ASTM F1890-98
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Softball Bat Performance Factor
Standard Test Method for Measuring Softball Bat Performance Factor
SCOPE
1.1 This specification defines a method for determining bat performance by measuring the coefficient of restitution (COR) of the bat-ball collision using a ball with a known COR then deriving a bat performance factor.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 1890 – 98
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
1
Measuring Softball Bat Performance Factor
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1890; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope impact efficiency calculated as the relative speed of the objects
after impact divided by the relative speed of the objects before
1.1 This specification defines a method for determining bat
impact.
performance by measuring the coefficient of restitution (COR)
3.1.7 moment of inertia (MOI), n—a measure of mass
of the bat-ball collision using a ball with a known COR then
distribution relative to an axis of rotation. It is the product of
deriving a bat performance factor.
the mass multiplied by the square of the distance to the mass,
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
summed over the entire bat.
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
3.1.8 period, n—the time required for a pendulum to oscil-
information only.
late through one complete cycle.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Significance and Use
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 This test method offers a laboratory means to compare
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
the overall performance of a bat as it relates to batted balls
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
speeds.
2. Referenced Documents 4.2 Use of this test method can provide sports governing
bodies a means to compare the anticipated batted ball speed,
2.1 ASTM Standards:
thus batted ball distance for the purposes of controlling the
F 1887 Test Method for Measuring the Coefficient of Res-
2
game and safety.
titution (COR) of Baseballs and Softballs
4.3 Batted ball speed can be related to bat performance
F 1888 Test Method for Compression-Displacement of
2
factor (BPF) using the following formulae:
Baseballs and Softballs
4.3.1 V 5 bat swing speed, mph—speed measured at the
3. Terminology
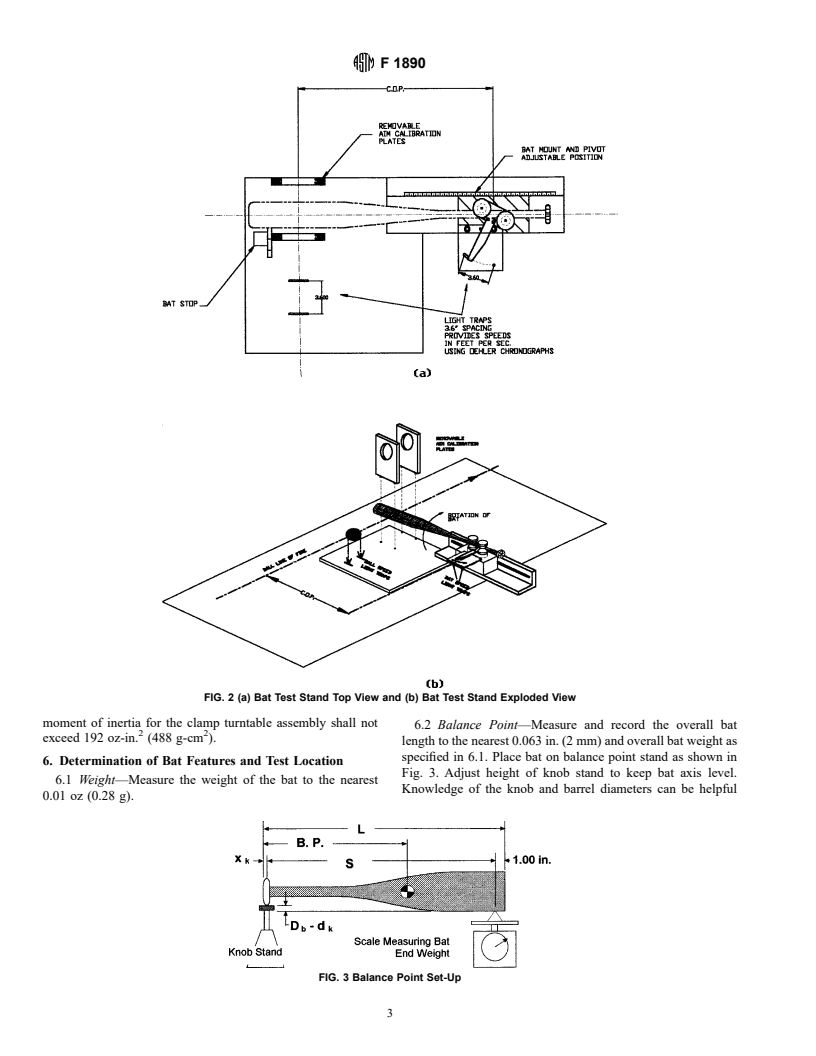
point of impact, at the sweet spot of the bat, otherwise specified
as the COP. Impacts as the COP offer essentially the highest
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
batted ball speeds due to the optimization of momentum
3.1.1 balance point, n—the distance to the center of mass
transfer. The BPF value has been measured at this point and
measured from the outermost edge of the knob end of the bat.
represents the maximum performance of the bat; therefore, the
3.1.2 bat-ball coeffıcient of restitution (COR), n—the COR
following calculations are correct only when the bat swing
of a specific ball colliding with a stationary bat as defined in
speed at the point impact are used. The swing speed at the COP
this test method. See coeffıcient of restitution (COR).
can be as much as 20 % slower than bat speeds measured at the
3.1.3 bat performance factor, n—the ratio of performance
end of the bat. Typical adult values are 60 mph for average
change a bat introduces to a ball collision, compared to a ball
players and 70 mph for top level non-super major softball
colliding with a solid wall as in Test Method F 1887.
players. It is recognized that a players swing speed varies
3.1.4 ball cover, n—the leather or equivalent material used
depending on skill level, conditioning, and bat swing weight
to cover the ball core.
(MOI).
3.1.5 center of percussion (COP), n—also known as the
4.3.2 v 5 pitch speed, mph—horizontal speed of the ball
center of oscillation, the length of a simple pendulum with the
incoming to the batter. Typical slow pitch values are 10 mph
same period. Forces and impacts at this location will not induce
while fast pitch speeds vary significantly with the level of play.
reactions at the pivot point.
4.3.3 W 5 bat weight, oz.
3.1.6 coeffıcient of restitution (COR), n—a measure of
4.3.4 w 5 ball weight, oz.
2
4.3.5 I 5 MOI, oz-in. —typical value for an average bat is
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-08 on Sports
9000.
Equipment and Facilities and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F08.26 on
4.3.6 e 5 bat-ball COR 5 BPF 3 ball COR. One must
Baseball and Softball Equipment and Facilities.
choose a ball COR to determine the batted ball speed.
Current edition approved June 10, 1998. Published February 1999.
2
4.3.7 a 5 distance from pivot to center of mass (balance
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.07.
1
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.