ASTM D6466-99(2005)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other Animal Fibers By Sirolan-Laserscan Fiber Diameter Analyser
Standard Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other Animal Fibers By Sirolan-Laserscan Fiber Diameter Analyser
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is considered satisfactory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wool and other animal fibers in raw and sliver form because current estimates of between-laboratory precision are acceptable. In cases of disagreement arising from differences in values reported by the purchaser and the supplier when using this test method for acceptance testing, Test Method D 2130 shall be used as a referee method.
This test method may be used for determining compliance with average fiber diameter and diameter variation to assign grades when determining conformance of shipments to material specifications given in Specifications D 2252, D 2816, D 3991, and D 3992.
The procedures for determining mean fiber diameter and standard deviation of fiber diameter provided in this test method and in IWTO-12 are in essential agreement.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a procedure, using the Sirolan-Laserscan, for the determination of the average fiber diameter and the fiber diameter variation in wool and other animal fibers in their various forms.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6466 – 99 (Reapproved 2005)
Standard Test Method for
Diameter of Wool and Other Animal Fibers By Sirolan-
Laserscan Fiber Diameter Analyser
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6466; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 Federal Standards:
Official Standards of the United States for Grades of
1.1 This test method covers a procedure, using the Sirolan-
Wool, Section 31.0
Laserscan, for the determination of the average fiber diameter
Measurement Method for Determining Grade ofWool, Sec-
and the fiber diameter variation in wool and other animal fibers
tion 31.204
in their various forms.
Official Standards of the United States for Grades of Wool
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
Top, Section 31.1
standard.
Measurement Method for Determining Grade of Wool
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Top, Section 31.301
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
IWTO-8 Method of Determining Wool Fiber Diameter by
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the Projection Microscope
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
IWTO-12 Measurement of the Mean and Distribution of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Fibre Diameter Using the Sirolan-Laserscan Fibre Diam-
2. Referenced Documents eter Analyser
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3. Terminology
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
3.1 Definitions:
D584 Test Method for Wool Content of Raw Wool—
3.1.1 average fiber diameter, n—the arithmetic width of a
Laboratory Scale
group of fibers.
D1060 Practice for Core Sampling of Raw Wool in Pack-
3.1.1.1 Discussion—In wool and other animal fibers, all
ages for Determination of Percentage of Clean Wool Fiber
animal fibers, regardless of species, can be measured using the
Present
Sirolan-Laserscan to determine average fiber diameter.
D1776 Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
3.1.2 grade, n—in wool and mohair, a numerical designa-
D2130 Test Method for Diameter of Wool and Other
tion used in classification of fibers in their raw, semi-processed
Animal Fibers by Microprojection
and processed forms based on average fiber diameter and
D2252 Specification for Fineness of Types of Alpaca
variation of fiber diameter.
D2816 Test Method for Cashmere Coarse-Hair Content in
3.1.3 snippet, n—a wool or other animal fiber which has
Cashmere
been cut to a specified length.
D3991 Specifications for Fineness of Wool or Mohair and
3.1.4 For definitions of other textile terms used in this test
Assignment of Grade
method, refer to Terminology D123.
D3992 Specifications for Fineness of Wool Top or Mohair
Top and Assignment of Grade
4. Summary of Test Method
E126 Test Method for Inspection, Calibration, and Verifica-
4.1 This test method describes procedures for sampling
tion of ASTM Hydrometers
variousformsofwool,thereductionofthesampletosmalltest
E1750 Guide for Use of Water Triple Point Cells
specimens, and measurement of the diameter of a number of
fibers from the test specimens using the Laserscan. Snippets
cutfromthevariousformsofwoolarecleanedwhererequired,
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 onTextiles
and dispersed in a mixture of isopropanol and water. The
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.13 on Wool and Wool Felt.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2005. Published December 2005. Originally
approved in 1999. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D6466 – 99. DOI:
10.1520/D6466-99R05.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Federal Register, Vol 30, No. 161, Aug. 20, 1965, pp. 10829–10833.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Federal Register, Vol 33, No. 248, Dec. 21, 1968, pp. 19073–19076.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Wool Textile Organization, International Wool Secretariat, Com-
the ASTM website. mercial Development Department, Valley Drive, Ilkley, LS298PB, England.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D6466 – 99 (2005)
FIG. 1 Block Diagram of Laserscan System
suspension of snippets is transported through a measuring cell 6.1.2 A means of measuring the reduction of light intensity
which is positioned in a beam of laser light. The reduction in of the beam due to the passage of a snippet and converting this
intensity of the laser beam as the individual snippets pass to digital form.
