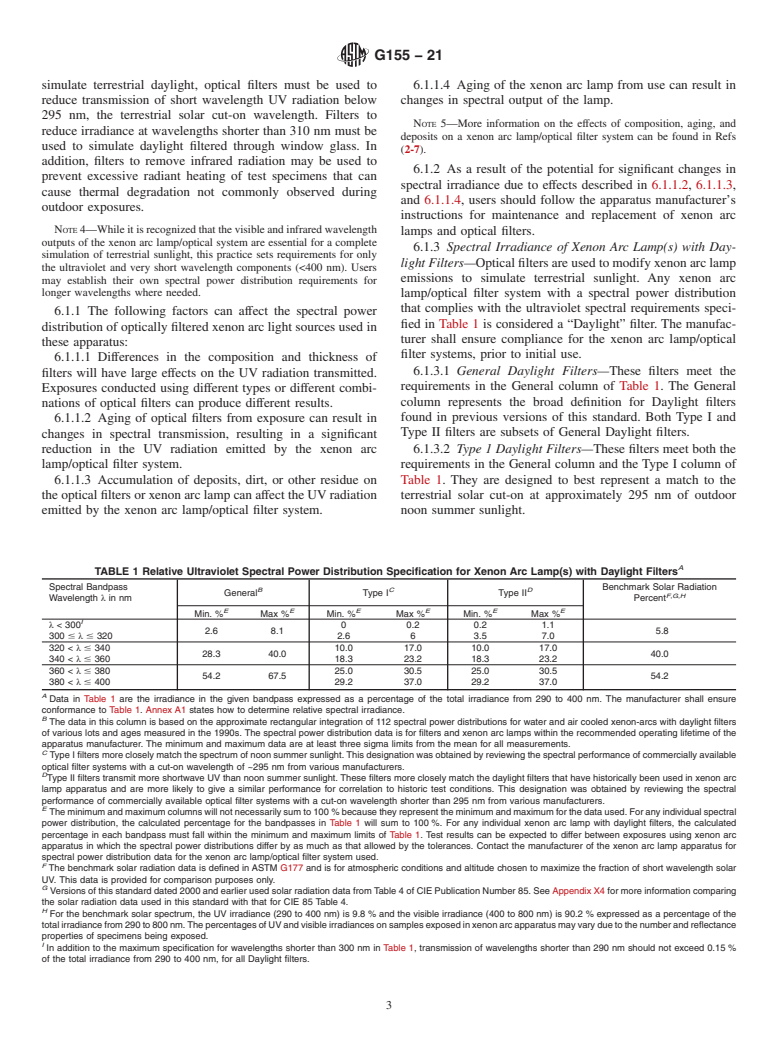
5.2.1 A control (a similar material of known performance) should be exposed simultaneously with the test specimen to provide a reference for comparative purposes. It is best practice to use two different control materials: one known to have relatively poor durability and one known to have relatively good durability. At least three replicates of each test specimen and control material should be exposed concurrently to permit statistical evaluation of results.
5.3 Comparison of results obtained from specimens exposed in different apparatus (even if the apparatus is the same model) using the identical setpoints and operational controls should not be made unless reproducibility has been established between apparatus for the material to be tested.
5.4 Refer to Practice G151 for cautionary guidance applicable to all laboratory weathering apparatus.
5.5 It is recommended that users follow good laboratory practices in order to reduce variability in exposures (1).8
SCOPE
1.1 This practice is limited to the basic principles and procedures for operating a xenon arc lamp and water apparatus; on its own, it does not deliver a specific result.
1.2 It is intended to be used in conjunction with a practice or method that defines specific exposure conditions for an application along with a means to evaluate changes in material properties. This practice is intended to reproduce the weathering effects that occur when materials are exposed to sunlight (either direct or through window glass) and moisture as humidity, rain, or dew in actual use. This practice is limited to the procedures for obtaining, measuring, and controlling conditions of exposure.
Note 1: A number of exposure procedures are listed in an appendix; however, this practice does not specify the exposure conditions best suited for the material to be tested.
Note 2: Practice G151 describes general procedures and performance requirements to be used when exposing materials in an apparatus that uses laboratory light sources.
1.3 Test specimens are exposed to light from an optically-filtered xenon arc lamp under controlled environmental conditions. Different types of optical filters in combination with xenon arc light sources are described.
1.4 Specimen preparation and evaluation of the results are covered in ASTM methods or specifications for specific materials. General guidance is given in Practice G151.
Note 3: General information about methods for determining the change in properties after exposure and reporting these results is described in Practice D5870.
1.5 This practice is not intended for corrosion testing of bare metals.
1.6 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.7 This practice is technically similar to the following ISO documents: ISO 4892-2, ISO 16474-2, ISO 105-B02, ISO 105-B04, ISO 105-B05, ISO 105-B06, and ISO 105-B10.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8.1 Should any ozone be generated from the operation of the la...
