ASTM D4400-18
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sag Resistance of Paints Using a Multinotch Applicator
Standard Test Method for Sag Resistance of Paints Using a Multinotch Applicator
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Evaluation of sag resistance is essential in quality control for both producers and purchasers of coatings. Practical application tests are poor in reproducibility, while viscometric methods, for example Test Methods D2196, are time-consuming and lack the convincing aspect of actual sagging. This method provides simple and rapid tests, whereby sag resistance is demonstrated by a visible sag pattern, and is rated objectively in terms of numerical values that correlate with brushout test observations.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of the sag resistance of aqueous and nonaqueous liquid coatings at any level of sag resistance.
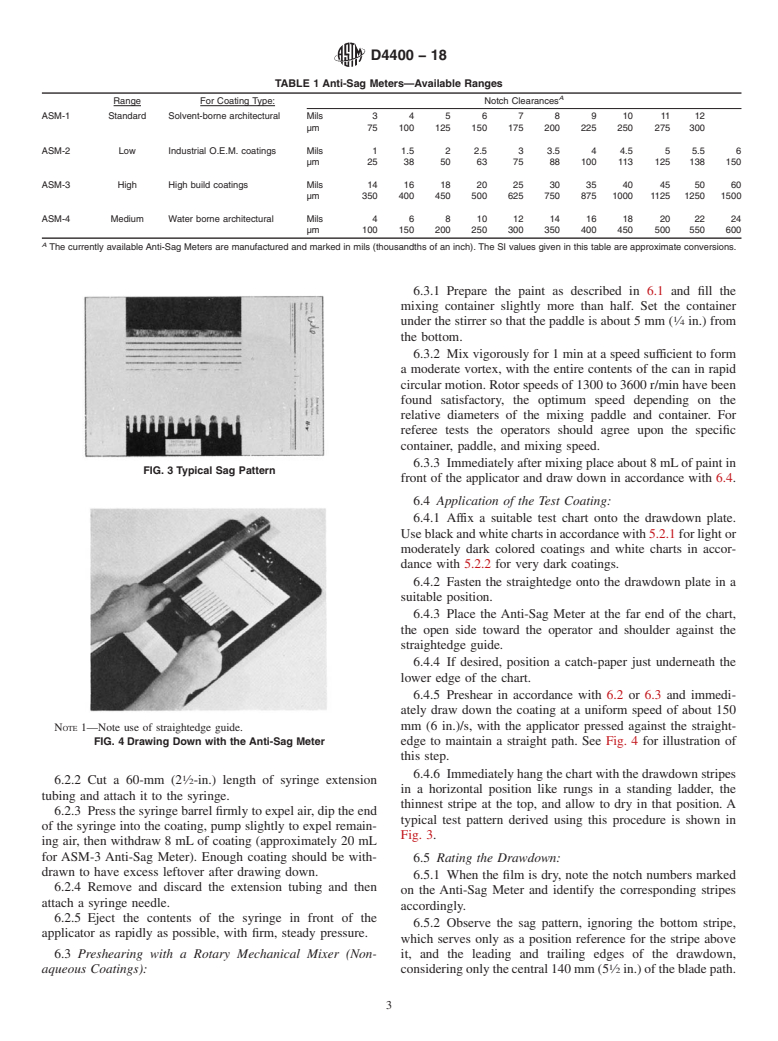
FIG. 1 Diagram of the Medium Range Anti-Sag Meter
FIG. 2 Medium Range Anti-Sag Meter
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
Note 1: Because the only manufacturer of the applicator know to the committee manufactures to inch-pound units, inch-pound units will be regarded as the standard when referring to the applicator.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4400 − 18
Standard Test Method for
1
Sag Resistance of Paints Using a Multinotch Applicator
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4400; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
The multinotch applicator used in this test method is a drawdown blade with a series of notches of
successively higher clearance, referred to as the Anti-Sag Meter. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 for a
representative diagram and photograph. The numerical value for sag resistance obtained with this
instrument is referred to as the Anti-Sag Index.
Anti-Sag Meters are made with several clearance ranges for different types of coatings (see 5.1 and
Table 1). In developing this standard the task group used an instrument with a range from 4 to 24 mils,
but the method is applicable to any clearance range, and results using instruments with overlapping
ranges correlate and have equal validity.
2
The basic method was developed in 1962 and is referenced in U.S. Federal specifications
TT-E-508, TT-E-506, and TT-P-1511.
