ASTM E2115-00
(Guide)Standard Guide for Conducting Lead Hazard Assessments of Residential Housing and Other Properties Frequented by Children
Standard Guide for Conducting Lead Hazard Assessments of Residential Housing and Other Properties Frequented by Children
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes how to conduct, document and report findings of a lead hazard assessment in residential dwellings and other buildings and related areas known to contain, or are suspected to contain, lead hazards. Lead hazard assessments are intended to be conducted by certified risk assessors. This guide is applicable for use in either occupied or unoccupied properties. The use of this guide to produce accurate results is dependent on the training, experience, and knowledge of the risk assessor conducting the lead hazard assessment. Use of the procedures in this guide, when supplemented by the evaluation and recommendation process that determines action plans for controlling assessed lead hazards, provides for the conduct of a lead risk assessment (see Note 1).
Note 1--A lead risk assessment, as defined by Federal regulation (40CFR745.227(d)), includes, as part of the reporting process, a description of interim controls and abatement options for each identified lead hazard and a suggested prioritization for addressing each hazard. This guide provides for the identification of lead hazards and the prioritization for addressing each hazard guidance on the determination of appropriate interim controls and abatement options for each identified lead hazard is beyond the scope of this guide and is included in a companion standard. Guidance on the determination of appropriate interim controls and abatement options for each identified lead hazard is beyond the scope of this guide and is the subject of a standard under development by E06.23.
1.2 This guide is insufficient as the sole means to determine causes of lead poisoning in young children having an elevated blood lead level (EBL). In these cases, procedures including investigation of the total living environment of the child and a pediatric medical evaluation is needed. Reference should be made to Preventing Childhood Lead Poisoning (CDC, 1991), the Guidelines for the Evaluation and Control of Lead-Based Paint Hazards in Housing (HUD, 1997), and Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning (CDC, 1997).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This guide contains notes, which are explanatory, and are not part of the mandatory requirements of this guide.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 2115 – 00
Standard Guide for
Conducting Lead Hazard Assessments of Residential
Housing and Other Properties Frequented by Children
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 2115; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 This guide describes how to conduct, document and
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
report findings of a lead hazard assessment in residential
1.5 This guide contains notes, which are explanatory, and
dwellings and other buildings and related areas known to
are not part of the mandatory requirements of this guide.
contain, or are suspected to contain, lead hazards. Lead hazard
assessments are intended to be conducted by certified risk
2. Referenced Documents
assessors.This guide is applicable for use in either occupied or
2.1 Wherever the requirements of a reference document or
unoccupied properties. The use of this guide to produce
applicable regulation differ from the requirements presented in
accurate results is dependent on the training, experience, and
this guide the more stringent of the two shall be used.
knowledge of the risk assessor conducting the lead hazard
2.2 ASTM Standards:
assessment. Use of the procedures in this guide, when supple-
E 1583 Practice for Evaluating Laboratories Engaged in the
mented by the evaluation and recommendation process that
Determination of Lead in Paint, Dust,Airborne Particulate,
determines action plans for controlling assessed lead hazards,
and Soil in and Around Buildings and Related Structures
provides for the conduct of a lead risk assessment (see Note 1).
E 1605 Terminology Relating to Abatement of Hazards
NOTE 1—A lead risk assessment, as defined by Federal regulation
from Lead-Based Paint in Buildings and Related Struc-
(40CFR745.227(d)), includes, as part of the reporting process, a descrip- 3
tures
tion of interim controls and abatement options for each identified lead
E 1613 Test Method for Analysis of Digested Samples for
hazard and a suggested prioritization for addressing each hazard. This
Lead by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission
guide provides for the identification of lead hazards and the prioritization
Spectrometry (ICP/AES), Flame Atomic Absorption
for addressing each hazard guidance on the determination of appropriate
interim controls and abatement options for each identified lead hazard is (FAAS),orGraphiteFurnaceAtomicAbsorption(GFAAS)
beyond the scope of this guide and is included in a companion standard.