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: G155 − 21
Standard Practice for
Operating Xenon Arc Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of
1
Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G155; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 1.7 This practice is technically similar to the following ISO
documents: ISO 4892-2, ISO 16474-2, ISO 105-B02, ISO
1.1 This practice is limited to the basic principles and
105-B04, ISO 105-B05, ISO 105-B06, and ISO 105-B10.
procedures for operating a xenon arc lamp and water apparatus;
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
on its own, it does not deliver a specific result.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.2 It is intended to be used in conjunction with a practice or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
method that defines specific exposure conditions for an appli-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
cation along with a means to evaluate changes in material
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
properties. This practice is intended to reproduce the weather-
1.9 Should any ozone be generated from the operation of the
ing effects that occur when materials are exposed to sunlight
lamp(s), it shall be carried away from the test specimens and
(either direct or through window glass) and moisture as
operating personnel by an exhaust system.
humidity, rain, or dew in actual use. This practice is limited to
1.10 This international standard was developed in accor-
the procedures for obtaining, measuring, and controlling con-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ditions of exposure.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
NOTE 1—A number of exposure procedures are listed in an appendix;
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
however, this practice does not specify the exposure conditions best suited
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
for the material to be tested.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
NOTE 2—Practice G151 describes general procedures and performance
requirements to be used when exposing materials in an apparatus that uses
laboratory light sources.
2. Referenced Documents
2
1.3 Test specimens are exposed to light from an optically-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
filtered xenon arc lamp under controlled environmental condi-
D2565 Practice for Xenon-Arc Exposure of Plastics In-
tions. Different types of optical filters in combination with
tended for Outdoor Applications
xenon arc light sources are described.
D5870 Practice for Calculating Property Retention Index of
Plastics
1.4 Specimen preparation and evaluation of the results are
D6695 Practice for Xenon-Arc Exposures of Paint and
covered in ASTM methods or specifications for specific
Related Coatings
materials. General guidance is given in Practice G151.
D7869 Practice for Xenon Arc Exposure Test with Enhanced
NOTE 3—General information about methods for determining the
Light and Water Exposure for Transportation Coatings
change in properties after exposure and reporting these results is described
G26 Practice for Operating Light-Exposure Apparatus
in Practice D5870.
(Xenon-Arc Type) With and Without Water for Exposure
1.5 This practice is not intended for corrosion testing of bare
of Nonmetallic Materials (Discontinued 2001) (With-
metals.
3
drawn 2000)
1.6 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
G113 Terminology Relating to Natural and Artificial Weath-
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
ering Tests of Nonmetallic Materials
standard.
1 2
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G03 on Weathering For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and Durability and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G03.03 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Simulated and Controlled Exposure Tests. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved July 1, 2021. Published September 2021. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as G155 – 13. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/G0155-21. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: G155 − 13 G155 − 21
Standard Practice for
Operating Xenon Arc LightLamp Apparatus for Exposure of
1
Non-Metallic Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G155; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*Scope
1.1 This practice is limited to the basic principles and procedures for operating a xenon arc lamp and water apparatus; on its own,
it does not deliver a specific result.
1.2 This practice covers the basic principles and operating procedures for using xenon arc light and water apparatus It is intended
to be used in conjunction with a practice or method that defines specific exposure conditions for an application along with a means
to evaluate changes in material properties. This practice is intended to reproduce the weathering effects that occur when materials
are exposed to sunlight (either direct or through window glass) and moisture as rain humidity, rain, or dew in actual use. This
practice is limited to the procedures for obtaining, measuring, and controlling conditions of exposure. A number of exposure
procedures are listed in an appendix; however, this practice does not specify the exposure conditions best suited for the material
to be tested.
NOTE 1—A number of exposure procedures are listed in an appendix; however, this practice does not specify the exposure conditions best suited for the
material to be tested.
NOTE 2—Practice G151 describes performance criteria for all exposure devices that usegeneral procedures and performance requirements to be used when
exposing materials in an apparatus that uses laboratory light sources. This practice replaces Practice G26, which describes very specific designs for devices
used for xenon-arc exposures. The apparatus described in Practice G26 is covered by this practice.
1.3 Test specimens are exposed to filtered light from an optically-filtered xenon arc lightlamp under controlled environmental
conditions. Different types of optical filters in combination with xenon arc light sources and different filter combinations are
described.
1.4 Specimen preparation and evaluation of the results are covered in ASTM methods or specifications for specific materials.
General guidance is given in Practice G151 and ISO 4892-1. More specific information about methods for determining the change
in properties after exposure and reporting these results is described in Practice D5870.
NOTE 3—General information about methods for determining the change in properties after exposure and reporting these results is described in Practice
D5870.
1.5 This practice is not intended for corrosion testing of bare metals.
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G03 on Weathering and Durability and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G03.03 on Simulated
and Controlled Exposure Tests.
Current edition approved June 1, 2013July 1, 2021. Published August 2013September 2021. Originally approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 20052013
as G155 – 05a.G155 – 13. DOI: 10.1520/G0155-13.10.1520/G0155-21.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G155 − 21
1.6 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.7 This practice is technically similar to the following ISO documents: ISO 4892-2, ISO 16474-2, ISO 105-B02, ISO 105-B04,
ISO 105-B05, ISO 105-B06, and ISO 105-B10.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of
the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.8.1 Should any ozone be generated from the operation of the lamp(s), it shall be carried away from the test specimens and
operating personnel by an exhaust system.
1.6 This practice is technically similar to the following ISO documents: ISO 4892-2, ISO 11341, ISO 105 B02, ISO 105 B04, ISO
105 B05, and I
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.