ASTM D1914-95(1999)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Conversion Units and Factors Relating to Sampling and Analysis Atmospheres
Standard Practice for Conversion Units and Factors Relating to Sampling and Analysis Atmospheres
SCOPE
1.1 This practice provides units and factors useful for members of the air pollution and meteorological communities.
1.2 This practice is used together with Practice E380, which discusses SI units and contains selected conversion factors for inter-relation of SI units and some commonly used non-metric units.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1914–95 (Reapproved 1999)
Standard Practice for
Conversion Units and Factors Relating to Sampling and
Analysis of Atmospheres
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 1914; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Significance and Use
1.1 This practice provides units and factors useful for 3.1 ASTM requires the use of SI units in all its publications
members of the air pollution and meteorological communities. and their use in reporting atmospheric measurement data.
1.2 This practice is used together with IEEE/ASTM SI 10, However, there are historic data and even data currently
which discusses SI units and contains selected conversion reported that are based on a variety of units of measurement.
factors for inter-relation of SI units and some commonly used This practice tabulates factors that are necessary to convert
non-metric units. such data to SI and other units of measurement.
3.2 IEEE/ASTM SI 10 does not list all the conversion
2. Referenced Documents
factors commonly used in air pollution and meteorological
2.1 ASTM Standards: fields. This practice supplements IEEE/ASTM SI 10.
D 1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
3.3 The values reported here were obtained from a number
Atmospheres ofstandardpublications.Theywereadjustedtofivefiguresand
E 11 Specification for Wire-Cloth Sieves for Testing Pur-
organized in a rational order. All values reflect the latest
poses information from the 16th General Conference on Weights and
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International
Measurements held in 1979.
System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System 3.4 The factors in Table 1 are provided to change units of
measurementfromonesystemtorelatedunitsinothersystems,
as well as to smaller or larger units in the same system.
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D-22 on Sampling
3.5 Values of units in the left column may be converted to
and Analysis of Atmospheres and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
values of units in the right column merely by multiplying by
D22.01 on Quality Control.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1995. Published November 1995. Originally the conversion factor provided in the center column.
published as D 1914 – 61 T. Last previous edition D 1914 – 91.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.03
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D1914
TABLE 1 Conversion Units
Multiply By To Obtain
Temperature
Degrees Fahrenheit (F) + 459.72 1 Degrees Fahrenheit Absolute or Rankine (R)
Degrees Fahrenheit (F) − 32 ⁄9 Degrees Celsius (C)
Degrees Celsius (C) + 273.15 1 Kelvins (K)
Degrees Celsius (C) + 17.78 1.8 Degrees Fahrenheit (F)
Degrees Rankine (R) − 459.72 1 Degrees Fahrenheit (F)
Kelvins (K) − 273.15 1 Degrees Celsius (C)
Pressure
−5
Dynes per square centimetre 1.4504 3 10 Pounds per square inch
−4
10.197 3 10 Grams per square centimetre
−6
1 3 10 Bars
0.1 Pascals
Pounds per square inch absolute (psia) 70.307 Grams per square centimetre absolute
51.715 Millimetres of mercury absolute
144 Pounds per square foot absolute
1 Pounds per square inch gage + 14.696
6894.8 Pascals
Pounds per square inch gage (psig) 70.307 Grams per square centimetre
51.715 Millimetres of mercury at 0°C
27.673 Inches of water at 4°C
1 Pounds per square inch absolute − 14.696
6894.8 Pascals
Inches of water (at 4°C) 0.03614 Pounds per square inch
0.07355 Inches of mercury
0.57818 Ounces per square inch
25.399 Kilograms per square metre
2490.8 Dynes per square centimetre
249.2 Pascals
Inches of mercury (at 0°C) 0.49116 Pounds per square inch
13.595 Inches of water at 4°C
345.31 Kilograms per square metre
3.3864 3 10 Dynes per square centimetre
3386.4 Pascals
Millimetres of mercury (at 0°C) 0.01934 Pounds per square inch
1.3595 Grams per square centimetre
1333.2 Dynes per square centimetre
133.32 Pascals
Centimetres of mercury (at 0°C) 1.3332 3 10 Dynes per square centimetre
135.95 Kilograms per square metre
27.845 Pounds per square foot
1333.2 Pascals
Atmosphere (normal) 760 Millimetres of mercury at 0°C
1.0133 Bars
14.696 Pounds per square inch
29.921 Inches of mercury at 0°C
1033.2 Grams per square centimetre
1.0133 3 10 Dynes per square centimetre
1.0132 3 10 Pascals
Bars 14.504 Pounds per square inch
1.0197 3 10 Kilograms per square metre
1.000 3 10 Dynes per square centimetre
750.06 Millimetres of mercury (0°C)
0.98692 Atmospheres
10 Pascals
Pascals 10 Dynes per square centimeter
−4
1.4504 3 10 Pounds per square inch absolute
−3
4.0128 3 10 Inches of water (at 4°C)
−4
2.9530 3 10 Inches of mercury (at 0°C)
−3
7.5007 3 10 Millimeter of mercury (at 0°C)
−6
9.8692 3 10 Atmosphere (normal)
