ASTM B103/B103M-09
(Specification)Standard Specification for Phosphor Bronze Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
Standard Specification for Phosphor Bronze Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
ABSTRACT
This specification covers plate, rolled bar, sheet, and strip of copper-tin alloy (phosphor bronze plate), copper-tin-lead alloy (leaded phosphor bronze), and copper-tin-lead-zinc alloy (bearing bronze). Copper alloys covered include UNS Nos. C51000, C51100, C51180, C51900, C52100, C52180, C52400, C53400, and C54400. Product shall be manufactured by hot or cold working, rolling, and annealing. Chemical composition of the materials shall conform to UNS designation of the material. Product shall conform to chemical analysis, tensile strength and Rockwell hardness tests specified in the specification. Chemical composition testing shall be performed for each element, namely, copper, iron, lead, phosphorus, tin, and zinc. Tension test shall be made so that the longitudinal axis of the specimen is parallel to direction of rolling.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes copper-tin alloy (phosphor bronze), copper-tin-lead alloy (leaded phosphor bronze), and copper-tin-lead-zinc alloy (bearing bronze), plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The phosphor bronzes commonly are used for deep drawing into bellows and stamping and forming into spring devices and into terminals and connectors for electrical apparatus because they combine high strength with high elongation. The leaded phosphor bronzes are used where strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability are required. The bearing bronze is used in bushings, bearings, and load-bearing thrust washers. The following alloys are covered:
Copper Alloy UNS No. Nominal Composition, %Previously Used Designation CopperTin ZincLead C51000955. . . . . .A1 C51100964. . . . . .A C51180964. . .. . .. . . C51900946. . . . . . C52100A92 8. . .. . .C C52180928. . . . . . . . . C524009010 . . . . . .D C53400945. . . 1B1 C5440088444B2 __________________
A SAE Specification CA 521 conforms to the requirements of UNS No. C52100.
Note 1—All of the above alloys contain small amounts of phosphorus, used as a deoxidant in melting, and to enhance the mechanical properties.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: B103/B103M – 09
Standard Specification for
1
Phosphor Bronze Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B103/B103M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* 2. Referenced Documents
3
1.1 This specification establishes copper-tin alloy (phosphor 2.1 ASTM Standards:
bronze), copper-tin-lead alloy (leaded phosphor bronze), and B248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought
copper-tin-lead-zinc alloy (bearing bronze), plate, sheet, strip, Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
and rolled bar. The phosphor bronzes commonly are used for Bar
deep drawing into bellows and stamping and forming into B248M Specification for General Requirements for
spring devices and into terminals and connectors for electrical Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and
apparatus because they combine high strength with high Rolled Bar (Metric)
elongation. The leaded phosphor bronzes are used where B601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper
strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability are required. and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
The bearing bronze is used in bushings, bearings, and load- B846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
bearing thrust washers. The following alloys are covered: E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materi-
Copper Alloy Nominal Composition, % Previously Used
2
4
UNS No. Copper Tin Zinc Lead Designation
als [Metric]
E54 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Special Brasses
C51000 95 5 . . . . . . A1
4
and Bronzes
C51100 96 4 . . . . . . A
C51180 96 4 . . .
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
C51900 94 6 . . . . . .
4
Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
A
C52100 92 8 . . C
C52180 92 8 . . . . . . . . . E75 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Copper-Nickel
C52400 90 10 . . . . . . D
and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys
C53400 94 5 . . . 1 B1
E255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for
C54400 88 4 4 4 B2
__________________ the Determination of Chemical Composition
A
E478 TestMethodsforChemicalAnalysisofCopperAlloys
SAE Specification CA521 conforms to the requirements of UNS No. C52100.
E527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
NOTE 1—All of the above alloys contain small amounts of phosphorus,
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
used as a deoxidant in melting, and to enhance the mechanical properties.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
3. Terminology
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this speci-
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
fication, refer to Terminology B846.
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance 4. Ordering Information
with the standard.
4.1 Contracts or purchase orders for product under this
specification should include the following information:
1 4.1.1 ASTM designation and year of issue (for example,
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
B103/B103M – 04);
andCopperAlloysandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeB05.01onPlate,
Sheet, and Strip.
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally
3
approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
B103/B103M – 07. DOI: 10.1520/B0103_B0103M-09. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E527) is a simple Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition the ASTM website.
