ASTM E1354-14
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Heat and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and Products Using an Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter
Standard Test Method for Heat and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and Products Using an Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used primarily to determine the heat evolved in, or contributed to, a fire involving products of the test material. Also included is a determination of the effective heat of combustion, mass loss rate, the time to sustained flaming, and smoke production. These properties are determined on small size specimens that are representative of those in the intended end use.
5.2 This test method is applicable to various categories of products and is not limited to representing a single fire scenario. Additional guidance for testing is given in X1.2.3 and X1.11.
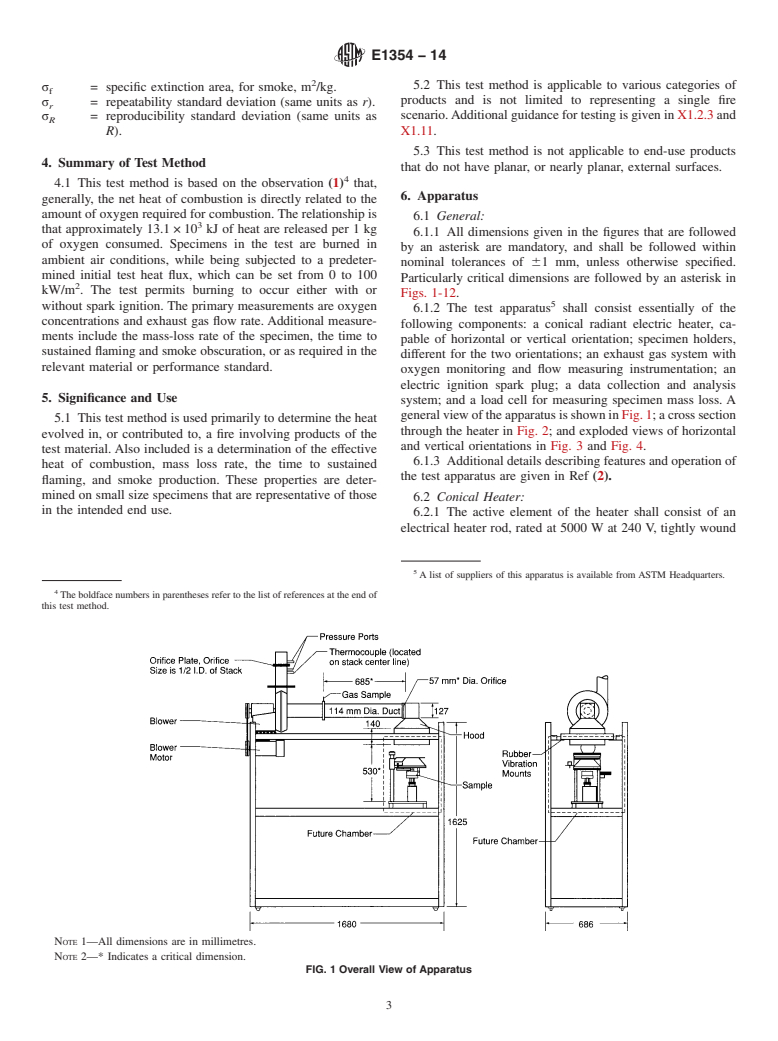
5.3 This test method is not applicable to end-use products that do not have planar, or nearly planar, external surfaces.
SCOPE
1.1 This fire-test-response standard provides for measuring the response of materials exposed to controlled levels of radiant heating with or without an external ignitor.
1.2 This test method is used to determine the ignitability, heat release rates, mass loss rates, effective heat of combustion, and visible smoke development of materials and products.
1.3 The rate of heat release is determined by measurement of the oxygen consumption as determined by the oxygen concentration and the flow rate in the exhaust product stream. The effective heat of combustion is determined from a concomitant measurement of specimen mass loss rate, in combination with the heat release rate. Smoke development is measured by obscuration of light by the combustion product stream.
1.4 Specimens shall be exposed to initial test heat fluxes in the range of 0 to 100 kW/m2. External ignition, when used, shall be by electric spark. The value of the initial test heat flux and the use of external ignition are to be as specified in the relevant material or performance standard (see X1.2). The normal specimen testing orientation is horizontal, independent of whether the end-use application involves a horizontal or a vertical orientation. The apparatus also contains provisions for vertical orientation testing; this is used for exploratory or diagnostic studies only.
