ASTM D3514-99
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Related Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics: Elastomeric Pad
Standard Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Related Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics: Elastomeric Pad
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resistance to the formation of pills and other surface distortions such as fuzzing of textile fabrics. The method utilizes the Stoll Quartermaster Universal Wear Tester with the frosting attachment. The procedure is generally applicable to all types of woven and knitted fabrics.
Note 1- For other current test methods of testing the pilling resistance of textiles, refer to Test Methods D 3511, D 3512, and D 4970.
1.2 The fabric may be laundered or dry cleaned before testing.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
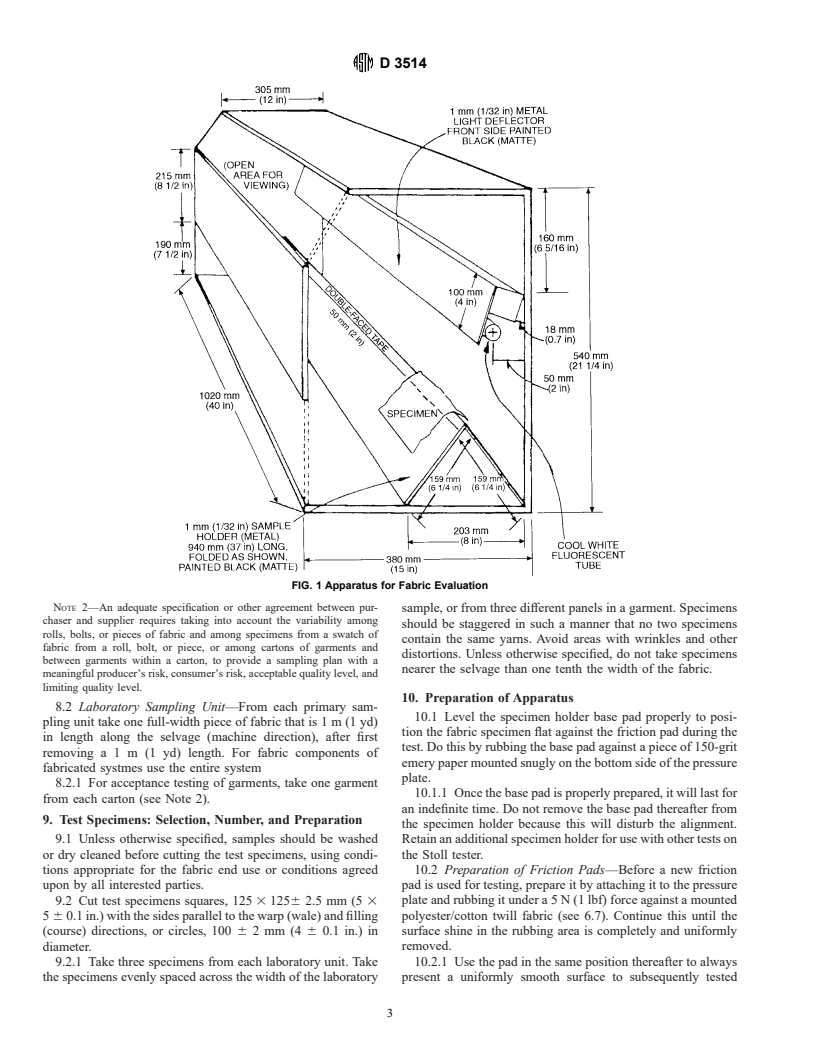
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: D 3514 – 99
Standard Test Method for
Pilling Resistance and Other Related Surface Changes of
1
Textile Fabrics: Elastomeric Pad
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3514; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the resis- 3.1 Definitions:
tance to the formation of pills and other surface distortions 3.1.1 fuzz, n—untangled fiber ends that protrude from the
such as fuzzing of textile fabrics. The method utilizes the Stoll surface of a yarn or fabric.
Quartermaster Universal Wear Tester with the frosting attach- 3.1.2 pilling resistance, n—resistance to the formation of
ment. The procedure is generally applicable to all types of pills on the surface of a textile fabric.
woven and knitted fabrics. 3.1.3 pills, n—bunches or balls of tangled fibers which are
held to the surface of a fabric by one or more fibers.
NOTE 1—For other current test methods of testing the pilling resistance
3.1.4 For definitions of other textile terms used in this test
of textiles, refer to Test Methods D 3511, D 3512, and D 4970.
method, refer to Terminology D 123.
1.2 The fabric may be laundered or dry cleaned before
testing.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
4.1 Pilling and other changes in surface appearance that
tions, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
occur in normal wear are simulated on a laboratory testing
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
machine. Fabric samples are washed or drycleaned, depending
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
on expected refurbishment, followed by controlled rubbing
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
against an elastomeric pad having specifically selected me-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
chanical properties. The degree of fabric pilling is evaluated by
comparison of the tested specimens with visual standards that
2. Referenced Documents
may be actual fabrics, or photographs of fabrics, showing a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
range of pilling resistance. The observed resistance to pilling is
2
D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
reported using an arbitrary rating scale.
2
D 1776 Practice for Conditioning Textiles for Testing
D 3511 Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Re-
5. Significance and Use
lated Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics: Brush Pilling
5.1 Acceptance Testing—This method of testing fabrics for
3
Tester
resistance to pilling is not recommended for acceptance testing.
D 3512 Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Re-
If it is used for acceptance testing, it should be used with
lated Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics: Random Tumble
caution because interlaboratory data are not available. In some
3
Pilling Tester
cases the purchaser and the supplier may have to test a
D 4970 Test Method for Pilling Resistance and Other Re-
commercial shipment of one or more specific materials by the
lated Surface Changes of Textile Fabrics (Martindale
best available method, even though the method has not been
3
Pressure Tester Method)
recommended for acceptance testing.
2.2 ASTM Adjuncts:
5.1.1 If there is a disagreement arising from differences in
12-43514 Three Sets of Five Photographic Standards for
values reported by the purchaser and the supplier when using
4
Elastomeric Pad Pilling Test
Test Method D 3514 for acceptance testing, the statistical bias,
if any, between the laboratory of the purchaser and the
laboratory of the supplier should be determined based on
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-13 on
testing specimens randomly drawn from one sample of mate-
Textiles, and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.60 on Fabric Test
Methods, Specific.
rial of the type being evaluated. Competent statistical assis-
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1999. Published January 2000. Originally
tance is recommended for the investigation of bias. A minimum
published as D 3514 – 76. Discontinued November 1995 and reinstated as
of two parties should take a group of test specimens which are
D 3514 – 96.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.01. as homogeneous as possible and which are from a lot of
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.02.
material of the type in question. The test specimens should then
4
Available from American Society for Testing and Materials, 100 Barr Harbor
be randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for
Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 3514
testing. The aver
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.