ASTM D4017-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Water in Paints and Paint Materials by Karl Fischer Method
Standard Test Method for Water in Paints and Paint Materials by Karl Fischer Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 Control of water content is often important in controlling the performance of paint and paint ingredients, and it is critical in controlling volatile organic compound (VOC) content.
4.2 Paint materials are often insoluble in common Karl Fischer solvents such as methanol. Pyridine has been found to be a nearly universal solvent for these materials; however, the Karl Fischer reaction is too slow in that solvent at room temperature. To speed it up, 1-ethylpiperidine is added at 5 % as a buffer, or “catalyst.”
4.3 For nonpyridine-based reagents, a number of different solvent systems are available to increase solubility and to minimize interferences from ketones and aldehydes.
SCOPE
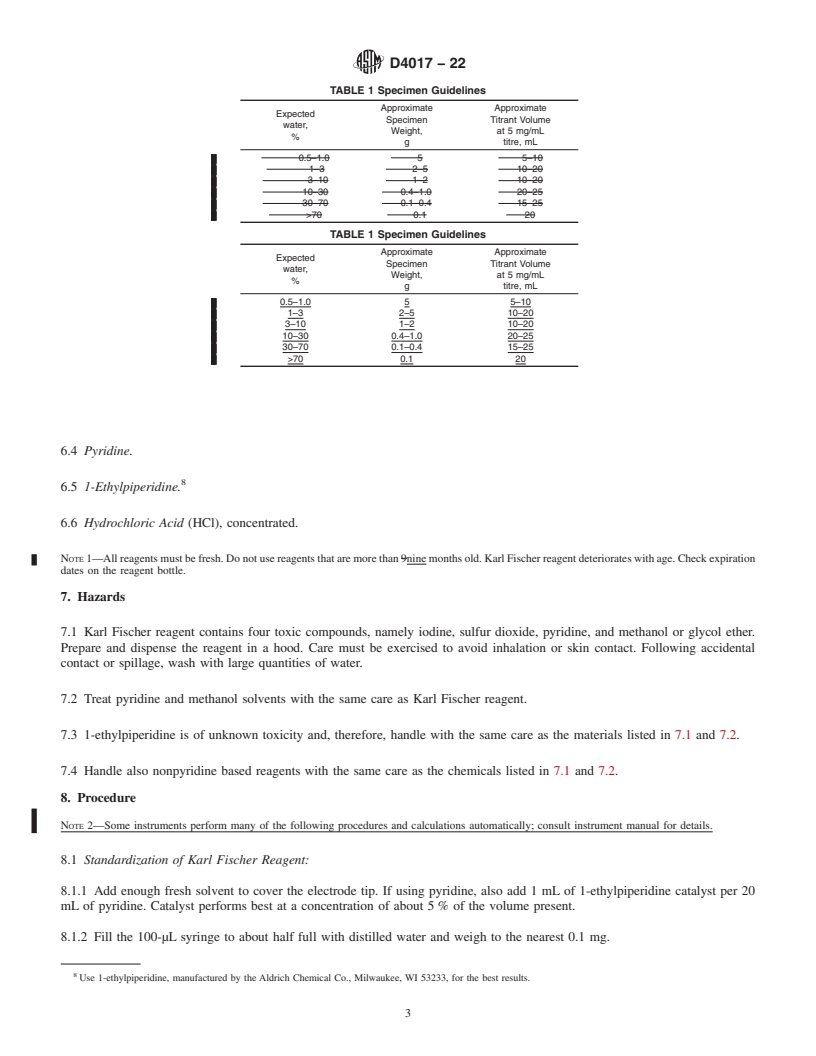
1.1 This test method is applicable to all paints and paint materials, including resins, monomers, and solvents, with the exception of aldehydes and certain active metals, metal oxides, and metal hydroxides. While the evaluation was limited to pigmented products containing amounts of water in the 30 % to 70 % range, there is reason to believe that higher and lower concentrations can be determined by this test method.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4017 − 22
Standard Test Method for
1
Water in Paints and Paint Materials by Karl Fischer Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4017; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
3
1. Scope cialty Chemicals (Withdrawn 2009)
E203Test Method for Water Using Volumetric Karl Fischer
1.1 This test method is applicable to all paints and paint
Titration
materials, including resins, monomers, and solvents, with the
2.2 Other Standard:
exceptionofaldehydesandcertainactivemetals,metaloxides,
EPAFederalReferenceMethod24DeterminationofVolatile
and metal hydroxides. While the evaluation was limited to
Matter Content, Density, Volume Solids, and Weight
pigmentedproductscontainingamountsofwaterinthe30%to
4
Solids of Surface Coatings
70% range, there is reason to believe that higher and lower
concentrations can be determined by this test method.
