ASTM B591-08
(Specification)Standard Specification for Copper-Zinc-Tin and Copper-Zinc-Tin-Iron-Nickel Alloys Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
Standard Specification for Copper-Zinc-Tin and Copper-Zinc-Tin-Iron-Nickel Alloys Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the requirements for plates, sheets, strips, and rolled bars of copper-zinc-tin and copper-zinc-tin-iron-nickel alloys with Copper Alloy UNS Nos. C40500, C40810, C40850, C40860, C41100, C41300, C41500, C42200, C42500, C42520, C43000, and C43400. Materials shall be processed by hot working, cold working, and annealing as to produce a uniform wrought structure in the finished product. Tempers shall be available in the rolled, as hot rolled, or annealed conditions. Products shall be sampled and prepared, then tested accordingly to examine their conformance to dimensional (thickness, length, width, mass, straightness, and edges), mechanical (tensile strength, and Rockwell hardness), chemical composition, and grain size requirements.
SCOPE
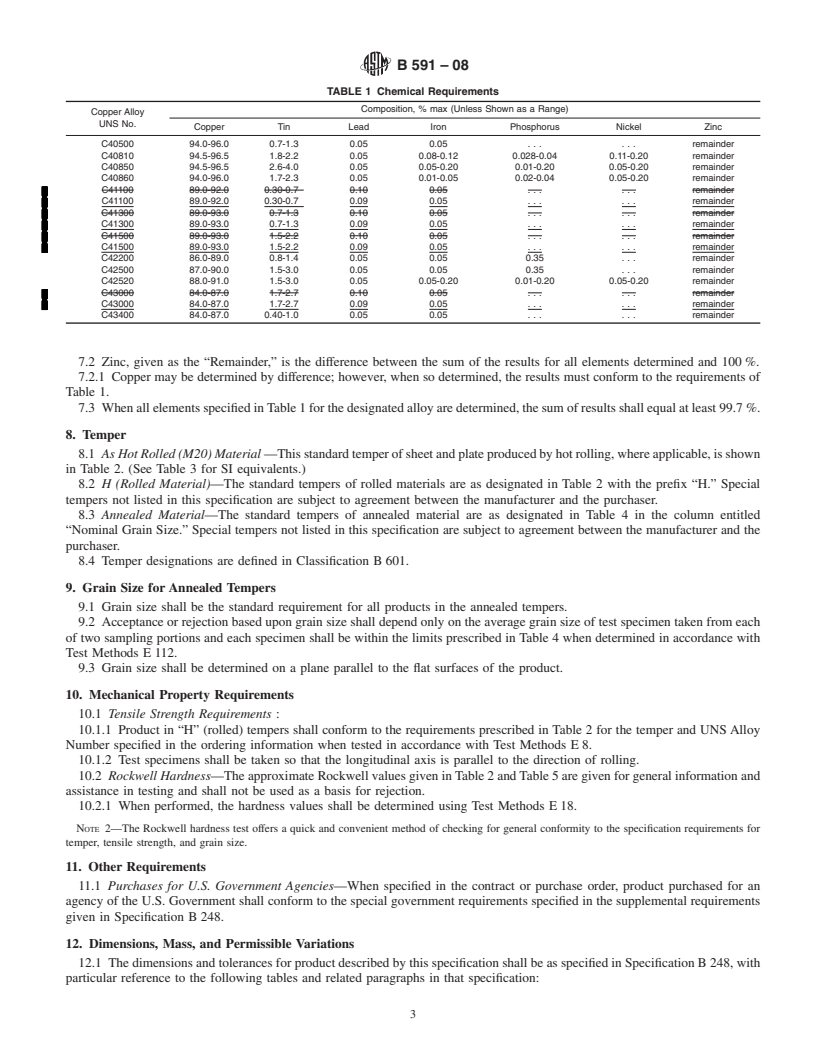
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for specified copper-zinc-tin alloys and copper-zinc-tin-iron-nickel alloys in the form of plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The alloys and nominal compositions are as follows:
Copper Alloy
UNS No. Copper,
%Tin,
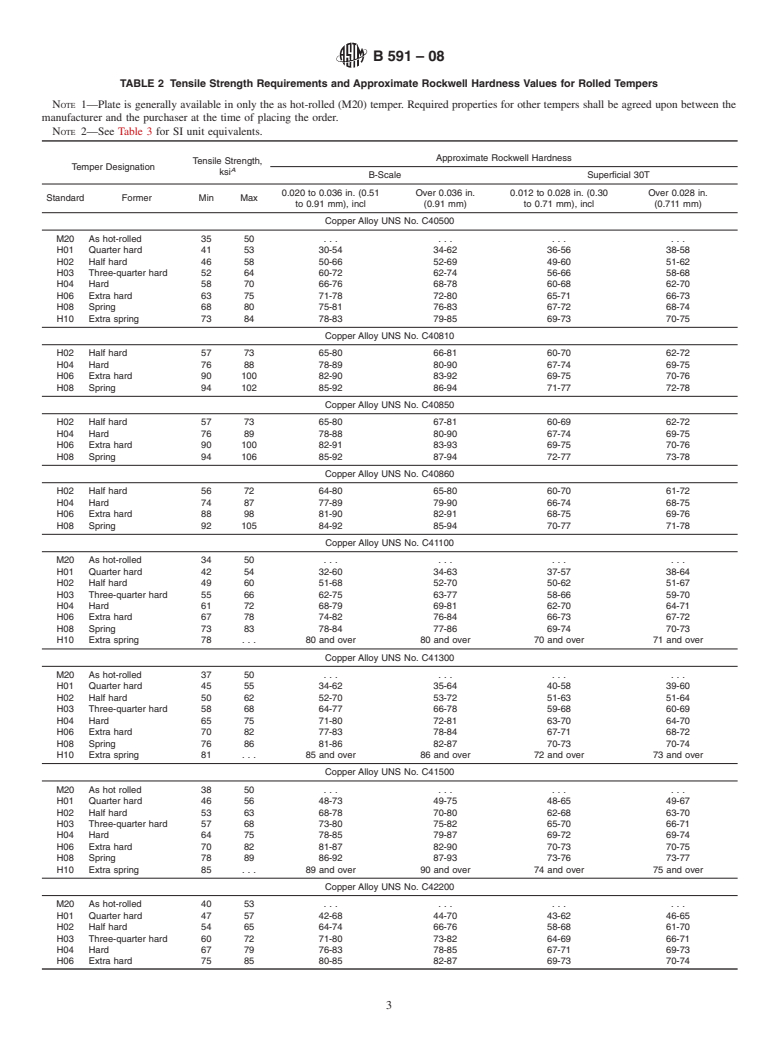
%Zinc,
%Phos.,
%%Iron,
%Nickel,
% C405009514 C4081095.52.02.220.030.10.15 C4085095.53.01.270.10.10.1 C4086094.82.03.040.030.030.1 C41100910.58.5 C413009118 C415009127 C4220087112 C4250088210 C4252089.82.07.970.10.10.1 C4300085213 C43400850.714.3
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B 591 – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper-Zinc-Tin and Copper-Zinc-Tin-Iron-Nickel Alloys
1
Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 591; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope* B 601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper
and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for specified
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
copper-zinc-tin alloys and copper-zinc-tin-iron-nickel alloys in
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