1.5 Ignitability is determined as a measurement of time from initial exposure to time of sustained flaming.
1.6 This test method has been developed for use for material and product evaluations, mathematical modeling, design purposes, or development and research. Examples of material specimens include portions of an end-use product or the various components used in the end-use product.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
1.10 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting these tests.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1354 − 14 AnAmerican National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Heat and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and
1
Products Using an Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1354; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.8 This standard is used to measure and describe the
response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and
1.1 This fire-test-response standard provides for measuring
flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself
the response of materials exposed to controlled levels of
incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk
radiant heating with or without an external ignitor.
assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under
1.2 This test method is used to determine the ignitability,
actual fire conditions.
heatreleaserates,masslossrates,effectiveheatofcombustion,
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
and visible smoke development of materials and products.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.3 The rate of heat release is determined by measurement
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
of the oxygen consumption as determined by the oxygen
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
concentration and the flow rate in the exhaust product stream.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
The effective heat of combustion is determined from a con-
statements, see Section 7.
comitant measurement of specimen mass loss rate, in combi-
1.10 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safe-
nation with the heat release rate. Smoke development is
guards for personnel and property shall be employed in
measured by obscuration of light by the combustion product
conducting these tests.
stream.
2. Referenced Documents
1.4 Specimens shall be exposed to initial test heat fluxes in
2
2
the range of 0 to 100 kW/m . External ignition, when used,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
shall be by electric spark. The value of the initial test heat flux
D5865Test Method for Gross Calorific Value of Coal and
and the use of external ignition are to be as specified in the
Coke
relevant material or performance standard (see X1.2). The
E176Terminology of Fire Standards
normal specimen testing orientation is horizontal, independent
E177Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
of whether the end-use application involves a horizontal or a
ASTM Test Methods
vertical orientation. The apparatus also contains provisions for
E603Guide for Room Fire Experiments
vertical orientation testing; this is used for exploratory or
E662Test Method for Specific Optical Density of Smoke
diagnostic studies only.
Generated by Solid Materials
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.5 Ignitability is determined as a measurement of time
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
from initial exposure to time of sustained flaming.
E906Test Method for Heat and Visible Smoke Release
1.6 Thistestmethodhasbeendevelopedforuseformaterial
Rates for Materials and Products Using a Thermopile
and product evaluations, mathematical modeling, design
Method
purposes, or development and research. Examples of material
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
specimens include portions of an end-use product or the
ISO 5657-1986(E)Fire Tests—reaction to fire—ignitability
various components used in the end-use product.
of building materials
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
ISO 5725-2 (1994)Accuracy (trueness and precision) of
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
measurementmethodsandresults—Part2:Basicmethod
standard.
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E05 on Fire For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Standardsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.21 on Smoke and contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Combustion Products. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved May 1, 2014. Published June 2014. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as E1354-13. DOI: Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
10.1520/E1354-14. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1354 − 14
for the dete
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1354 − 13 E1354 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Test Method for
Heat and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and
1
Products Using an Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1354; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This fire-test-response standard provides for measuring the response of materials exposed to controlled levels of radiant
heating with or without an external ignitor.
1.2 This test method is used to determine the ignitability, heat release rates, mass loss rates, effective heat of combustion, and
visible smoke development of materials and products.
1.3 The rate of heat release is determined by measurement of the oxygen consumption as determined by the oxygen
concentration and the flow rate in the exhaust product stream. The effective heat of combustion is determined from a concomitant
measurement of specimen mass loss rate, in combination with the heat release rate. Smoke development is measured by
obscuration of light by the combustion product stream.
2
1.4 Specimens shall be exposed to initial test heat fluxes in the range of 0 to 100 kW/m . External ignition, when used, shall
be by electric spark. The value of the initial test heat flux and the use of external ignition are to be as specified in the relevant
material or performance standard (see X1.2). The normal specimen testing orientation is horizontal, independent of whether the
end-use application involves a horizontal or a vertical orientation. The apparatus also contains provisions for vertical orientation
testing; this is used for exploratory or diagnostic studies only.
1.5 Ignitability is determined as a measurement of time from initial exposure to time of sustained flaming.
1.6 This test method has been developed for use for material and product evaluations, mathematical modeling, design purposes,
or development and research. Examples of material specimens include portions of an end-use product or the various components
used in the end-use product.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard is used to measure and describe the response of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under
controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials,
products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Section 7.
1.10 Fire testing is inherently hazardous. Adequate safeguards for personnel and property shall be employed in conducting
these tests.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D5865 Test Method for Gross Calorific Value of Coal and Coke
E176 Terminology of Fire Standards
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
E603 Guide for Room Fire Experiments
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E05 on Fire Standardsand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E05.21 on Smoke and Combustion
Products.
Current edition approved April 1, 2013May 1, 2014. Published April 2013June 2014. Originally approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 20112013 as
E1354 - 11b.E1354 - 13. DOI: 10.1520/E1354-13.10.1520/E1354-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1354 − 14
E662 Test Method for Specific Optical Density of Smoke Generated by Solid Materials
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E906 Test Method for Heat and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and Products U
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.