Apreshear program is essential for a drawdown sag test to duplicate the breakdown in structure that
occurs when thixotropic paints are applied by brushout or other practical application methods. The
procedures therefore include the preshearing of paints just prior to making test applications.
1. Scope 1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
thesagresistanceofaqueousandnonaqueousliquidcoatingsat
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
any level of sag resistance.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
2. Referenced Documents
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
D2196 Test Methods for Rheological Properties of Non-
with the standard.
Newtonian Materials by Rotational Viscometer
NOTE 1—Because the only manufacturer of the applicator know to the
4
2.2 U.S. Federal Specifications:
committee manufactures to inch-pound units, inch-pound units will be
regarded as the standard when referring to the applicator. Fed. Spec. TT-E-508 Alkyd semi-gloss enamel
Fed. Spec. TT-E-506 Alkyd gloss enamel
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Fed. Spec. TT-P-1511 Interior latex gloss and semi-gloss
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
finishes
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3. Summary of Test Method
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1 After preshearing, the coating is applied to a test chart
with a multinotch applicator. The charts are immediately hung
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
and Related Coatings, Materials, andApplications and is the direct responsibility of
3
Subcommittee D01.42 on Architectural Coatings. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2018. Published October 2018. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ɛ1
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D4400 – 99 (2012) . Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
DOI: 10.1520/D4400-18. the ASTM website.
2 4
“Design of an Improved Sag Tester,” Offıcial Digest, Vol 34, No. 453, October Available from DLA Document Services, Building 4/D, 700 Robbins Ave.,
1962. Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, http://quicksearch.dla.mil.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4400 − 18
FIG. 1 Diagram of the Medium Range Anti-Sag Meter
5
5.2.1 Black and White Charts, about 193 by 288 mm (7 ⁄8
3 1
by 11 ⁄8 in.), the black area comprising about 140 mm (5 ⁄2 in.)
centered on the
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D4400 − 99 (Reapproved 2012) D4400 − 18
Standard Test Method for
1
Sag Resistance of Paints Using a Multinotch Applicator
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4400; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Sole source of supply footnote was removed editorially and new footnote placed in Precision section in Novem-
ber 2012.
INTRODUCTION
The multinotch applicator used in this test method is a drawdown blade with a series of notches of
successively higher clearance, referred to as the Anti-Sag Meter. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 for a
representative diagram and photograph. The numerical value for sag resistance obtained with this
instrument is referred to as the Anti-Sag Index.
Anti-Sag Meters are made with several clearance ranges for different types of coatings (see 5.1 and
Table 1). In developing this standard the task group used an instrument with a range from 4 to 24 mils,
but the method is applicable to any clearance range, and results using instruments with overlapping
ranges correlate and have equal validity.
2
The basic method was developed in 1962 and is referenced in U.S. Federal specifications
TT-E-508, TT-E-506, and TT-P-1511.
A preshear program is essential for a drawdown sag test to duplicate the breakdown in structure that
occurs when thixotropic paints are applied by brushout or other practical application methods. The
procedures therefore include the preshearing of paints just prior to making test applications.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of the sag resistance of aqueous and nonaqueous liquid coatings at any
level of sag resistance.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as the standard. The values given in
parentheses are for information only.stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used
independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
NOTE 1—Because the only manufacturer of the applicator know to the committee manufactures to inch-pound units, inch-pound units will be regarded
as the standard when referring to the applicator.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.42 on Architectural Coatings.
Current edition approved May 15, 2012Sept. 15, 2018. Published May 2012October 2018. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 20072012 as
ɛ1
D4400 – 99 (2007).(2012) . DOI: 10.1520/D4400-99R12E01.10.1520/D4400-18.
2
“Design of an Improved Sag Tester,” Offıcial Digest, Vol 34, No. 453, October 1962.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4400 − 18
FIG. 1 Diagram of the Medium Range Anti-Sag Meter
FIG. 2 Medium Range Anti-Sag Meter
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2196 Test Methods for Rheological Properties of Non-Newtonian Materials by Rotational Viscometer
4
2.2 U.S. Federal Specifications:
Fed. Spec. TT-E-508 Alkyd semi-gloss enamel
Fed. Spec. TT-E-506 Alkyd gloss enamel
Fed. Spec. TT-P-1511 Interior latex gloss and semi-gloss finishes
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 After preshearing, the coating is applied to a test chart with a multinotch applicator. The charts are immediately hung
vertically with the drawdown stripes horizontal, similar to rungs of a ladder, with
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.