ISO 12125:1997
(Main)Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B
Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B
Écrous hexagonaux à embase, autofreinés (à anneau non métallique), à filetage métrique à pas fin — Grades A et B
General Information
- Status
- Withdrawn
- Publication Date
- 05-Nov-1997
- Withdrawal Date
- 05-Nov-1997
- Technical Committee
- ISO/TC 2/SC 12 - Fasteners with metric internal thread
- Drafting Committee
- ISO/TC 2/SC 12 - Fasteners with metric internal thread
- Current Stage
- 9599 - Withdrawal of International Standard
- Start Date
- 17-Aug-2012
- Completion Date
- 12-Feb-2026
Relations
- Effective Date
- 16-Feb-2012
ISO 12125:1997 - Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread -- Product grades A and B
ISO 12125:1997 - Écrous hexagonaux a embase, autofreinés (a anneau non métallique), a filetage métrique a pas fin -- Grades A et B
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 12125:1997 is a standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Its full title is "Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B". This standard covers: Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B
Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B
ISO 12125:1997 is classified under the following ICS (International Classification for Standards) categories: 21.060.20 - Nuts. The ICS classification helps identify the subject area and facilitates finding related standards.
ISO 12125:1997 has the following relationships with other standards: It is inter standard links to ISO 12125:2012. Understanding these relationships helps ensure you are using the most current and applicable version of the standard.
ISO 12125:1997 is available in PDF format for immediate download after purchase. The document can be added to your cart and obtained through the secure checkout process. Digital delivery ensures instant access to the complete standard document.
Standards Content (Sample)
INTERNATIONAL ISO
STANDARD 12125
First edition
1997-11-15
Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with
flange (with non-metallic insert) with metric
fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B
Écrous hexagonaux à embase, autofreinés (à anneau non métallique), à
filetage métrique à pas fin — Grades A et B
A
Reference number
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide
federation of national standards bodies (ISO member bodies). The work of
preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which
a technical committee has been established has the right to be represented
on that committee. International organizations, governmental and non-
governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO
collaborates closely with the International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
Draft International Standards adopted by the technical committees are
circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an International
Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting
a vote.
International Standard ISO 12125 was prepared by Technical Committee
ISO/TC 2, Fasteners, Subcommittee SC 1, Mechanical properties of
fasteners.
Annex A forms an integral part of this International Standard.
© ISO 1997
All rights reserved. Unless otherwise specified, no part of this publication may be reproduced
or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and
microfilm, without permission in writing from the publisher.
International Organization for Standardization
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Genève 20 • Switzerland
Internet central@iso.ch
X.400 c=ch; a=400net; p=iso; o=isocs; s=central
Printed in Switzerland
ii
©
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO ISO 12125:1997(E)
Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert)
with metric fine pitch thread – Product grades A and B
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies the characteristics of prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange
(with non-metallic insert) with metric fine pitch thread with nominal thread diameters d from 8 mm up to and
including 20 mm, in product grade A for sizes d ≤ 16 mm and product grade B for sizes d > 16 mm, and with
property classes 6, 8 and 10.
If other specifications are required, they should be selected from existing International Standards, for example
ISO 261, ISO 965-2, ISO 2320 and ISO 4759-1.
2 Normative references
The following standards contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this
International Standard. At the time of publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards are subject to
revision, and parties to agreements based on this International Standard are encouraged to investigate the
possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards indicated below. Members of IEC and ISO
maintain registers of currently valid International Standards.
ISO 225:1983, Fasteners – Bolts, screws, studs and nuts – Symbols and designations of dimensions.
1)
ISO 261:– , ISO general purpose metric screw threads – General plan.
2)
ISO 965-2:– , ISO general purpose metric screw threads – Tolerances – Part 2: Limits of sizes for general
purpose bolt and nut threads – Medium quality.
ISO 2320:1997, Prevailing torque type steel hexagon nuts – Mechanical and performance properties.
ISO 3269:1988, Fasteners – Acceptance inspection.
3)
ISO 4042:– , Fasteners – Electroplated coatings.
4)
ISO 4759-1:– , Tolerances for fasteners – Part 1: Bolts, screws, studs and nuts – Product grades A, B and C.
ISO 6157-2:1995, Fasteners – Surface discontinuities – Part 2: Nuts.
ISO 8992:1986, Fasteners – General requirements for bolts, screws, studs and nuts.