Techniques
Guidance on the determination of appropriate interim controls and
E 1644 Practice for Hot Plate Digestion of Dust Wipe
abatement options for each identified lead hazard is beyond the scope of
Samples for the Determination of Lead by Atomic Spec-
this guide and is the subject of a standard under development by E06.23.
trometry
1.2 This guide is insufficient as the sole means to determine
E 1645 Practice for Preparation of Dried Paint Samples for
causes of lead poisoning in young children having an elevated
Subsequent Lead Analysis by Atomic Spectrometry
blood lead level (EBL). In these cases, procedures including
E 1726 Practice for The Sample Digestion of Soils for the
investigation of the total living environment of the child and a
Determination of Lead by Atomic Spectrometry
pediatric medical evaluation is needed. Reference should be
E 1727 Practice for Field Collection of Soil Samples for
made to Preventing Childhood Lead Poisoning (CDC, 1991),
Lead Determination by Atomic Spectrometry Techniques
the Guidelines for the Evaluation and Control of Lead-Based
E 1728 Practice for Field Collection of Settled Dust
Paint Hazards in Housing (HUD, 1997), and Screening Young
Samples Using Wipe Sampling Methods for Lead Deter-
Children for Lead Poisoning (CDC, 1997).
mination by Atomic Spectrometry Techniques
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
E 1729 Practice for Field Collection of Dried Paint Samples
standard.
for Lead Determination by Atomic Spectrometry Tech-
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
niques
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
E 1792 Specification for Wipe Sampling Materials for Lead
in Surface Dust
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on Performance
of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.23 onAbatement
of Hazards from Lead in Buildings and Related Structures. Discontinued. See 1997 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol .
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 2000. Published March 2001. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.11.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
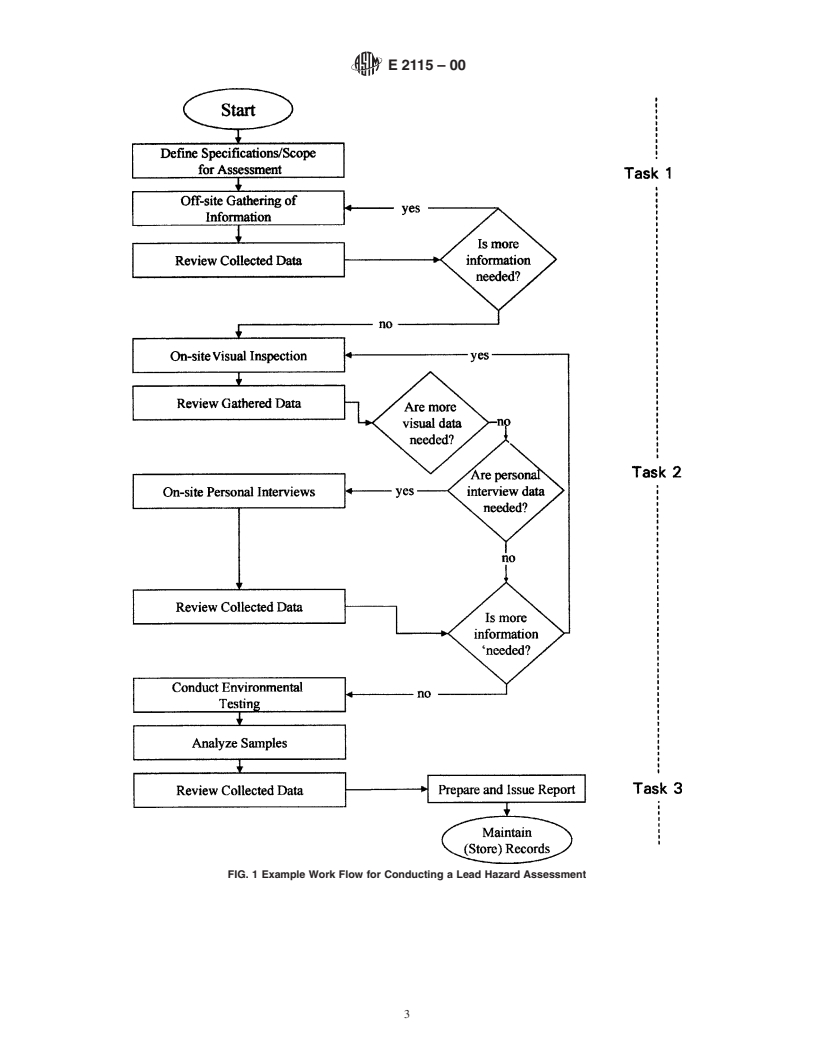
E2115–00
E 1864 Practice for Evaluating Quality Systems of Organi- application of the three general tasks listed below. Simulta-
zations Engaged in Conducting Facility and Hazard As- neous conduct of several activities within these tasks generally
sessments to Determine the Presence and Extent of Lead in is performed using a looping feedback structure shown in Fig.