3. Summary of Test Method
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1 The material is dissolved in a suitable solvent, and
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
titrated directly with standardized Karl Fischer reagent, to an
only.
electrometric end point. The sluggish reaction with water in
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
pyridine is accelerated with a chemical catalyst,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1-ethylpiperidine.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.1 Karl Fischer reagent is a mixture of iodine, amine,
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
sulfur dioxide, and an alcohol. In the reaction with water,
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
iodine is reduced to hydrogen iodide. Once all the water is
Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
consumed, the appearance of free iodine is detected electro-
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
chemically and the titration is stopped. The following depicts
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
the chemistry that takes place:
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
ROH+SO +RN↔ (RNH)SO R
2 3
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
HO+I +(RNH)SO R+2RN→ (RNH)SO R+2(RNH)I
2 2 3 4
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.2 In classical Karl Fischer titrations the base used is
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
pyridine, and the solvent either methanol or methoxy ethanol.
In order to accelerate the reaction when pyridine is used,
2. Referenced Documents
1-ethylpiperidine is used as a catalyst/buffer. The additional
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
buffer capacity is usually already built in to most nonpyridine
5
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
based reagents such as hydranal (see Hydranal Manual).
D3960PracticeforDeterminingVolatileOrganicCompound
(VOC) Content of Paints and Related Coatings
4. Significance and Use
E180Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM
4.1 Control of water content is often important in control-
Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Spe-
ling the performance of paint and paint ingredients, and it is
critical in controlling volatile organic compound (VOC) con-
tent.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint
andRelatedCoatings,Materials,andApplicationsandisthedirectresponsibilityof
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials.
3
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2022. Published December 2022. Originally The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D4017–02 (2015). www.astm.org.
4
DOI: 10.1520/D4017-22. AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.access.gpo.gov.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on AvailablefromHoechstCelaneseCorporation,HydranalTechnicalCenter,U.S.
the ASTM website. Highway 43, Bucks, AL 36512.
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4017 − 02 (Reapproved 2015) D4017 − 22
Standard Test Method for
1
Water in Paints and Paint Materials by Karl Fischer Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4017; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is applicable to all paints and paint materials, including resins, monomers, and solvents, with the exception
of aldehydes and certain active metals, metal oxides, and metal hydroxides. While the evaluation was limited to pigmented
products containing amounts of water in the 3030 % to 70 % range, there is reason to believe that higher and lower concentrations
can be determined by this test method.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 7.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D3960 Practice for Determining Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Content of Paints and Related Coatings
E180 Practice for Determining the Precision of ASTM Methods for Analysis and Testing of Industrial and Specialty Chemicals
3
(Withdrawn 2009)
E203 Test Method for Water Using Volumetric Karl Fischer Titration
2.2 Other Standard:
EPA Federal Reference Method 24 Determination of Volatile Matter Content, Density, Volume Solids, and Weight Solids of
4
Surface Coatings
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D01 on Paint and Related Coatings, Materials, and Applications and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D01.21 on Chemical Analysis of Paints and Paint Materials.
Current edition approved June 1, 2015Dec. 1, 2022. Published June 2015December 2022. Originally approved in 1981. Last previous edition approved in 20082015 as
ε1
D4017 – 02 (2008)(2015). . DOI: 10.1520/D4017-02R15.10.1520/D4017-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office Superintendent of Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
www.access.gpo.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4017 − 22
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The material is dissolved in a suitable solvent, and titrated directly with standardized Karl Fischer reagent, to an electrometric
end point. The sluggish reaction with water in pyridine is accelerated with a chemical catalyst, 1-ethylpiperidine.
3.1.1 Karl Fischer reagent is a mixture of iodine, amine, sulfur dioxide, and an alcohol. In the reaction with water, iodine is
reduced to hydrogen iodide. Once all the water is consumed, the appearance of free iodine is detected electrochemically and the
titration is stopped. The following depicts the chemistry that takes place:
ROH + SO + RN ↔ (RNH)SO R
2 3
H O + I + (RNH)SO R + 2RN→ (RNH)SO R + 2(RNH)I
2 2 3 4
3.2 In classical Karl Fischer titrations the base used is pyridine, and the solvent either methanol or methoxy ethanol. In order to
accelerate the reaction when pyridine is used, 1-ethylpiperidine is used as a catalyst/buffer. The additional buffer capacity is usually
5
already built in to most nonpyridine based reagents
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.