1) To be published. (Revision of ISO 261:1973)
2) To be published. (Revision of ISO 965-2: 1980)
3) To be published. (Revision of ISO 4042:1989)
4) To be published. (Revision of ISO 4759-1:1978)
©
ISO
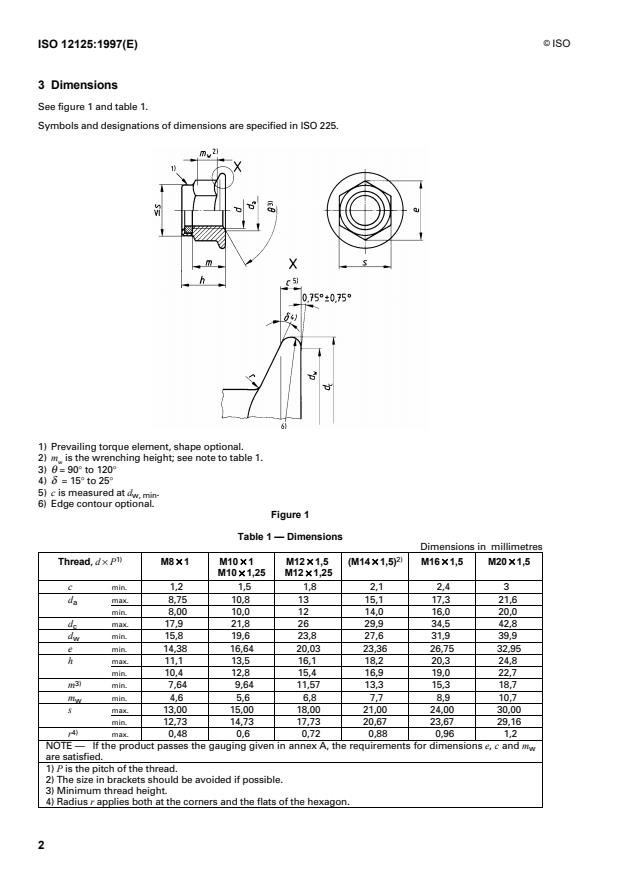
3 Dimensions
See figure 1 and table 1.
Symbols and designations of dimensions are specified in ISO 225.
1) Prevailing torque element, shape optional.
2) m is the wrenching height; see note to table 1.
w
3) q = 90° to 120°
4) d = 15° to 25°
5) c is measured at
...
NORME ISO
INTERNATIONALE 12125
Première édition
1997-11-15
Écrous hexagonaux à embase, autofreinés
(à anneau non métallique), à filetage
métrique à pas fin — Grades A et B
Prevailing torque type hexagon nuts with flange (with non-metallic insert)
with metric fine pitch thread — Product grades A and B
A
Numéro de référence
Avant-propos
L'ISO (Organisation internationale de normalisation) est une fédération
mondiale d'organismes nationaux de normalisation (comités membres de
l'ISO). L'élaboration des Normes internationales est en général confiée aux
comités techniques de l'ISO. Chaque comité membre intéressé par une
étude a le droit de faire partie du comité technique créé à cet effet. Les
organisations internationales, gouvernementales et non gouvernementales,
en liaison avec l'ISO participent également aux travaux. L'ISO collabore
étroitement avec la Commission électrotechnique internationale (CEI) en
ce qui concerne la normalisation électrotechnique.
Les projets de Normes internationales adoptés par les comités techniques
sont soumis aux comités membres pour vote. Leur publication comme
Normes internationales requiert l'approbation de 75 % au moins des
comités membres votants.
La Norme internationale ISO 12125 a été élaborée par le comité technique
ISO/TC 2, Éléments de fixation, sous-comité SC 1, Propriétés mécaniques
des éléments de fixation.
L'annexe A fait partie intégrante de la présente Norme internationale.
© ISO 1997
Droits de reproduction réservés. Sauf prescription différente, aucune partie de cette publi-
cation ne peut être reproduite ni utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun pro-
cédé, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les microfilms, sans l'accord
écrit de l'éditeur.
Organisation internationale de normalisation
Case postale 56 • CH-1211 Genève 20 • Suisse
Internet central@iso.ch
X.400 c=ch; a=400net; p=iso; o=isocs; s=central
Imprimé en Suisse
ii
©
NORME INTERNATIONALE ISO ISO 12125:1997(F)
Écrous hexagonaux à embase, autofreinés (à anneau non
métallique), à filetage métrique à pas fin – Grades A et B
1 Domaine d'application
La présente Norme internationale prescrit les caractéristiques des écrous hexagonaux à embase, autofreinés (à
anneau non métallique), à filetage métrique à pas fin, de diamètre nominal de filetage d de 8 mm à 20 mm
inclus, de grade A pour les diamètres d < 16 mm et de grade B pour les diamètres d > 16 mm, et de classes de
qualité 6, 8 et 10.