Paint,Dust,AirborneParticulate,andSoilinBuildingsand 1.
Related Structures 4.2.1 Task 1—Pre-site visit activities developing work
E 1973 Practice for Collection of Surface Dust by Air specifications.
Sampling Pump Vacuum Technique for Subsequent Lead 4.2.2 Task 2—On-site activities conducting field work.
Determination 4.2.3 Task 3—Post-site visit activities data reporting.
E 1979 Practice for Ultrasonic Extraction of Paint, Dust,
5. Significance and Use
Soil, and Air Samples for Subsequent Determination of
5.1 This guide is intended to help prevent lead poisoning of
Lead
children by providing standardized procedures to be used by a
E 2051 Practice for Determination of Lead in Paint, Settled
lead risk assessor when gathering and reporting findings and
Dust, Soil, and Air Particulate by Field-Portable Elec-
information needed to develop and recommend lead hazard
troanalysis
control options (see Note 2).
E 2119 Practice for Quality Systems for Conducting In Situ
Measurements of Lead Content in Paint or Other Coatings
NOTE 2—Development of lead hazard control recommendations for
Using Field-Portable X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Devices
identified lead hazards, which is an important part of a risk assessment, is
2.3 CDC Document:
outside the scope of this guide and is contained in a separate document.
CDC Preventing Lead Poisoning in Young Children, Cen-
5.2 Thisguideisintendedtobefollowedinaccordancewith
ters for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta, CDC
all applicable local, state, and federal regulations.
October, 1991.
5.3 A lead hazard is conducted as part of a lead risk
CDC Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning, Cen-
assessment to determine and report the location, type, and
ters for Disease Control and Prevention Atlanta CDC,
severity of lead hazards in buildings and associated property
1997.
surroundings that are accessible to children. The local risk
2.4 HUD Document:
assessment uses the findings from a lead hazard assessment in
HUD Guidelines for the Evaluation and Control of Lead-
developing a report providing appropriate, cost effective lead
Based Paint Hazards in Housing,”
hazard control recommendation options to the client (see Note
2.5 EPA Documents:
1).
EPA Risk Assessment Guidance, Federal Register, Vol 60,
5.4 This guide does not include the formal investigation of
47248, September 11, 1995.
personal items that may contribute to lead hazards, such as
EPA Lead-Based Paint Poisoning Prevention in Certain
toys, dishes, hobby materials, etc.; however, the risk assessor
Residential Structures 40 CFR Part 745.
should report such hazards if they are identified during the
conduct of a lead hazard assessment.
3. Terminology
5.5 Lead hazard assessment findings only represent the
3.1 Definitions:
condition of the property at the time the assessment is
3.1.1 For definition of terms used in this guide see Termi-
performed. Lead hazards identified during a lead hazard
nology E 1605.
assessment often are related to the condition of the property.
3.1.2 assessed unit, n—a dwelling or property that has been
The presence of lead hazards can change over time as a result
the subject of the investigation.
of property improvement or deterioration, significant changes
3.1.3 lead activity summary, n—a document that summa-
in property use, and other factors.
rizes lead evaluation data and management activities on a
5.6 Lead risk assessors must be certified for the conduct of
specific structure or property presented in a single page format.
lead-basedpaintactivitiesundertheappropriatestateorfederal
3.1.3.1 Discussion—This practice will provide a means of
program (see 2.6).
communicating summarized results of lead evaluation and
5.7 In addition to direct use by a lead risk assessor, this
management activities to occupants and others of a residential
guide is applicable for assisting professionals, homeowners,
dwelling.
owners or occupants of rental property, lenders, insurers and
3.1.4 lead hazard assessment, n—an investigation of an
others with a property interest in determining the presence of
assessed unit conducted to determine and report the location,
lead hazards (see Note 3). This guide also is applicable for
type, severity of lead hazards which are accessible to children.
assisting designers of lead hazard mitigation projects to target
theirresourcestowardleadhazardcontrolsmostlikelytoresult
4. Summary of Guide
in the prevention of lead poisoning in young children.