through the beam of light, approximately 500 µm in diameter, 6.1.3 A system for discrimination against the measurement
is sensed by a detector and transformed, using a calibration of fibers that do not properly intersect the beam and contami-
look-up table, into a diameter in micrometres. Each diameter nants such as fiber fragments, dirt, and vegetable matter
measurement is allocated to a diameter class, and when the particles.
specified number of fibers has been measured, the class 6.1.4 A computing system to transform and collate results.
contents are statistically analysed to produce the mean and 6.2 Fiber Sectioning Device—One or more of the follow-
standard deviation of fiber diameter for the specimen. Full ing:
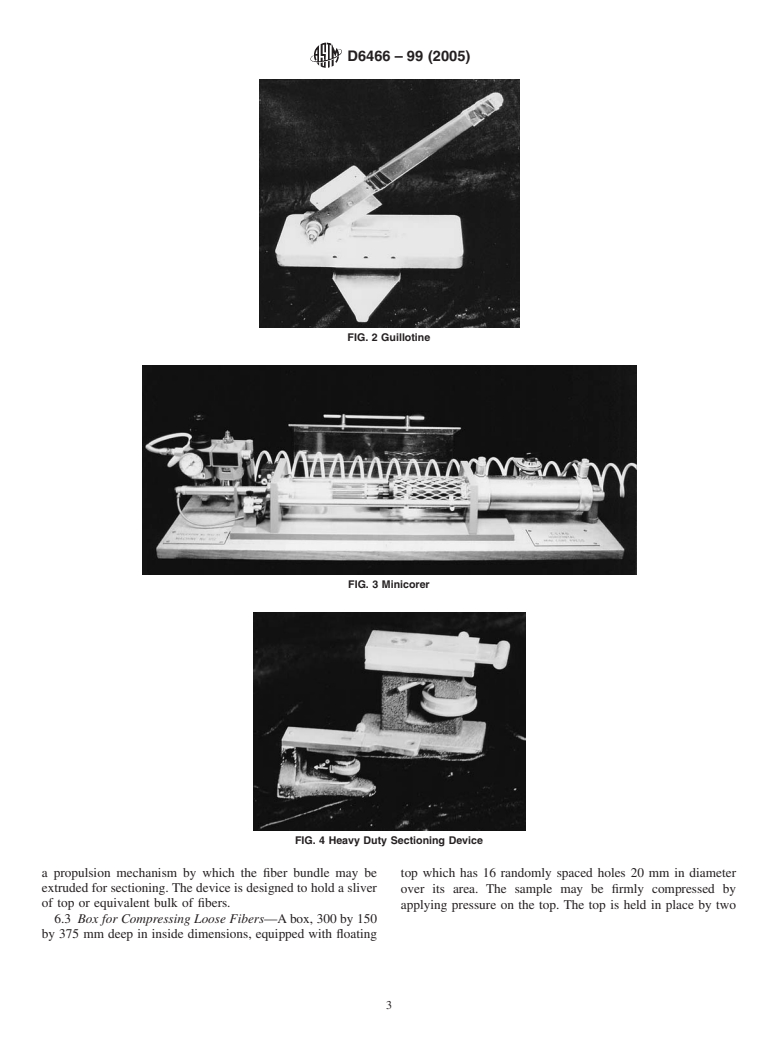
distribution data are also available in the form of a printed 6.2.1 Guillotine —Fig. 2, having two parallel cutting edges
histogram. between 1.8 and 2.0 mm apart.
