ASTM E1840-96(2002)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Raman Shift Standards for Spectrometer Calibration
Standard Guide for Raman Shift Standards for Spectrometer Calibration
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers Raman shift values for common liquid and solid chemicals that can be used for wavenumber calibration of Raman spectrometers. The guide does not include procedures for calibrating Raman instruments. Instead, this guide provides reliable Raman shift values that can be used as a complement to low-pressure arc lamp emission lines which have been established with a high degree of accuracy and precision.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.34Some of the chemicals specified in this guide may be hazardous. It is the responsibility of the user of this guide to consult material safety data sheets and other pertinent information to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to their use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 1840 – 96 (Reapproved 2002)
Standard Guide for
Raman Shift Standards for Spectrometer Calibration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1840; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope mostcommonsourceofwavenumbervaluesiseitheremission
lines from low-pressure discharge lamps (for example, mer-
1.1 This guide covers Raman shift values for common
cury,argon,orneon)orfromthenon-lasingplasmalinesofthe
liquid and solid chemicals that can be used for wavenumber
laser. There are several good compilations of these well-
calibration of Raman spectrometers. The guide does not
established values (1-8). The disadvantages of using emission
includeproceduresforcalibratingRamaninstruments.Instead,
lines are that it can be difficult to align lamps properly in the
thisguideprovidesreliableRamanshiftvaluesthatcanbeused
sample position and the laser wavelength must be known
as a complement to low-pressure arc lamp emission lines
accurately.Withargon,krypton,andotherionlaserscommonly
which have been established with a high degree of accuracy
used for Raman the latter is not a problem because lasing
and precision.
wavelengths are well known. With the advent of diode lasers
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
and other wavelength-tunable lasers, it is now often the case
standard.
that the exact laser wavelength is not known and may be
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
difficult or time-consuming to determine. In these situations it
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
is more convenient to use samples of known relative wave-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
numbershiftforcalibration.Unfortunately,accuratewavenum-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ber shifts have been established for only a few chemicals.This
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
guide provides the Raman spectroscopist with average shift
1.4 Some of the chemicals specified in this guide may be
values determined in seven laboratories for seven pure com-
hazardous. It is the responsibility of the user of this guide to
pounds and one liquid mixture.
consult material safety data sheets and other pertinent infor-
mation to establish appropriate safety and health practices and
5. Raman Shift Standards
determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
5.1 Reagents and Methodology—Raman shifts were mea-
their use.
sured in seven laboratories for the following eight materials:
2. Referenced Documents
Compound Source
Naphthalene Mallinckrodt
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1,4-Bis(2-methylstyryl)benzene (a laser dye) Aldrich
E131 Terminology Relating to Molecular Spectroscopy
Sulfur Aldrich
50/50 (v/v) toluene/acetonitrile Mallinckrodt
E1683 Practice for Testing the Performance of Scanning
6 5
4-Acetamidophenol Aldrich
Raman Spectrometers
Benzonitrile Aldrich
Cyclohexane Mallinckrodt
3. Terminology
Polystyrene Aldrich
3.1 Definitions—Terminology used in this guide conforms
5.1.1 The eight materials were selected to cover a wide
−1
to the definitions set forth in Terminology E131.
wavenumber range (from 85 to 3327 cm ) for both solids and
liquids. They have no known polymorphs, and several batches
4. Significance and Use
were examined. All of the chemicals are readily available at
4.1 Wavenumber calibration is an important part of Raman
high purity from commercial sources such as Aldrich. Six of
analysis.ThecalibrationofaRamanspectrometerisperformed
the laboratories in the study used FT-Raman spectrometers;
or checked frequently in the course of normal operation and
one used a scanning Raman system; and one employed a
even more often when working at high resolution.To date, the
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E-13 on Molecular the text.
Spectroscopy and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E13.08 on Raman Available from Mallinckrodt, 16305 Swingley Ridge Dr., Chesterfield, MO
Spectroscopy. 63017.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1996. Published December 1996. Available from Aldrich, 1001 W. St. Paul Ave., Milwaukee, WI 53233.
