ASTM F2412-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Foot Protection
Standard Test Methods for Foot Protection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The purpose of these test methods is to provide measurable criteria for various hazards.
The protection that can be demonstrated by evaluation of footwear includes the following:
4.2.1 The effectiveness of impact resistant footwear to eliminate or diminish the severity of injury to the toe area of the foot when subjected to a falling object.
4.2.2 The effectiveness of compression resistant footwear to eliminate or diminish the severity of injury to the toe area of the foot when subjected to a compressive force.
4.2.3 The effectiveness of metatarsal protective footwear to eliminate or diminish the severity of injury to the metatarsal area adjacent to where the toes and the bones of the upper foot intersect.
4.2.4 The effectiveness of conductive footwear to safely reduce the buildup of static electricity from wearer to ground so as to reduce the possibility of ignition of explosives and volatile chemicals.
4.2.5 The effectiveness of electric shock resistant footwear to provide resistance to electric shock when accidental contact is made with live wires.
4.2.6 The effectiveness of static dissipative footwear to reduce the hazards due to excessively low footwear electrical resistance that may exist where SD footwear is required.
4.2.7 The effectiveness of puncture resistant footwear to reduce the possibility of puncture injury to the bottom of the human foot.
4.2.8 The effectiveness of chain saw cut resistant footwear to reduce the chance of injury when exposed to a running power chain saw.
4.2.9 The effectiveness of dielectric insulative footwear to reduce the possibility of injury when exposed to a high voltage charge.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods measure the resistance of footwear to a variety of hazards that can potentially result in injury.
1.2 These test methods may be used to test for compliance to minimum performance requirements in established safety standards.
1.2.1 By agreement between the purchaser and the supplier, or as required by established safety standards, these test methods can be used to determine any one, or all of the following: (1) impact resistance, (2) compression resistance, (3) metatarsal impact resistance, (4) resistance to electrical conductivity, (5) resistance to electric shock, (6) static dissipative performance, (7) puncture resistance of outsoles, (8) chain saw cut resistance, and (9) dielectric insulation.
1.3 &si-value;
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F2412–05
Standard Test Methods for
Foot Protection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2412; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
For more than sixty years, the predecessor to these test methods, ANSI Z41, established the
performance criteria for a wide range of footwear to protect from the hazards that affect the personal
safetyofworkers.ThevalueofthesestandardswasrecognizedearlyinthehistoryoftheOccupational
Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and incorporated as a reference standard in the Code of
Federal Regulation (CFR) Section 1910.
ThesetestmethodscontainstestprotocolsdevelopedinconjunctionwithANSIZ41aswellasother
ASTM standards that are used to evaluate the performance of footwear when exposed to a variety of
hazards: (1) impact resistance for the toe area of footwear; (2) compression resistance for the toe area
of footwear; (3) metatarsal impact protection that reduces the chance of injury to the metatarsal bones
at the top of the foot; (4) conductive properties that reduces hazards that may result from static
electricity buildup and reduce the possibility of ignition of explosives and volatile chemicals; (5)
electric shock resistant non-conductive; (6) static dissipative (SD) properties to reduce hazards due to
excessively low footwear resistance that may exist where SD footwear is required; (7) puncture
resistance of foot bottoms; (8) chain saw cut resistance hazards; and (9) dielectric hazard.
1. Scope priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 These test methods measure the resistance of footwear
to a variety of hazards that can potentially result in injury.
2. Referenced Documents
1.2 These test methods may be used to test for compliance
2.1 ASTM Standards:
to minimum performance requirements in established safety
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
standards.
F1116 Test Method for Determining Dielectric Strength of
1.2.1 By agreement between the purchaser and the supplier,
Dielectric Footwear
or as required by established safety standards, these test
F1458 Test Method for Measurement of Cut Resistance to
methods can be used to determine any one, or all of the
Chain Saw of Foot Protective Devices
following: (1) impact resistance, (2) compression resistance,
2.2 CSA Standard:
(3) metatarsal impact resistance, (4) resistance to electrical
CAN/CSA Z195 Protective Footwear
conductivity, (5) resistance to electric shock, (6) static dissipa-
tive performance, (7) puncture resistance of outsoles, (8) chain
3. Terminology
saw cut resistance, and (9) dielectric insulation.
3.1 Definitions:
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1.1 footwear, n—wearing apparel for the feet (such as
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
shoes, boots, slippers, or overshoes), excluding hosiery.
only.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—Thistermcanrefertoeitherleftfootor
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
right foot units or pairs.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F13 on contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Pedestrian/Walkway Safety and Footwear and are the direct responsibility of Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Subcommittee F13.30 on Footwear. the ASTM website.
