ASTM D7680-10
(Practice)Standard Practice for Preparing Prints of Paste Printing Inks by a Motor-Driven Printability Tester
Standard Practice for Preparing Prints of Paste Printing Inks by a Motor-Driven Printability Tester
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
It is generally recognized that the best method for evaluating printing properties of ink-substrate combinations is by actual printing. this practice provides a convenient method for preparing repeatable laboratory prints at realistic conditions of printing speed, printing pressure and ink film thickness.
This practice is useful for quality control, specification acceptance between producer and user, product development and research. Printed samples have found widespread applications for color matching, gloss-ink holdout and other appearance properties, permanency, abrasion, drying time and many other tests of interest to the printing ink, paper and allied industries.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes the procedure for preparing laboratory prints of paste printing inks using a motor-driven printability tester.
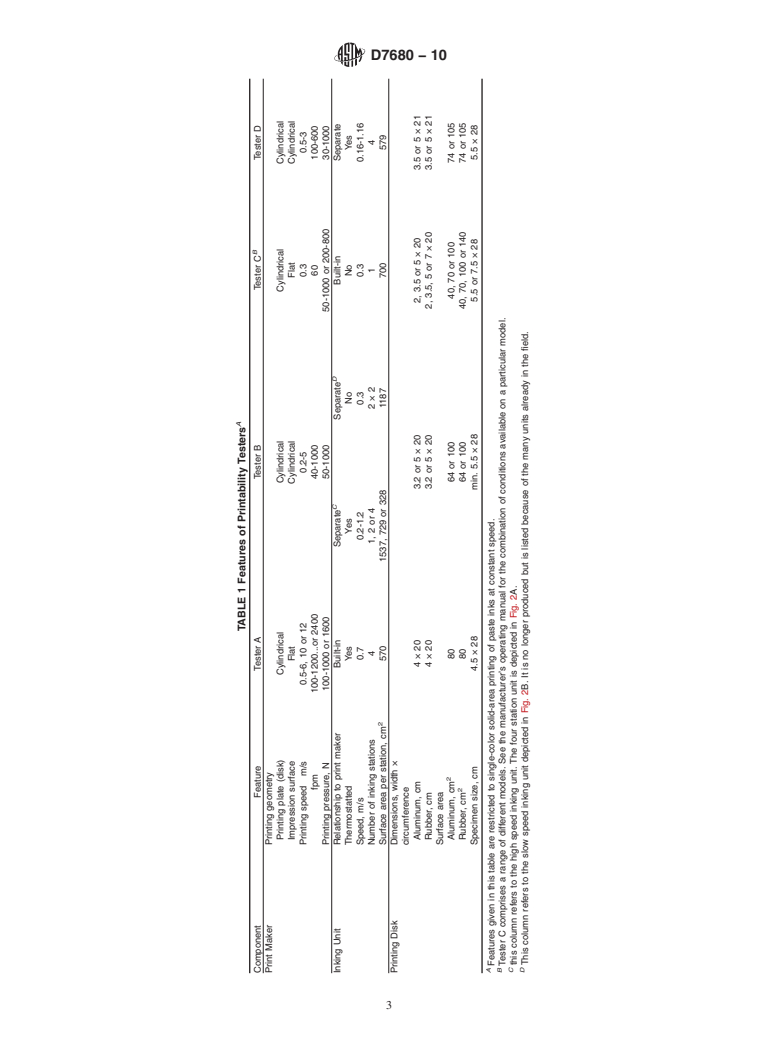
1.2 This practice covers printability testers of four different designs, referred to as Tester A, B, C, and D. These testers feature “push-button” control of printing speed and pressure and facilitate measurement of exact ink film thickness.
1.3 This practice is intended primarily for lithographic and letterpress inks that dry by oxidation or penetration. With appropriate drying or curing equipment, it is also applicable to other systems such as heat-set or energy curable.
1.4 This practice is applicable to the preparation of single-color solid-area prints by dry offset (also know as letterset) or by letterpress on any flat surface including paper, paperboard, plastic film, textiles, and metal.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The only other unit of measurement used is fpm.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7680 − 10
Standard Practice for
Preparing Prints of Paste Printing Inks by a Motor-Driven
1
Printability Tester
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7680; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D5039TestMethodsforIdentificationofWireSideofPaper
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
1.1 This practice describes the procedure for preparing
D6073Test Method for Relative Setting of Heatset Printing
laboratory prints of paste printing inks using a motor-driven
Inks
printability tester.
D7189Test Method for Relative Mileage of News Ink on
1.2 This practice covers printability testers of four different
Newsprint
designs, referred to as Tester A, B, C, and D. These testers
D7305TestMethodforReflectionDensityofPrintedMatter
4
feature “push-button” control of printing speed and pressure
2.2 Other Standards:
and facilitate measurement of exact ink film thickness.
ISO 187Paper, board and pulps—Standard atmosphere for
1.3 This practice is intended primarily for lithographic and conditioning and testing and procedure for monitoring the
letterpress inks that dry by oxidation or penetration. With atmosphere and conditioning of samples
appropriate drying or curing equipment, it is also applicable to ISO/DIS 2835–1Graphic technology—Laboratory prepara-
other systems such as heat-set or energy curable. tion test prints–Part 1: Paste inks
ISO 2846–1Graphic technology—Specification for color
1.4 This practice is applicable to the preparation of single-
and transparency of printing ink sets–Part 1: Inks for
color solid-area prints by dry offset (also know as letterset) or
heat-set web offset lithographic printing
by letterpress on any flat surface including paper, paperboard,
ISO 2846–2Graphic technology—Specification for color
plastic film, textiles, and metal.
and transparency of printing ink sets–Part 2: Inks for
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
coldset offset lithographic printing
standard. The only other unit of measurement used is fpm.
3. Terminology
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1 Symbols:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
fpm = feet per minute
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
(fpm ÷ 200 = m/s)
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
kgf = kilograms of force
(kgf = 9.81 N)
2. Referenced Documents
kp = kilopascals of pressure
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
(kp = 9.81 N)
D528Test Method for Machine Direction of Paper and
m/s = meters per second
3
Paperboard (Withdrawn 2010)
(m/s × 200 = fpm)
D1475Test Method For Density of Liquid Coatings, Inks,
3.2 Symbols for ink film thickness calculations:
and Related Products
2
A = printed area on the substrate, cm
S
2
D = density of the ink, g/cm
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and
IFT = ink film thickness on the plate, µm
P
Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
IFT = ink film thickness on the substrate, µm
Subcommittee D01.56 on Printing Inks. S
CurrenteditionapprovedDec.1,2010.PublishedFebruary2011.DOI:10.1520/ µm = micrometers
D7680-10.
W = weight of inked plate after printing, g
A
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
W = weight of inked plate before printing, g
B
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3 4
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
www.astm.org. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7680 − 10
6.1.3 Printing Disk,toserveastheprintingplate.Asseenin
W = weight of ink carried on the plate, g
P
Table 1, disks are 2 to 7 cm wide and ~ 20 cm in circumfer-
W = weight of the clean uninked plate, g
PO
ence. They are constructed of light-weight polished aluminum
W = weight of ink on the substrate, g
S
2
W = weight of ink on the substrate per unit area, g/m or rubber-covered aluminum or as a core with an aluminum or
SA
rubber covering. If rubber disks are used, it it recommended to
4. Summary of Practice
procure two or more so as to minimize waiting time after
cleanup.
4.1 Thedesignatedprintingspeedandpressurearepreseton
the print maker of the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.