the form of plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The alloys and
E18 Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic
nominal compositions are as follows:
Materials
Copper Alloy Copper, Tin, Zinc, Phos., Iron, Nickel,
2
E62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and
UNS No. % % % %% % %
Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
C40500 95 1 4
E76 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Nickel-Copper
C40810 95.5 2.0 2.22 0.03 0.1 0.15
4
Alloys
C40850 95.5 3.0 1.27 0.1 0.1 0.1
C40860 94.8 2.0 3.04 0.03 0.03 0.1
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
C41100 91 0.5 8.5
E 255 Practice for Sampling Copper and CopperAlloys for
C41300 91 1 8
C41500 91 2 7 the Determination of Chemical Composition
C42200 87 1 12
E 478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper
C42500 88 2 10
Alloys
C42520 89.8 2.0 7.97 0.1 0.1 0.1
E 527 Practice for Numbering Metals and Alloys in the
C43000 85 2 13
C43400 85 0.7 14.3
Unified Numbering System (UNS)
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. General Requirements
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1 The following sections of Specification B 248 constitute
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
a part of this specification:
and are not considered standard.
3.1.1 Terminology—Definitions,
2. Referenced Documents
3.1.2 Materials and Manufacturing,
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance,
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the
3.1.4 Sampling—except for chemical analysis,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards form a part of this specifi-
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests,
cation to the extent referenced herein:
3
3.1.6 Specimen Preparation,
2.2 ASTM Standards:
3.1.7 Test Methods—except for chemical analysis,
B 248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought
3.1.8 Significance of Numerical Limits,
Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
3.1.9 Inspection,
Bar
3.1.10 Rejection and Rehearing,
3.1.11 Certification,
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB05onCopper
3.1.12 Test Reports (Mill),
and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on
3.1.13 Packaging and Package Marking, and
Plate, Sheet, and Strip.