Current edition approved March 1, 2005. Published March 2005. DOI: 10.1520/ Available from Canadian Standards Association (CSA), 178 Rexdale Blvd.,
F2412-05. Toronto, ON Canada M9W1R3.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F2412–05
3.1.2 insert, n—footbed normally made of a foam product 4.2.4 The effectiveness of conductive footwear to safely
with leather or fabric cover shaped to cover the entire insole reduce the buildup of static electricity from wearer to ground
which can be inserted between the foot and insole board. so as to reduce the possibility of ignition of explosives and
volatile chemicals.
3.1.3 insole, n—foundation of the shoe; the inner sole of the
shoe which is next to the foot, under the sock liner or insert, 4.2.5 The effectiveness of electric shock resistant footwear
to provide resistance to electric shock when accidental contact
onto which the upper is lasted.
is made with live wires.
3.1.4 last, n—solid hinged form, in the general shape of a
foot, around which footwear is constructed. 4.2.6 The effectiveness of static dissipative footwear to
reduce the hazards due to excessively low footwear electrical
3.1.5 lasting, v—building of footwear around a specific foot
resistance that may exist where SD footwear is required.
form.
4.2.7 The effectiveness of puncture resistant footwear to
3.1.6 lining, n—term used to describe all components that
reduce the possibility of puncture injury to the bottom of the
can be used to construct the interior of the upper portion of the
human foot.
footwear.
4.2.8 The effectiveness of chain saw cut resistant footwear
3.1.7 outsole and heel, n—exterior bottom platform of the
to reduce the chance of injury when exposed to a running
footwear; the bottom surface.
power chain saw.
3.1.8 product category, n—description for a type of foot-
4.2.9 The effectiveness of dielectric insulative footwear to
wear designed and manufactured for a specific hazard or
reduce the possibility of injury when exposed to a high voltage
hazards.
charge.
3.1.9 product classification, n—footwear manufactured to
meet a minimum performance requirement for a specific
5. Impact Resistance
hazard or hazards.
3.1.10 protective footwear, n—footwear that is designed, 5.1 Summary of Method:
constructed, and classified to protect the wearer from a
5.1.1 Footwear with a protective toe cap is impacted with a
potential hazard or hazards.
specified force.
3.1.11 protective toe cap, n—component designed to pro- 5.1.2 After impact, the height of the clay cylinder is
vide toe protection that is an integral and permanent part of the
measured.
footwear.
5.2 Apparatus:
3.1.12 quarter, n—entire back portion of the footwear
5.2.1 The apparatus as shown in Fig. 1 consists of a frame
upper.
structure that permits the impactor to be constrained to fall
3.1.13 size, n—length and breadth measurements of foot- along a known and repeatable path.
wear determined by using a specific grading; the American
5.2.1.1 The impactor consists of a steel weight having a
system of footwear grading.
massof22.7 60.23kg(50 60.5lb).Thenoseoftheimpactor
3.1.14 socklining, n—material placed over the insole which is a steel cylinder having a diameter of 25.4 6 0.8 mm (1 6
is imprinted with a brand name or other designation. 0.03in.)andlengthof50.8mm(2.0in.).Theimpactsideofthe
cylinder has a smooth spherical surface with a radius of 25.4 6
3.1.15 specimen, for protective footwear, n—footwear units
0.127mm(1.00 60.005in.).Thelongitudinalcenterlineofthe
evaluated for various hazards.
cylinderisparallelandcoincidentwith3.175mm(0.125in.)to
3.1.15.1 Discussion—Footwear units may be a left foot, a
the symmetry of its vertical axis.
right foot, or a matched pair. The exact number and type of
5.2.1.2 Apparatus incorporates a means of measuring the
footwear units is indicated by test method.
velocity at impact with a tolerance of 62 %. The use of a
3.1.16 upper, n—parts of a shoe or boot that are above the
velocity metering system allows for determining the time
sole.
required for a 25.4-mm (1-in.) wide blade to pass completely
through a beam of light prior to the impactor striking the
4. Significance and Use
specimen. The result, referred to as gate time, is measured in
4.1 The purpose of these test methods is to provide measur-
ms. The speed in in./s can be calculated using the following
able criteria for various hazards.
formula:
4.2 The protection that can be demonstrated by evaluation
of footwear includes the following:
V 5 (1)
t
g
4.2.1 The effectiveness of impact resistant footwear to
eliminate or diminish the severity of injury to the toe area of
where:
the foot when subjected to a falling object.