Si d'autres spécifications sont requises, il est recommandé de les choisir dans les Normes internationales
existantes, par exemple ISO 261, ISO 965-2, ISO 2320 et ISO 4759-1.
2 Références normatives
Les normes suivantes contiennent des dispositions qui, par suite de la référence qui en est faite, constituent
des dispositions valables pour la présente Norme internationale. Au moment de la publication, les éditions
indiquées étaient en vigueur. Toute norme est sujette à révision et les parties prenantes des accords fondés
sur la présente Norme internationale sont invitées à rechercher la possibilité d'appliquer les éditions les plus
récentes des normes indiquées ci-après. Les membres de la CEI et de l'ISO possèdent le registre des Normes
internationales en vigueur à un moment donné.
ISO 225:1983, Éléments de fixation – Vis, goujons et écrous – Symboles et désignations des dimensions.
1)
ISO 261:– , Filetages métriques ISO pour usages généraux – Vue d'ensemble.
2)
ISO 965-2:– , Filetages métriques ISO pour usages généraux – Tolérances – Partie 2: Dimensions limites pour
la boulonnerie d'usage courant – Qualité moyenne.
ISO 2320:1997, Écrous hexagonaux autofreinés en acier – Caractéristiques mécaniques et performances.
ISO 3269:1988,
Éléments de fixation – Contrôle de réception.
3)
ISO 4042:– , Éléments de fixation – Revêtements électrolytiques.
4)
ISO 4759-1:– , Tolérances des éléments de fixation – Partie 1: Vis, goujons et écrous – Grades A, B et C.
ISO 6157-2: 1995, Éléments de fixation – Défauts de surface – Partie 2: Écrous.
ISO 8992:1986, Éléments de fixation – Prescriptions générales relatives aux vis, goujons et écrous.
1) À publier. (Révision de l'ISO 261:1973)
2) À publier. (Révision de l'ISO 965-2:1980)
3) À publier. (Révision de l'ISO 4042:1989)
4) À publier. (Révision de l'ISO 4759-1:1978)
©
ISO
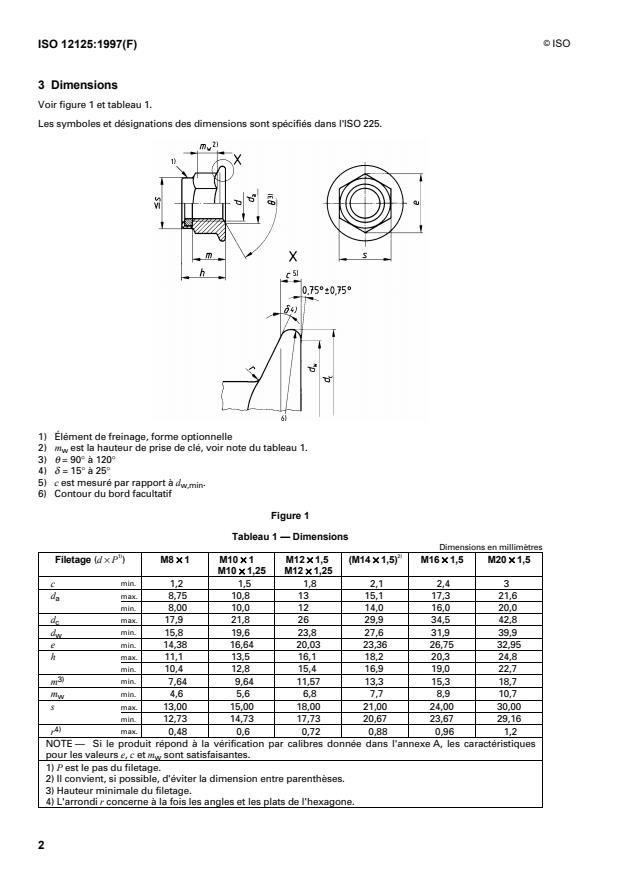
3 Dimensions
Voir figure 1 et tableau 1.
Les symboles et désignations des dimensions sont spécifiés dans l'ISO 225.
1) Élément de freinage, forme optionnelle
2) m est la hauteur de prise de clé, voir note du tableau 1.
w
3) q = 90° à 120°
4) d = 15° à 25°
5) c est mesuré par rapport à d .
w,min
6) Contour du bord facultatif
Figure 1
Tableau
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.
Loading comments...