6.2.2 Minicore —Fig. 3, a cylindrical sample holder, de-
5. Significance and Use
signedforlargesamples,inwhichasampleismanuallypacked
and a coring head which is driven pneumatically into the
5.1 This test method is considered satisfactory for accep-
sample. The sample is compacted by a spring-loaded platen
tance testing of commercial shipments of wool and other
and 6 minicore tubes with 2-mm diameter tips pass through
animal fibers in raw and sliver form because current estimates
perforations in the platen when the force supplied by the
of between-laboratory precision are acceptable. In cases of
pneumatic cylinder exceeds the force (300 N) from the
disagreement arising from differences in values reported by the
preloaded spring.At the end of the stroke, the cutting tips have
purchaser and the supplier when using this test method for
penetrated to within 0.5 mm of the base of the sample holder.
acceptance testing, Test Method D2130 shall be used as a
The sample collected by the minicore tubes is automatically
referee method.
expelled into a collection device upon retraction of the coring
5.2 This test method may be used for determining compli-
head.
ance with average fiber diameter and diameter variation to
6.2.3 Heavy-Duty Sectioning Device —Fig. 4, comprised of
assign grades when determining conformance of shipments to
ametalplatewithslotandcompressingkey,andequippedwith
material specifications given in Specifications D2252, D2816,
D3991, and D3992.
5.3 Theproceduresfordeterminingmeanfiberdiameterand
standard deviation of fiber diameter provided in this test Sirolan-Laserscan analyser, minicorer, and guillotine obtainable from Loptex
S.r.l.,Via L. Leoni 20, 2210 0 COMO (Italia).Tel: 39 31 273502; Fax: 39 1 273255.
method and in IWTO-12 are in essential agreement.
If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM
International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a
6. Apparatus and Materials
meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Obtainable from MICO Instruments, 1944 Main St., P.O. Box 451, Marshfield
6.1 Fiber Diameter Analyser —Fig. 1, consisting of the
Hills, MA02051-0451. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this
following:
information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive
6.1.1 A means of transporting fiber snippets in an 1
careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which
isopropanol/water mixture through a laser beam. you may attend.
D6466 – 99 (2005)
FIG. 2 Guillotine
FIG. 3 Minicorer
FIG. 4 Heavy Duty Sectioning Device
a propulsion mechanism by which the fiber bundle may be top which has 16 randomly spaced holes 20 mm in diameter
extruded for sectioning. The device is designed to hold a sliver
over its area. The sample may be firmly compressed by
of top or equivalent bulk of fibers.
applying pressure on the top. The top is held in place by two
6.3 Box for Compressing Loose Fibers—Abox, 300 by 150
by 375 mm deep in inside dimensions, equipped with floating
D6466 – 99 (2005)
rodsextendingthroughholesinthesideoftheboxandoverthe 9.1.2 Major Sort—Packaged grease wool in fleece from
top. The coring tube is thrust through the holes in the top to which a diameter test is needed, hand sample by drawing one
obtain a sample. ormorehandfulsofwoolfromthemajorsortportionofatleast
6.4 Pressure Coring Tube —A 13-mm inside-diameter 50 fleeces taken at random from the lot.The aggregate mass of
metaltube,approximately760mmlong,reamedandtappedon the sample shall be at least 1.5 kg.
one end to hold a sharp 10 or 13-mm diameter cutting tip. The 9.1.3 Piles of Graded or Sorted Wool—Sample piles of
tube is fitted with a “T” cross bar about 500 mm long. graded or sorted wool by taking from random locations in the
6.5 Core Extruder—A6-mm wood dowel or aluminum rod pile at lease 50 handfuls of wool, the aggregate mass of which
slightlylongerthanthecoringtubetopushthesamplefromthe shall be at least 1.5 kg. If the wool is in fleece form and a test
tube. isneededforonlythemajorsort,takethesampleinaccordance
6.6 Apparatus for Measuring the Water Content of Isopro- with 9.1.2.
panol. 9.1.4 Card Sliver—Sample the wool card sliver by drawing
6.6.1 Hydrometer, for the range density from 0.800 to 0.900 ten 600-mm lengths at random from the lot, preferably during
Mg/m and calibrated in accordance with Test Method E126. the carding operation.