V = velocity in in./s, and
4.2.2 The effectiveness of compression resistant footwear to t = gate time in ms.
g
eliminate or diminish the severity of injury to the toe area of 5.2.2 The base of the apparatus consists of a steel plate with
2 2
the foot when subjected to a compressive force. a minimum area 0.3 m (1 ft ) and minimum thickness of 25.4
mm (1 in.). The base is anchored to a structure having a
4.2.3 The effectiveness of metatarsal protective footwear to
minimum mass of 909.1 kg (2000 lb) to provide sufficient
eliminate or diminish the severity of injury to the metatarsal
stability to the apparatus before, during, and after testing.
area adjacent to where the toes and the bones of the upper foot
intersect. 5.3 Sampling:
F2412–05
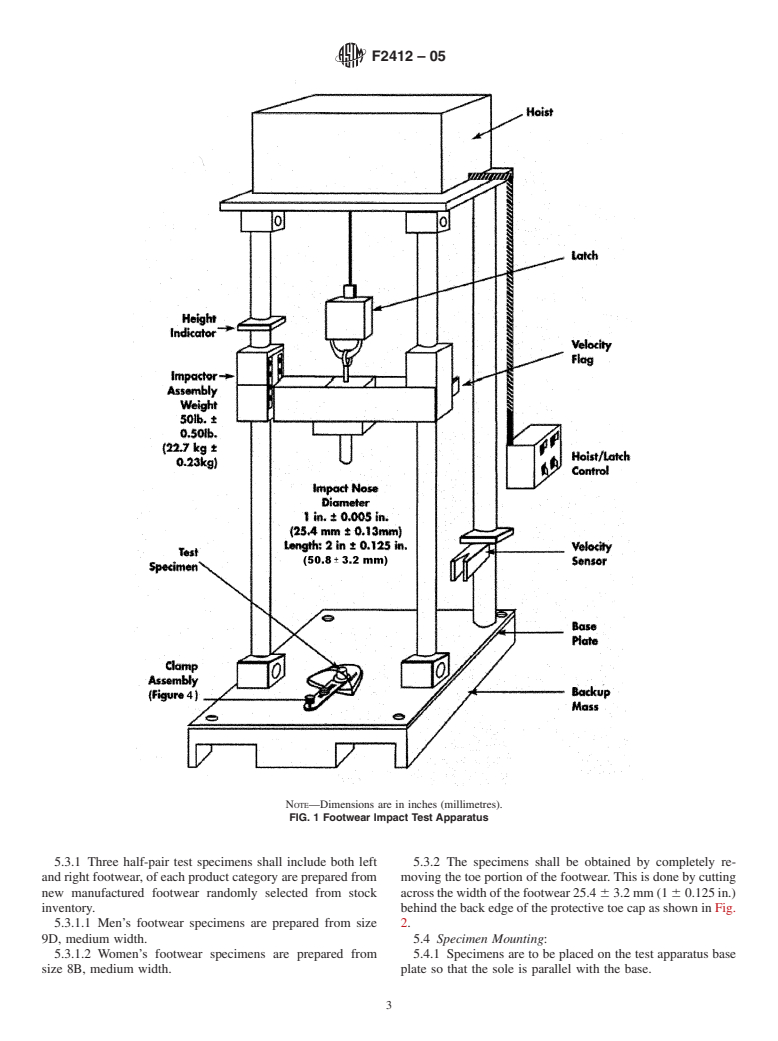
NOTE—Dimensions are in inches (millimetres).
FIG. 1 Footwear Impact Test Apparatus
5.3.1 Three half-pair test specimens shall include both left 5.3.2 The specimens shall be obtained by completely re-
and right footwear, of each product category are prepared from moving the toe portion of the footwear. This is done by cutting
new manufactured footwear randomly selected from stock acrossthewidthofthefootwear25.4 63.2mm(1 60.125in.)
inventory. behind the back edge of the protective toe cap as shown in Fig.
5.3.1.1 Men’s footwear specimens are prepared from size 2.
9D, medium width. 5.4 Specimen Mounting:
5.3.1.2 Women’s footwear specimens are prepared from 5.4.1 Specimens are to be placed on the test apparatus base
size 8B, medium width. plate so that the sole is parallel with the base.