4.1 This guide provides procedures for gathering informa-
NOTE 3—Whenever lead is present in a building in any form, the term
tion, conducting a lead hazard assessment, and documenting
“lead-free” should never be used to describe the absence of lead hazards
and reporting the findings of the lead hazard assessment.
because testing methodologies are not designed to measure freedom from
4.2 This guide discusses the conduct of a lead hazard
any level of lead. Small amounts of lead present in substrates or on
assessment, in a stepwise progression, using a systematic
coatings below an applicable Federal, state, or local action level may
become a hazard if the components are subjected to conditions or
activities that create lead containing dust. Changes in property conditions
Discontinued 1999; Replaced by E 2051. andchangesinchildren’shabitsrelatedtothefrequencyofhand-to-mouth
E2115–00
FIG. 1 Example Work Flow for Conducting a Lead Hazard Assessment
E2115–00
activity, which vary over time, further contribute to this inability to
7.2.1.2 Cost—If the lead hazard assessment is performed
provide absolute assurance that a child will not become lead poisoned in
for compensation, the cost for conducting the work shall be
the future.
identified.
7.2.1.3 Personnel Qualifications—Qualifications of all per-
5.8 The tasks and procedures outlined in this guide are
sonnel to be involved in the lead hazard assessment shall be
basedondevelopingtechnologies;therefore,thisguideshallbe
identified. At a minimum, a summary of the relevant certifica-
reviewed periodically and amended to incorporate new infor-
tions, licenses, training, and experience for persons participat-
mation to ensure its continuing suitability in minimizing lead
ing in the conduct of the lead hazard assessment shall be
poisoning of children.
identified. This may be done generically and specific individu-
als need not be named.
6. Experience Requirements for a Risk Assessor
7.2.1.4 Regulatory Requirements—A summary of the regu-
6.1 Lead hazard assessments shall be carried out by quali-
latory requirements for the area and structures being assessed
fied risk assessors as required through certification or licensing
including identification of the regulatory agencies having
under appropriate federal, state, or local regulations.
jurisdiction over the assessment activity, or subsequent hazard
mitigation, or both, shall be included. Specific assessment
7. Conducting a Lead Hazard Assessment
requirements imposed by these regulatory agencies shall be
7.1 Lead hazard assessments are conducted using a system-
identified and performed. Current regulatory levels of concern
atic approach consisting of a series of activities within three
shall be specified.
general tasks. Although several of the activities within a task
7.2.1.5 Laboratory Qualifications—Qualifications for all
may be conducted simultaneously, they are discussed in a
laboratories to be involved in the assessment shall be identi-
stepwise progression under each task labeled (A) through (K).
fied. Laboratories selected for use shall hold all accrediations,
Task 1—Pre-site Visit Activities: Developing Work Specifications:
certifications, and recognitions needed to conduct lead testing
(A) Create a specifications document and define
servicesasgovernedbyregulatoryagencieshavingjurisdiction
scope.
oversuchwork.Ataminimum,theselectedlaboratoryshallbe
(B) Gather information and review procedures.
(C) Review collected data.
recognized by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
Task 2—On-Site Visit Activities: Conducting Field Work:
(EPA) National Lead Laboratory Accrediation Program
(D) Conduct visual inspection.
(NLLAP).
(E) Review collected data.
(F) Conduct personal interviews.
7.2.2 (B) Gather Information and Review Procedures—
(G) Review collected data.
Prior to traveling to the site where the lead hazard assessment
(H) Conduct environmental testing.
is to be conducted, a number of activities shall be performed to
Task 3—Post-Site Visit Activities: Data Reporting:
(I) Analyze collected samples
plan for the on-site visit of the property. These activities
(J) Review collected data
include the following:
(K) Prepare and issue a lead hazard findings re-
port (see Note 4). 7.2.2.1 Acquire whatever signed permission releases are
needed to enter the property to conduct the lead hazard
NOTE 4—A complete risk assessment report to a client also should
assessment (see Note 6).
contain identification of acceptable abatement and control strategies for
controlling any identified lead hazards. Guidance on how to provide this
NOTE 6—Permission releases may include any of the following items:
information is not part of this guide.
Permission to enter the property;
Permission to acquire and review availa
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.