2 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.06. The active ingredient of Tylenol, a registered trademark of McNeil-PPC.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E 1840 – 96 (2002)
multichannel spectrometer. The shift values were determined are included to help the user match spectral peaks with the
independently by each laboratory; only an approximate spec- tabulated shift values. Average shifts and standard deviations
trum without peak frequencies was provided as a guide. No
(s ) appear in the tables.With the exception of a few values
N−1
wavenumber calibration procedure was recommended, but
at low and high Raman shifts, only values with standard
−1
each laboratory used their own calibration procedure to obtain
deviations less than 1.0 cm are reported. Most of the
the most accurate data possible.
unreported peaks were weak, had poor shape, or overlapped
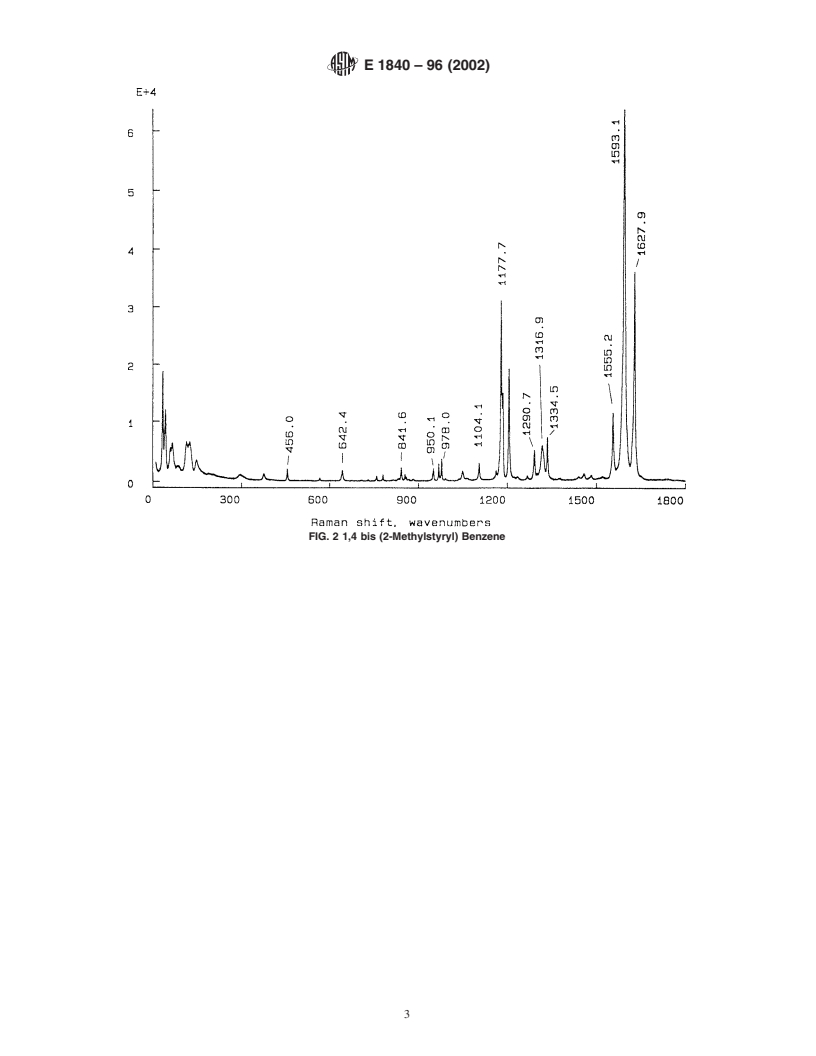
5.2 Data—Figs. 1-8 and Tables 1-8 give representative
other bands causing unacceptably high uncertainty in the data.
spectra and peak data for the eight standards. Uncorrected,
relative peak intensities determined with a SPEX 1403 scan-
6. Keywords
ning double monochromator (1200- lines/mm gratings) and
6.1 Raman s
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.