F2412–05
FIG. 2 Specimen Prepared for Compression Testing
either the bottom side or top side of the cylinder to prevent the clay from
5.4.1.1 The specimen is positioned so that the longitudinal
adhering to either the insert/sock liner or dome.
center of the nose of the impactor strikes the approximate
centeroftheprotectivetoecapatapointthatis12.7 61.6mm
5.5.1.2 The diameter of the cylinder shall not exceed 25.4
(0.50 60.0625in.)towardthefrontasmeasuredfromtheback
mm (1 in.).
edge of the protective toe cap (see Fig. 3).
5.5.2 After impact, carefully remove the clay cylinder from
5.4.2 The specimen is held in position during test by use of
inside the specimen and measure the height of the cylinder at
a clamping device as shown in Fig. 4.
its lowest point using a measuring device capable of measuring
5.4.2.1 The stabilizing fork clamp device rests on the insert
to the nearest 0.1 mm (0.004 in.).
and can be adjusted by means of a screw.
5.5.2.1 This value is reported as the impact minimum
5.4.2.2 The adjustment secures the specimen parallel to the
interior height clearance for the specimen.
base plate and prevents movement when the impactor strikes
5.5.3 To measure Class 75 product classification footwear,
the specimen.
the impactor is dropped from a height that results in an impact
5.4.2.3 Clamping screw shall be tightened using a force less
velocity of 2995 6 61 mm/s (117.9 6 2.4 in./s), creating a
than 28 Nm (25 in. lbs).
force of 101.75 J (75 ft-lbf).
5.5 Procedure:
NOTE 2—In a vacuum, the distance would be 457 mm (18 in.). Due to
5.5.1 Prior to impact testing, a lump of modeling clay
friction and air resistance, the height used for the test is somewhat greater.
formed as a vertical cylinder is positioned inside the specimens
directly under the point of impact (see Fig. 3). 5.5.4 To measure Class 50 Product Classification footwear,
5.5.1.1 The clay shall be shaped so that the cylinder the impactor is dropped from a height that results in an impact
velocity of 2438 6 48.3 mm/s (96 6 1.9 in./s), creating a force
simultaneously makes contact with the insole/sock of the
footwear and the dome of the protective toe cap. of 67.8 J (50 ft-lbf).
NOTE 1—A small piece of wax paper or cellophane can be placed on NOTE 3—In a vacuum, the distance would be 305 mm (12 in.). Due to
FIG. 3 Specimen Prepared for Impact Testing
F2412–05
NOTE—Dimensions are in inches (millimetres).
FIG. 4 Position/Clamping/Impact Arrangement
friction and air resistance, the height used for the test is somewhat greater.
6.1.1 Footwear with a protective toe cap is exposed to a
compressive force.
5.6 Test Report—Report the minimum height of the clay
cylinder,withoutroundingup,tothenearest0.1mm(0.004in.) 6.1.2 During application of the compressive force, the
as the clearance result for the product category for all three
interior space of the toe cap is measured using a clay cylinder.
specimens.
6.2 Apparatus:
6.2.1 Compression testing equipment that is equipped with
6. Compression Resistance
smooth steel compression test surfaces.
6.1 Summary of Method:
F2412–05
6.2.1.1 Test surfaces must remain parallel during applica- 7.2 Apparatus:
tion of force up to 44 482 N (10 000 lbf).
7.2.1 The same apparatus as used in 5.2 (Fig. 1) for impact
6.2.1.2 Pressure head has a minimum diameter of 76.2 mm
testing of protective footwear, with certain modifications, is
(3 in.) and a bed plate with a minimum width of 152.4 mm (6
used for metatarsal impact testing. The modifications to the
in.).
apparatus are shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6.
6.2.1.3 Equipment must be graduated in increments so as to
7.2.1.1 The striking surface that impacts the metatarsal
measure compressive force between 222.4 N (50 lbf) to 44 482
protection is a horizontal bar that is perpendicular to the
N (10 000 lbf).
vertical traverse of the test apparatus. The bar of polished steel
6.3 Sampling:
has a diameter of 25.4 6 0.5 mm (1 6 0.02 in.) and a length
6.3.1 A total of three half pair specimens, which shall
of 152.4 6 3.2 mm (6 6 0.125 in.).
include both left and right footwear of each product category,
7.2.1.2 The striking bar is positioned so that the impact is
are prepared from new manufactured footwear randomly
perpendicular to the longitudinal plane of the heel/toe axis at
selected from stock inventory.
the appropriate impact point for men’s and women’s footwear
6.3.1.1 Men’s footwear specimens are
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.