3.1.14 Supplementary Requirements.
Current edition approved April 1, 2008. Published May 2008. Originally
approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as B 591 – 04.
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that
2
New designations established in accordance with Practice E 527. In the new
referenced in 3.1 appears in this specification, it contains
UNS system the designations for copper alloys are simply expansions of the present
additional requirements, which supplement those appearing in
standard designations by a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.”
3
Specification B 248.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
4
the ASTM website. Withdrawn.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B591–08
4. Terminology 6.2.2 Theproductshallbehotorcoldworkedtothefinished
size and subsequently annealed, when required, to meet the
4.1 Definitions—For standard terms related to copper and
temper properties specified in the ordering information.
copper alloys, refer to Terminology B 846.
6.2.3 Edges—Slit edges shall be furnished unless otherwise
5. Ordering Information
specified in the contract or purchase order.
5.1 Contracts or purchase orders for product under this
7. Chemical Composition
specification should include the following information:
5.1.1 ASTM designation and year of issue (for example, 7.1 The mat
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:B591–04 Designation: B 591 – 08
Standard Specification for
Copper-Zinc-Tin and Copper-Zinc-Tin-Iron-Nickel Alloys
1
Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 591; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for specified copper-zinc-tin alloys and copper-zinc-tin-iron-nickel alloys in the
form of plate, sheet, strip, and rolled bar. The alloys and nominal compositions are as follows:
Copper Alloy Copper, Tin, Zinc, Phos., Iron, Nickel,
2
UNS No. % % % %% % %
C40500 95 1 4
C40810 95.5 2.0 2.22 0.03 0.1 0.15
C40850 95.5 3.0 1.27 0.1 0.1 0.1
C40860 94.8 2.0 3.04 0.03 0.03 0.1
C41100 91 0.5 8.5
C41300 91 1 8
C41500 91 2 7
C42200 87 1 12
C42500 88 2 10
C42520 89.8 2.0 7.97 0.1 0.1 0.1
C43000 85 2 13
C43400 85 0.7 14.3
1.2The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 The following documents in the current issue of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards form a part of this specification to
the extent referenced herein:
3
2.2 ASTM Standards:
B 248 Specification for General Requirements for Wrought Copper and Copper-Alloy Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled Bar
B 601 Classification for Temper Designations for Copper and Copper Alloys—Wrought and Cast
B 846 Terminology for Copper and Copper Alloys
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E 18TestMethodsforRockwellHardnessandRockwellSuperficialHardnessofMetallicMaterials TestMethodsforRockwell
Hardness of Metallic Materials
E 62 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper and Copper Alloys (Photometric Methods)
E 76 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Nickel-Copper Alloys
E 112 Test Methods for Determining the Average Grain Size
E 255 Practice for Sampling Copper and Copper Alloys for the Determination of Chemical Composition
E 478 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Copper Alloys
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B05 on Copper and Copper Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B05.01 on Plate,
Sheet, and Strip.
Current edition approved Oct.April 1, 2004.2008. Published October 2004.May 2008. Originally approved in 1973. Last previous edition approved in 19982004 as
B591–98a.B 591 – 04.
2
New designations established in accordance with Practice E 527. In the new UNS system the designations for copper alloys are simply expansions of the present standard
designations by a prefix “C” and a suffix “00.”
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*ASummary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B591–08
E 527Practice for Numbering Metals andAlloys (UNS) Practice for Numbering Metals andAlloys in the Unified Numbering
System (UNS)
3. General Requirements
3.1 The following sections of Specification B 248 constitute a part of this specification:
3.1.1 Terminology—Definitions,
3.1.2 Materials and Manufacturing,
3.1.3 Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance,
3.1.4 Sampling—except for chemical analysis,
3.1.5 Number of Tests and Retests,
3.1.6 Specimen Preparation,
3.1.7 Test Methods—except for chemical analysis,
3.1.8 Significance of Numerical Limits,
3.1.9 Inspection,
3.1.10 Rejection and Rehearing,
3.1.11 Certification,
3.1.12 Test Reports (Mill),
3.1.13 Packaging and Package Marking, and
3.1.14 Supplementary Requirements.
3.2 In addition, when a section with a title identical to that referenced in 3.1 appears in this specification, it contains additional
requirements, which supplement those appearing in Specification B 248.
4. Terminology
4.1 D
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.