6.6.2 Thermometer, for the range from 0 to 50°C and 9.1.5 Top—Sample the top by drawing from each 9000 kg
calibrated in accordance with Guide E1750. or fraction thereof, four sections of sliver, each of which shall
6.7 Calibration Standards, for instrument calibration. be at least1min length and taken from different balls of top
6.7.1 Current Interwoollabs III Standard Tops, for wood. selected at random. Take only one ball from any one bale or
6.7.2 Current International Mohair Association Standard carton. For broken top, take an equivalent aggregate length of
Tops, for mohair. sliver at random.
10. Test Samples and Test Specimens, Number and
7. Reagents
Preparation
7.1 The following reagents are used:
10.1 Test Samples (one from each laboratory sampling
7.1.1 Water, distilled, or equivalent.
unit):
7.1.2 Alcohol, isopropyl (CH CH CH OH).
3 2 2
10.1.1 Grease Wool, Pulled Wool, and Scoured Wool:
7.1.3 Petroleum Spirit, boiling range from 40 to 70°C, for
10.1.1.1 Sub-Coring—Randomly pack the core or hand
cleaning sliver subsamples.
sample (see 9.1.1, 9.1.2, and 9.1.3), into a suitable container
7.1.4 1,1,1 Trichlorethane (CH CCl ), for cleaning sliver
3 3
(see 6.3) and compress to approximately 14 kPa by loading a
subsamples.
weight of 667 N on the floating top. By means of a pressure
coring tube (6.4) extract at least five cores to provide a test
8. Hazards
specimen of at least 20 g of scoured wool. Scour or otherwise
8.1 Refer to the manufacturer’s material safety data sheet
clean the test specimen in accordance with Test Method D584
(MSDS) for information on handling, storage, use, and dis-
if it is grease wool or pulled wool.
posal of chemicals used in this test method.
10.1.1.2 Gridding, Core Test Residue—If the sample com-
prises an adequate amount of scoured wool resulting from core
9. Sampling
testing a lot for clean wool fiber present (see 9.1.1), divide the
9.1 Loose Fibers—The test method for obtaining a repre-
sample into 40 portions of approximately equal size. From
sentative sample of wool differs according to circumstances.
each portion, draw at random at least 0.5 g. Mix or blend these
The sampling procedures and major circumstances encoun-
40 portions to form the test specimen.
tered are as follows:
10.1.1.3 Gridding and Machine Blending—For samples
9.1.1 Lots of Packaged, Grease, Pulled, or Scoured Wool—
other than those specified in 10.1.1 and 10.1.2, divide the
Take core samples in accordance with Practice D1060. Clean
sample into 40 portions of approximately equal size. From
or scour the raw wool sample in accordance with Test Method
each portion draw at random a sufficient quantity of fiber to
D584. If a representative portion of the scoured wool core
provide a clean test specimen of 20 g. Scour or otherwise clean
sample resulting from the test for clean wool fiber present is
the specimen of grease or pulled wool.
available, it may be used for fiber diameter determination. If
10.1.2 Card Sliver—Strip off portions of each of the ten
core sampling is not feasible, take at random, by hand, at least
600-mm lengths of sliver (see 9.1.4). Combine these portions
50 handfuls of wool from not less than 10 % of the packages.
to form a composite sliver about 600 mm in length. This
The aggregate mass of the sample shall be at least 1.5 kg.
constitutes the test specimen.
10.1.3 Top—Each of the four sections of sliver comprising
the sample (see 9.1.5) constitutes a test specimen.
Obtainable from Yocom-McColl Testing Laboratories, Inc., 540 West Elk
10.2 Test Specimens:
Place,Denver,CO80216andAcroAssociates,Inc.,163MerrimacSt.,Woburn,MA
10.2.1 Testonetestspecimenfromeachbulksubsampleand
01801. If you are aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to
two specimens from each sliver and top subsample. Prepare
ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consider-
ation at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
approximately 0.3 g test specimens by cutting enough fiber
Available from Interwoollabs Secretariat, Boit 14, Rue du Luxembourg 19/21,
snippets to measure the diameters of 2000 fiber segments for
1040 Brussels, Belgium.
each test specimen measured. Obtain snippets using a minicore
Available from International Mohair Association, Mohair House, 68 The
Grove, Ilkley, West Yorkshire, LS29 9PA, England, U.K. (10.2.1.1) or guillotine (10.2.1.2). Where required to achieve
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.