4
of a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
composition variations of the base alloy. on www.astm.org.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
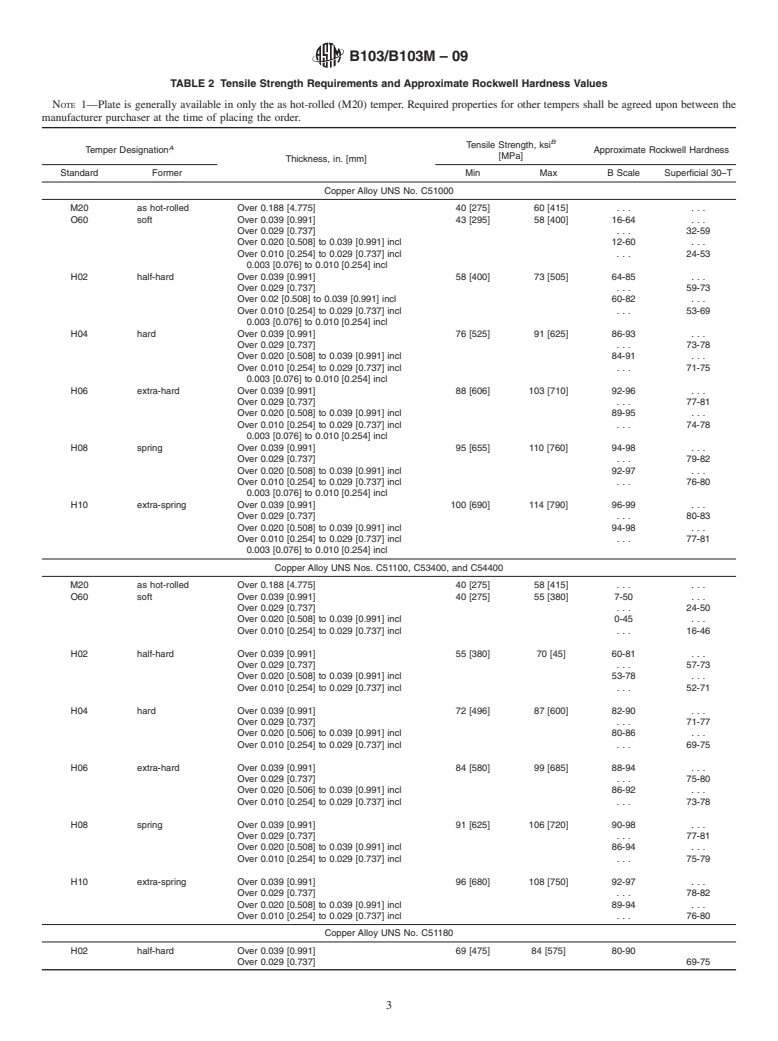
B103/B103M – 09
4.1.2 Copper Alloy UNS No. designation (for example, 6.1.1 The material of manufacture shall be a cast bar, cake,
C51000); slab, or Copper Alloy UNS No. C51000, C51100, C51180,
4.1
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B103/B103M–07 Designation: B 103/B 103M – 09
Standard Specification for
1
Phosphor Bronze Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 103/B 103M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes copper-tin alloy (phosphor bronze), copper-tin-lead alloy (leaded phosphor bronze), and
copper-tin-lead-zinc alloy (bearing bronze), plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The phosphor bronzes commonly are used for deep
drawing into bellows and stamping and forming into spring devices and into terminals and connectors for electrical apparatus
because they combine high strength with high elongation. The leaded phosphor bronzes are used where strength, corrosion
resistance, and machinability are required. The bearing bronze is used in bushings, bearings, and load-bearing thrust washers. The
following alloys are covered:
Copper Alloy Nominal Composition, % Previously Used
2
UNS No. Copper Tin Zinc Lead Designation
C51000 95 5 . . . . . . A1
C51100 96 4 . . . . . . A
C51180 96 4 . . .
C51900 94 6 . . . . . .
A
C52100 92 8 . . C
C52180 92 8 . . . . . . . . .
C52400 90 10 . . . . . . D
C53400 94 5 . . . 1 B1
C54400 88 4 4 4 B2
__________________
A
SAE Specification CA 521 conforms to the requirements of UNS No. C52100.
NOTE 1—All of the above alloys contain small amounts of phosphorus, used as a deoxidant in melting, and to enhance the mechanical properties.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-poundSI units or SIinch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the
text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system aremay not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
specification. standard.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B 248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
B 248M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
(Metric)
B 601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper AlloysWrought and Cast
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials [Metric]
E54 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Special Brasses and Bronzes
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate,
Sheet, and Strip.
´1
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2007. Published October 2007. Originally approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B103/B103M–04 .
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as
B 103/B 103M – 07.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of
a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B 103/B 103M – 09
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys
E 255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for the Determination of Chemical Composition
E 478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions— For definitions of te
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B103/B103M–07 Designation: B 103/B 103M – 09
Standard Specification for
1
Phosphor Bronze Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 103/B 103M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification establishes copper-tin alloy (phosphor bronze), copper-tin-lead alloy (leaded phosphor bronze), and
copper-tin-lead-zinc alloy (bearing bronze), plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The phosphor bronzes commonly are used for deep
drawing into bellows and stamping and forming into spring devices and into terminals and connectors for electrical apparatus
because they combine high strength with high elongation. The leaded phosphor bronzes are used where strength, corrosion
resistance, and machinability are required. The bearing bronze is used in bushings, bearings, and load-bearing thrust washers. The
following alloys are covered:
Copper Alloy Nominal Composition, % Previously Used
2
UNS No. Copper Tin Zinc Lead Designation
C51000 95 5 . . . . . . A1
C51100 96 4 . . . . . . A
C51180 96 4 . . .
C51900 94 6 . . . . . .
A
C52100 92 8 . . C
C52180 92 8 . . . . . . . . .
C52400 90 10 . . . . . . D
C53400 94 5 . . . 1 B1
C54400 88 4 4 4 B2
__________________
A
SAE Specification CA 521 conforms to the requirements of UNS No. C52100.
NOTE 1—All of the above alloys contain small amounts of phosphorus, used as a deoxidant in melting, and to enhance the mechanical properties.
1.2 The values stated in either inch-poundSI units or SIinch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the
text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system aremay not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system
shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the
specification. standard.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B 248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
B 248M Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
(Metric)
B 601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper AlloysWrought and Cast
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E8M Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials [Metric]
E54 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Special Brasses and Bronzes
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate,
Sheet, and Strip.
´1
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2007. Published October 2007. Originally approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B103/B103M–04 .
Current edition approved April 1, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally approved in 1936. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as
B 103/B 103M – 07.
2
The UNS system for copper and copper alloys (see Practice E 527) is a simple expansion of the former standard designation system accomplished by the addition of
a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.” The suffix can be used to accommodate composition variations of the base alloy.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B 103/B 103M – 09
E75 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper-Nickel and Copper-Nickel-Zinc Alloys
E 255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for the Determination of Chemical Composition
E 478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the Unified Numbering System (UNS)
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions— For definitions of te
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.