−5
10 Bars
Density
Grams per cubic centimetre 1 Grams per millilitre
0.03613 Pounds per cubic inch
8.3452 Pounds per gallon (U. S.)
62.428 Pounds per cubic foot
Pounds per cubic foot 0.01602 Grams per cubic centimetre
−4
5.7870 3 10 Pounds per cubic inch
D1914
TABLE 1 Continued
Multiply By To Obtain
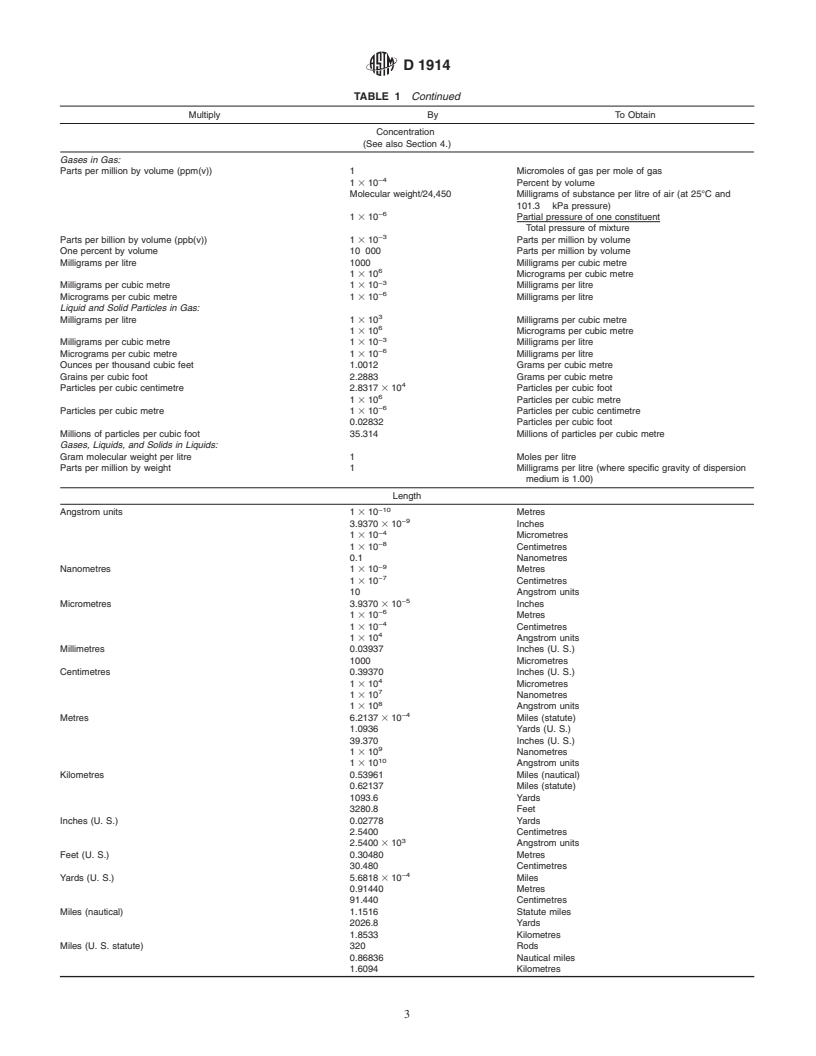
Concentration
(See also Section 4.)
Gases in Gas:
Parts per million by volume (ppm(v)) 1 Micromoles of gas per mole of gas
−4
1 3 10 Percent by volume
Molecular weight/24,450 Milligrams of substance per litre of air (at 25°C and
101.3 kPa pressure)
−6
1 3 10 Partial pressure of one constituent
Total pressure of mixture
−3
Parts per billion by volume (ppb(v)) 1 3 10 Parts per million by volume
One percent by volume 10 000 Parts per million by volume
Milligrams per litre 1000 Milligrams per cubic metre
1 3 10 Micrograms per cubic metre
−3
Milligrams per cubic metre 1 3 10 Milligrams per litre
−6
Micrograms per cubic metre 1 3 10 Milligrams per litre
Liquid and Solid Particles in Gas:
Milligrams per litre 1 3 10 Milligrams per cubic metre
1 3 10 Micrograms per cubic metre
−3
Milligrams per cubic metre 1 3 10 Milligrams per litre
−6
Micrograms per cubic metre 1 3 10 Milligrams per litre
Ounces per thousand cubic feet 1.0012 Grams per cubic metre
Grains per cubic foot 2.2883 Grams per cubic metre
Particles per cubic centimetre 2.8317 3 10 Particles per cubic foot
1 3 10 Particles per cubic metre
−6
Particles per cubic metre 1 3 10 Particles per cubic centimetre
0.02832 Particles per cubic foot
Millions of particles per cubic foot 35.314 Millions of particles per cubic metre
Gases, Liquids, and Solids in Liquids:
Gram molecular weight per litre 1 Moles per litre
Parts per million by weight 1 Milligrams per litre (where specific gravity of dispersion
medium is 1.00)
Length
−10
Angstrom units 1 3 10 Metres
−9
3.9370 3 10 Inches
−4
1 3 10 Micrometres
−8
1 3 10 Centimetres
0.1 Nanometres
−9
Nanometres 1 3 10 Metres
−7
1 3 10 Centimetres
10 Angstrom units
−5
Micrometres 3.9370 3 10 Inches
−6
1 3 10 Metres
−4
1 3 10 Centimetres
1 3 10 Angstrom units
Millimetres 0.03937 Inches (U. S.)
1000 Micrometres
Centimetres 0.39370 Inches (U. S.)
1 3 10 Micrometres
1 3 10 Nanometres
1 3 10 Angstrom units
−4
Metres 6.2137 3 10 Miles (statute)
1.0936 Yards (U. S.)
39.370 Inches (U. S.)
1 3 10 Nanometres
1 3 10 Angstrom units
Kilometres 0.53961 Miles (nautical)
0.62137 Miles (stat
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.